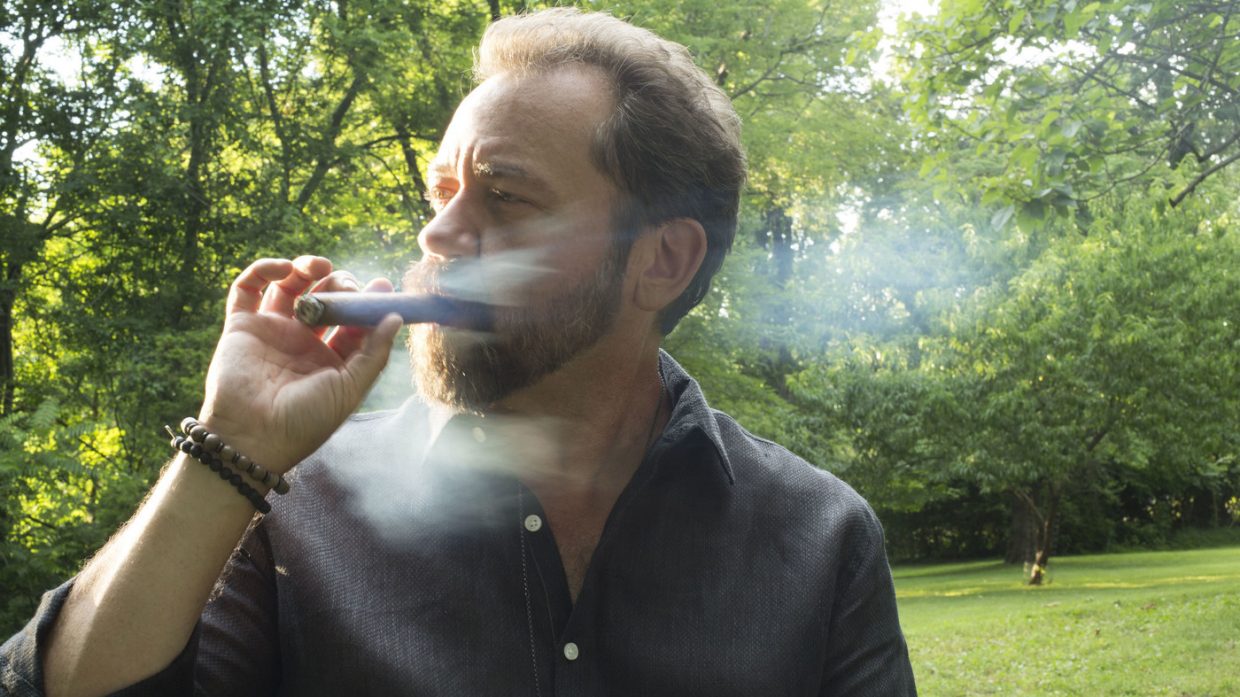
“One of the worst ice storms in my life was in Nashville,” says Dan Tyminski. “Go figure. I grew up in Vermont, and I had to go to Tennessee to get the ice.”
Kaki King remembers that ice storm, because she was stuck in the Volunteer State, as well. She had two nights booked at OZ Arts, a venue just outside of Nashville. “The night before, everything was fine. We set up everything, all of our gear, then went back to the hotel. We ended up getting trapped there for two days. We could make it to the highway, but we couldn’t get our stuff!”
These two instrumentalists may come from very different musical worlds, but their experiences during ice storms — and not during ice storms — are actually very similar. Tyminski is a bluegrass veteran, playing countless festivals as a kid and serving as a lynchpin with Alison Krauss + Union Station for a quarter-century. King, on the other hand, spent her teenage years playing in pick-up punk bands before developing a very complex playing style that treats her acoustic guitar like a drum set.
And yet, both of them kick and push against the strictures of their chosen genres, constantly ripping it up and starting again. Tyminski is most famous to younger generations of listeners for his collaboration with Swedish DJ Avicii, and on his new solo record, Southern Gothic, he mixes country and bluegrass with EDM production techniques and looped beats. And King recorded her latest album, Live at Berklee, live at Berklee, with a small orchestra of student musicians filling out new arrangements of old compositions. Both releases are outliers in catalogs full of outliers.
First of all, do you know each other? Are you familiar with each other’s work?
Dan Tyminski: Just a little bit.
Kaki King: I know a little bit about you, Dan, and the things that you’ve done.
