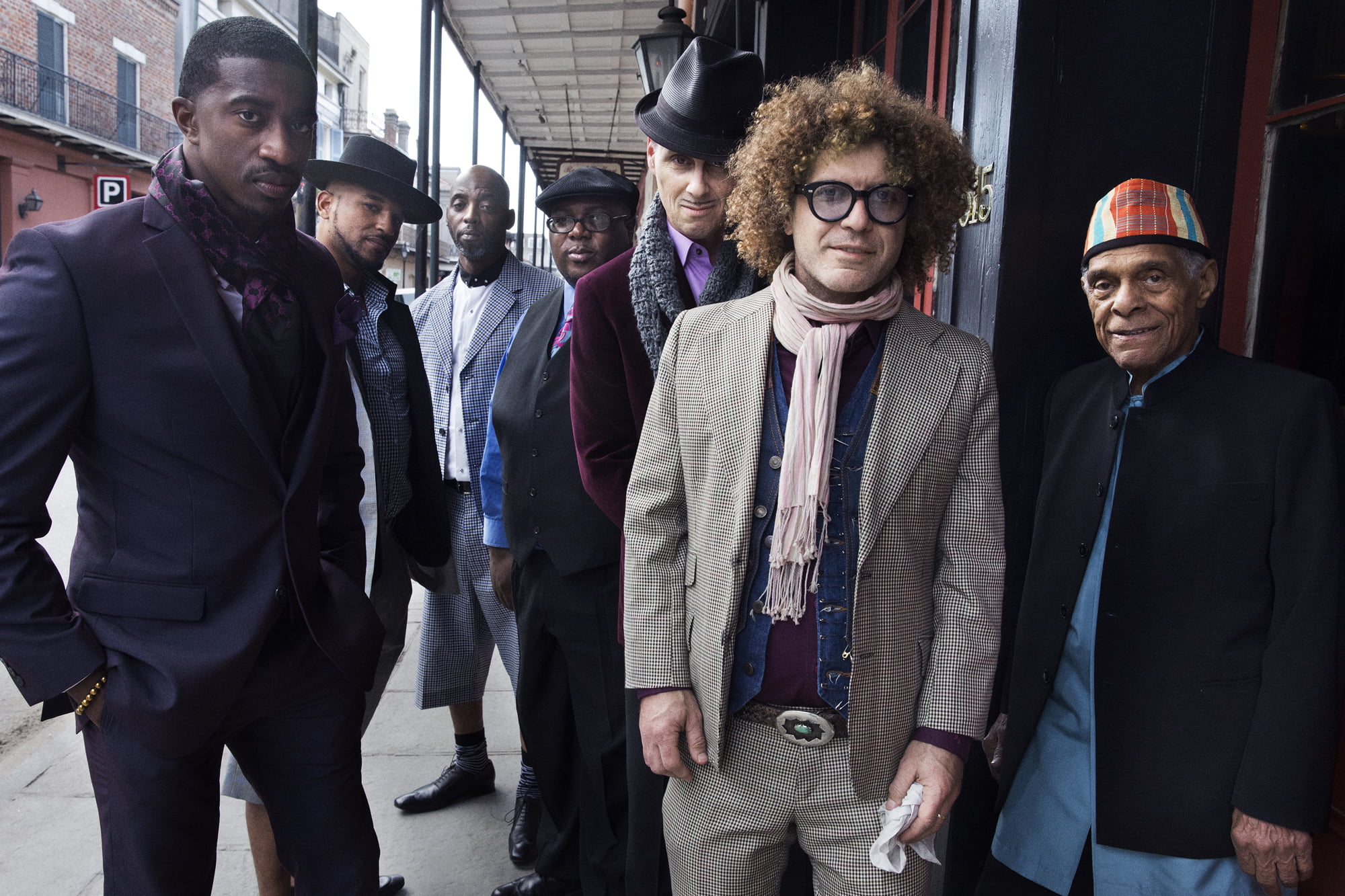
New Orleans is home of the Bs: bayous, beignets, broils, Bourbon Street, and, most importantly, brass bands. Day and night, music wafts into the streets, carrying with it the history, traditions, and culture of this vibrant city. This is especially true on Sundays. In the afternoon, the air is thick with horn melodies and drum lines, as the time-honored tradition known as the second line parade takes place. Second lines are a derivative of the customary jazz funerals that used to occur in New Orleans: Marching bands would play during the procession to the cemetery to lay the casket, and they were known as the first line. Prior to integration, Black cemeteries were located outside of town, meaning that the walk back was a long one. But the band would continue to play. Passersby who heard the music were welcome to join in the procession behind the band, even if they didn’t know who had died. These people formed what was dubbed the second line.