DT: I just did a little bit of recon before the call. I heard some wonderful guitar playing, and then the phone rang.
You’re both known for your guitar playing, but you’ve both released albums where that instrument takes a back seat to these larger arrangements.
DT: It’s funny. On my album … I actually opted out. This is the first album I’ve done where I really opted out of the playing. I had Jesse Frasure produce this record. We were going down a different avenue of sound and, when he was putting together the band to track all of this stuff, I really felt like I would have a better chance of getting in the way from having him have the freedom that he needed to explore. So, I really stayed out of the playing on most of my record. I’m on new ground, where I let someone else come in and do it all.
KK: That’s cool.
DT: The bad part is, now I have to learn how to play all this stuff. And, it turns out, that some of it is hard.
KK: The idea for Live at Berklee was to put together an ensemble and reimagine a bunch of older tunes with strings, and brass, and woodwinds — and then do it live. This wasn’t the kind of thing we wanted to go a studio and make perfect. The liveness of it is what’s exciting. For me, it was doubly hard because, on one hand, I had to write a few arrangements, which is out of my wheelhouse. But I enjoyed it. And then … I had to go to college. I was working in a classroom with a conductor and 13 really good players. I never went to music school, and I haven’t been conducted since I was in high school band. I really had to buckle down. It challenged my guitar playing to be able to keep up with these really great players. It wasn’t something where I could do this freeform thing that I do, or change the tempo, or drop a measure. I had to be perfectly accurate every time.
DT: From what I heard, it sounds like it was no problem whatsoever. It does not sound like you were struggling.
KK: Well, thank you. The end result was fine, but the initial rehearsals were a bit like, “Oof. This is gonna be a hell of a ride.”
DT: In a way, it’s somewhat similar, playing the live stuff on my album. This is the first time in my life where I’m playing with some tracks. It’s a very strict arrangement and, if you veer off at any point — miss a bar, add a bar — it’s a train wreck. I’ve never had to pay so much attention, and I am easily the weak link of the live band version of all of this new stuff.

It sounds like these two projects kind of forced you not to improvise.
DT: I can definitely say that what she’s doing is much more difficult. Most of the effort in what I did with Southern Gothic was in the creation of the music, and then I was able to let someone else take the reins. Whereas, it sounds like you had to really step up to the plate and get outside the comfort zone a little bit.
KK: Well outside my comfort zone. But there was really no improvisation. I’ve been working with strings and arrangers for about five years, in one form or another. Every couple of months, I’ll get a gig with a string quartet or do a little tour. And, each time, I learn something new. It always is along the theme of, “You can actually change that. You can give directions. Just because you didn’t go to music school and you’re not the brightest kid in the class, doesn’t mean you can’t say, ‘Don’t play that.'” The process, for me, was learning how to sit in an ensemble and play a song I was familiar with but not to deviate too much from my original arrangement. But there was constant conversation and feedback among the musicians and the conductor.
DT: What a beautiful thing to get into a situation like that, where you have that type of canvas to work with. It sounds like we did the same exact thing, but we just did it so differently. You had string sections with people working together, and I had one guy trying to say, “Okay, now this is where the string sections are, and let’s do this.” I’ve got someone creating these string sections on a computer, which then we later went back and had live people play. It’s a weird process. But there are a lot of ways to get there.
KK: That’s what people want to hear, especially people who are being trained now. They realize that the people they play with are not all going to have the same background.
DT: What matters is, does someone have a vision? And is it translatable?

What are your backgrounds? Are you both self-taught? It sounds like you’re taking very different approaches that maybe aren’t the norm for people.
KK: I can’t find anyone who does the norm anymore.
DT: I was gonna ask, “What is the norm?”
Fair question.
DT: There are so many ways to get there — even when it comes down to writing the songs. Of all the different songs that have made their way onto this project of mine, no two of them came about the same way. They all started differently. They were all from different conversations. Some started lyrically and we found music. Some started with music and we found lyrics. Yeah, there is no normal. There’s just, “Does something make you feel what it’s supposed to make you feel?”
KK: I can certainly say that all my previous records started with a riff here, a drum thing there. Some songs wrote themselves in an hour. Some songs took a year to get out. I cannot sight-read guitar music, and since I play in different tunings anyway, it would just be … Well, there are, like, two people in the world who can sight-read guitar music in different tunings, and they have social problems. I am fortunate that I understand enough about music, and about intervals, and about turning a major into a minor to be able to convey that style of information to other players. I was fortunate enough to just be given enough basic information to have something like this not just explode my brain.
DT: I had this conversation with someone earlier this morning, but I would have loved to have spent some time on a theory and be able to verbalize things. But anything you ask me to do, there’s a reasonable chance I could do it, if I hear it. But there’s nothing that I can see or hear explained that would get me there. I have to hear it.
KK: Everyone comes from a different background. I’ve seen enough to know that no one who has serious musical training is going to judge you if you don’t. They’re very accepting of talent or excellence in all of its form, even if it’s a very simple thing that you do.
DT: That’s the truth. I’ve never run into it as a roadblock or something that’s stopped me from completing my gig. On a personal level, it would be nice to feel like I was more in tune with changes that are going on. I’ve found myself in settings before, playing with orchestras, and having people say, “Could we try this and this?” I hear it all going down, but I have to wait until it passes before I understand what was said. It would have been nice to have a little training.
KK: It’s never too late.
DT: Well, I’m starting to think that way now. Maybe it’s time to get back to the drawing board.
But you two have both been challenging yourselves throughout your careers, right up to these new albums.
DT: Any time I’ve ever stepped outside of the box, or any time that I’ve heard other people stretch beyond what I normally hear them do, it’s always been rewarding. I’ve always been happy when I’ve made myself uncomfortable, when I put myself in that weird spot where I had to dig, you know? And when I hear other people do it, I feel the same thing. There’s a reward there. It’s easy to stay in your little box and do what you’ve done before. But when you stretch, that’s when you really get to discover who you are.
KK: I couldn’t agree more. In some strange way, I feel the most comfortable when I’m uncomfortable. I had done two solo guitar records in my early 20s, and I’d already had a lot of success, even though I didn’t really know what was happening to me at the time. But the last thing in the world I wanted to do for a third record was another solo guitar record. I just couldn’t fathom it. So I made a record that was a little more than half-instrumental. I worked with John McEntire from Tortoise, who’s a very post-rock kind of producer. We played a ton of different instrumentation and a lot of electric stuff, which was outside the box for me, at that moment. Each subsequent album started to take on a different hue. Prior to doing the Berklee thing, my last project was a multimedia show integrating video lights to the guitar and having the guitar control what you see.
DT: There’s something in the whole process of creation that people can connect to. I’ve been a big advocate of live music my whole life. For me, there’s all the room in the world for recorded music, and people need that in their lives to take home and be able to turn something on. But I’ve found that, when I watch something being created in front of me, it touches my soul in a different way than when I hear recorded music. So, when you say your guitar can control what people see with your lights, that’s beautiful. That’s the missing element to what you get when you just hear recorded music. When you get to see the effect of what’s being created right there and feel that new emotion … oh man, there’s just nothing else like it.
KK: I agree. Especially when I see a group of people playing together and I know they’re all feeling it, and they’re hitting their stride, it doesn’t get better than that. I’ll never hear that on any record. I’ll never see those musicians onstage smiling at each other. People getting in the zone is such an incredible thing to watch, and it’s an incredible thing to feel when you’re doing it.
DT: There’s nothing else like it. There’s nothing to compare it to.
KK: I’ve been playing my whole life — since I was a little kid. I grew up playing in bands and I was normally the bass player or the drummer, but I have this strange thing happen where I can be in a room with a bunch of people, men or women, who I normally don’t want to hang out with. Maybe our tastes run a little different, but something brought us together musically. Especially as a teenager, when we would play songs that we all wrote our own parts for, and then we play them together perfectly, all of a sudden we’re sharing the same heartbeat. It’s weird, because these are guys who would otherwise be making fart jokes or talking about some stupid movie. That has rung true throughout all types of ensembles that I’ve played with.
DT: Exactly. Music is its own language. I’ve been with the same group of people for 25 years, and what we have is rare, in that we have five people who truly love music for music’s sake. Everyone is able to listen and respond. It’s a language that you speak with each other. You can be upset with somebody in your personal life and still speak words of love, musically. When you have people who you can communicate with that way, there’s beauty in music. There’s a language there that you can only hear through it being played.
I definitely think music, as a social medium, is very important right now. Not to get political, but when things are so divisive, anything that brings people together from different backgrounds is a pretty profound vehicle.