Back in 1961, Pennsylvania natives Allan and Sandra Jaffe came upon one of these parades when they were visiting New Orleans on their honeymoon. They followed a brass band down the French Quarter and wound up at an art gallery at 726 St. Peter Street. A gathering place for artists, musicians, writers, and actors, the gallery immediately drew the Jaffes in. They permanently relocated to New Orleans and bought the gallery, transforming it into Preservation Hall. Although he wasn’t a jazz player, Allan had strong ties to horn instruments: He went to military college on a tuba scholarship and played in the marching band. With Preservation Hall, Allan and his wife set out to do just that — preserve. At that time, jazz was dying, and the couple wanted to bolster and continue the distinctly American tradition.
Together, they pulled it off. Sandra would work the door, taking money and deciding who could come into the club, while Allan would scout musicians around town and put bands together. Although Preservation Hall is now considered an institution, it was revolutionary when it opened. New Orleans was still segregated during that time and it was against the law for Black and white musicians to perform together. Nevertheless, legendary musicians like Allen Toussaint and Mac Rebennack (better known as Dr. John) would find each other and collaborate. In fact, Allan broke the 1956 law outlawing integrated entertainment when he joined the band on tuba. Preservation Hall became the only place in New Orleans where Black and white people were congregating openly, both in the crowd and on stage.
The Preservation Hall Jazz Band formed in 1963, becoming the touring version of the club’s house band. For over 50 years, the rotating eight-piece has kept its home base at Preservation Hall while cultivating and spreading New Orleans brass band jazz around the world. Allan and Sandra’s son, Ben Jaffe, is the current creative director and plays tuba and upright bass in the band. In 2014, he appeared on Sonic Highways, an HBO special chronicling the recording of the Foo Fighters’ album by the same name. The group went to eight different cities to record individual tracks, and Preservation Hall was one of the selected recording spots. Throughout the course of the featured episode, Ben explains the significance of the New Orleans sound, which spawned musical heavyweights like Louis Armstrong, Fats Domino, the Neville Brothers, the Meters, and even Little Richard, who recorded his early hits in the city.
“Rock ‘n’ roll is really the evolution of jazz,” Ben Jaffe says. “When Louis Armstrong’s Hot Seven albums came out, people lost their minds. It was punk-rock. It was out of control. A lot of the jazz musicians became the first wave of rock ‘n’ roll musicians.”
Sonic Highways is one of countless documentaries and collaborations Preservation Hall Jazz Band has participated in over the years. Their project with frequent collaborators My Morning Jacket was the subject of Danny Clinch’s 2011 documentary Live from Preservation Hall: A Louisiana Fairytale. In one notable scene, My Morning Jacket frontman Jim James sums up the power of Preservation Hall: “Every time I’m in this space, I feel like there’s something inside of me that wasn’t there before,” he says.
Perhaps it has something to do with that New Orleans voodoo, but Preservation Hall certainly has a vibe all its own. It was built in 1750 as a Spanish tavern and once served as a photography studio where uptown aristocrats would come to get their portraits taken. But the small space hasn’t changed much. About 100 people can pack tightly into the room and there’s no air conditioning, no microphones, and hardly any seating. It’s all part of the mojo.
After Hurricane Katrina hit, there was an even bigger focus on the city’s intrinsic sound and, by proxy, Preservation Hall. Seven of the band’s eight members lost their houses and they, along with the rest of the city, used the culture to help guide them home. Although New Orleans is known as the Deep South, part of its rich heritage stems from being the northern-most part of the Caribbean. It was the largest port for a century, serving as the entry point for Africa, South America, and Central America. It was the port where Africans were brought into the United States and sold for slavery. It was also where goods and ideas were exchanged, leading to a giant mixing pot of musical stylings including Spanish melodies to African rhythms.
At Preservation Hall, traditions are passed on in the same way they were handed down. In this way, Preservation Hall Jazz Band has managed to celebrate the essence of New Orleans while maintaining cultural relevancy. At the Country Music Awards, they shared the stage with Maren Morris and the McCrary Sisters and, this summer, they’re hitting major festivals like Bonnaroo and Coachella to support the release of their new album, So It Is, a collection of new original music dropping April 21. Meanwhile, Preservation Hall still hosts music every night of the week. To ensure that the music thrives in the next generation, Jaffe also runs an after-school program at the Hall where young students learn from seasoned veterans, most of whom inherited their spots in the band. New Orleans is music, and it’s through this sense of community that it maintains its vitality.
Photo credit: Danny Clinch