DT: It always surprises me. I remember the last time I was way outside of my comfort zone: I had gone with Jerry Douglas to Europe to do Celtic Connections, and we decided we were going to play a couple of songs we’d been playing for a while, but all of a sudden we’re playing with whistles and pipes and accordions. And I was looking at Jerry thinking, “Why would we choose this song? How can this even work?” But then I realized that we were all speaking to each other through the song? It’s like someone who spoke Chinese or French or some language you didn’t understand, but yet you knew everything they were saying. That’s how I felt with being over there. We were speaking in different tongues, but we were communicating. There’s a beauty in that.
Even just being in a crowd and watching an artist playing, I know I’m having a similar experience to the stranger next to me.
DT: Songs definitely hit everyone differently, as they listen to them. Depending on the mood that you go in with, you can draw completely different conclusions out of what you’re hearing. That’s one of the things I love about listening to music. It speaks to you in a way that nothing else can. Music has saved me, my whole life. It’s been my food. If I’m happy, I play music. When I’m sad, I need it even more.
KK: These days I’m more often the person on stage than the person in the audience. I wish I could flip that ratio because I love going to see live music. I’ve just got two young children right now. Recently, I had a friend named Matt Sheehy come and open shows for me in a couple of towns. I’d been listening to his music for a long time and I think he’s amazing. We first toured together in Italy, years ago. On this recent tour, he started to play this really beautiful song, uplifting in a lot of ways, and it took me back 10 years to listening to him play in Europe. I was suddenly a decade younger, and I was just sobbing. I was seated to the side of the stage and the lights were on me. I wasn’t trying to make a scene, but I found myself just bawling my eyes out. The acknowledgement of time passing, the feeling that something about this music and this feeling is eternal … it was a profound experience.
DT: That’s amazing. That’s what music should do.
I feel like I’ve talked to a lot of people recently who’ve said similar things. At a certain point, they find themselves playing more shows than they see, so they try to find ways to flip that around and become part of the audience again.
KK: I don’t know if you feel this way, Dan, but when being in a venue is your job and you’re backstage, I get really spoiled. There are a lot of shows I want to see, but then I think about buying a ticket, standing in line, being in a crowd. Then it becomes the last place I want to be. It’s something that’s severely lacking from my life, that I have been really missing.
DT: I share that with you. All the live music that I’ve heard, by and large, most of it was before the age of 16. From the point of being 15 or 16 years old on, I’ve always been the one on the stage, so attending shows … I can count on my two hands every show I’ve been to as an adult. It’s less than 10. Less than 10!
KK: We should go to more shows, man.
DT: I know. Going to more shows is on my to-do list. I should definitely be spending more time in the audience.
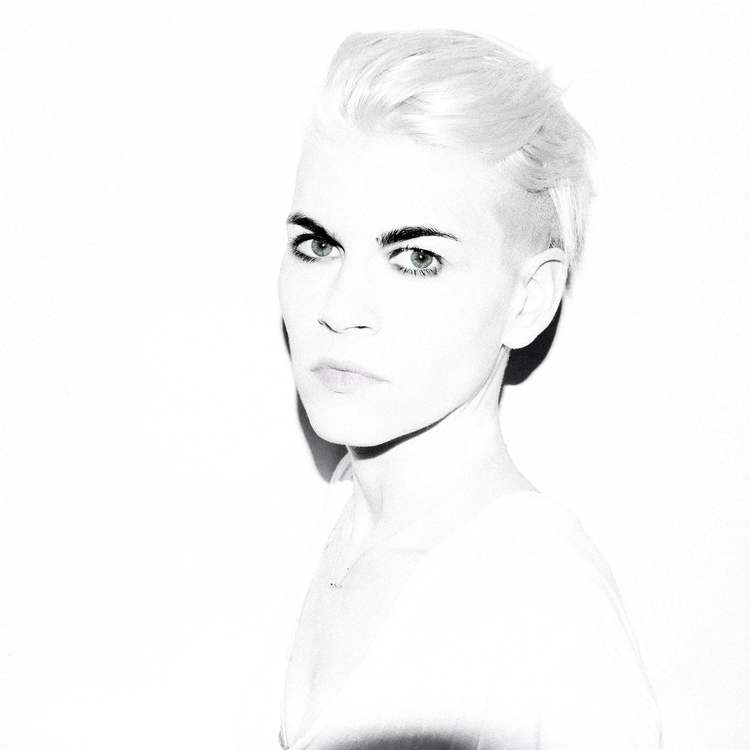
Kaki King photo credit: Shervin Lainez