On April 22, 1989, Cityfolk, a Dayton, Ohio-based concert series, mounted their most ambitious evening to date, The Dayton Bluegrass Reunion, “An All-Star Salute to Dayton’s 40 Year Bluegrass History.” It was held at Memorial Hall in downtown Dayton.
I’m reminded of this concert now because of an essay I wrote for its program booklet: “Industrial Strength Bluegrass.” That is the title of a new book by Fred Bartenstein and Curtis W. Ellison, subtitled “Southwestern Ohio’s Musical Legacy.” This anthology presents a remarkable in-depth portrait of a key regional bluegrass scene, which co-author Bartenstein has likened to seminal regional scenes in other genres like blues (Chicago) and jazz (New Orleans).
In March, Smithsonian Folkways released a 16-track album with the same title, edited by Joe Mullins and son Daniel Mullins. On it are 16 contemporary recordings by today’s leading bluegrass artists, doing the region’s key repertoire — like “Once More,” the Osborne Brothers and Red Allen’s 1958 high lead trio, recreated on the album by The Grascals; and “20/20 Vision” by Jimmy Martin and Osborne Brothers in 1954, done here by Dan Tyminski. Joe Mullins opens the album with his band, The Radio Ramblers, doing “Readin’, Rightin’, Route 23,” an anthem to the Appalachian migrants who nurtured bluegrass in the region.
Phyllis grew up with Irish dancing in Dayton. By 1978 she had a Celtic music radio show on WYSO-FM, the Antioch College station, and began booking bands. “A band I knew from Pittsburgh called ‘Devilish Mary’ was coming through town. They were a great dance band that played ole’ timey music and Irish traditional music.” She and a friend organized a “ceili” at a downtown club in Dayton. By 1981 she’d formed Cityfolk.
By 1987, Cityfolk had branched out from Irish to include other roots music in their events — including bluegrass. In the 1980s a broadening of interest in the traditional arts was nurtured through public sector folklore lobbying in Washington. The Festival of American Folklife, established in 1967 by Ralph Rinzler at the Smithsonian, led to the establishment of a Folk Arts department at the National Endowment for the Arts and the creation of the American Folklife Center at the Library of Congress. The National Folk Festival, around since the ’30s, moved to Washington and became the National Council for Traditional Arts (NCTA) in 1976.
These national institutions supported performing arts markets for traditional artists. Local and regional arts organizations like Cityfolk and PineCone grew and flourished during the ’80s, and public folklorists were active in the AFS. Phyllis was wanting to talk with me because I’d written a book about bluegrass. She was planning a reunion concert to celebrate 40 years of bluegrass in Dayton, applying for funding from the Ohio Arts Council and the Dayton Performing Arts Fund. She asked me if I would work as a consultant and writer for this event’s program.
Brzozowska wanted to tell the story of bluegrass in Dayton as dramatically as possible, so they were hiring Don Baker, “one of the leading theater directors in the South.” Baker had grown up in Appalachia and started his career at Appalshop in Whitesburg, Kentucky. In 1984 he co-founded Lime Kiln, a theater in Lexington, Virginia.
For the Reunion, Brzozowska later recalled, Baker “constructed a theatrical foundation on which the music and narrative would be presented. He also designed the set, contributed input to the script, set the pacing of the show and when the lights went up, was the perfect stage M.C. for the evening.”
In producing the show Brzozowska took counsel from three Dayton old hands — Harley Allen, Fred Bartenstein, and Paul “Moon” Mullins. Additional input came from old-time fiddler and Dayton City librarian Barb Kuhns and writer-musician Larry Nager. As a consultant and writer, I worked with them on the planning of the concert and on program booklet. I also helped backstage on the night of the concert.
My experiences with southwestern Ohio bluegrass began in the late fifties. Oberlin classmate Jeff Piker came from Cincinnati as a freshman in ’58. Inspired by a Pete Seeger concert at Antioch, he’d bought a used Vega banjo at a music shop in the Appalachian migrant neighborhood of Over-The-Rhine that Nathan McGee writes about in Industrial Strength Bluegrass (pp. 164, 166). It had homemade Scruggs pegs!
That made Piker a popular guy with us campus bluegrass jammers. We all borrowed the banjo to learn how to use the pegs. During the January 1959 winter break we took it with us when we went to Yellow Springs to visit Antioch College friends. Bluegrass was catching on there.
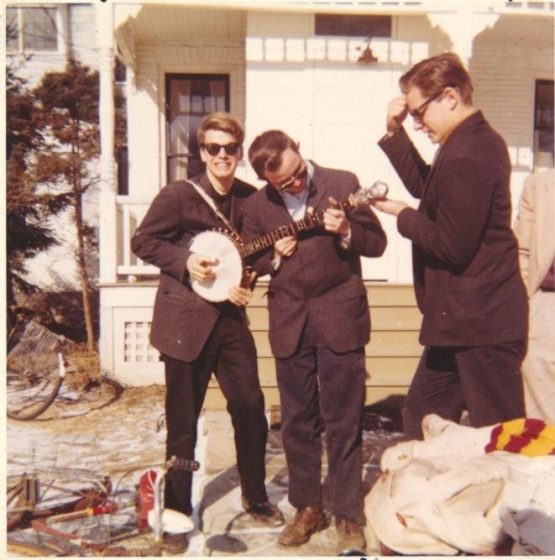

A year later, in March 1960, our band opened for the Osborne Brothers at Antioch. I’ve written about that in Bluegrass: A History (pp. 155-58). In 1962, another band I was in opened at Antioch, for Sid Campbell and Frank Wakefield, and I’ve written about that too, in Bluegrass Generation: A Memoir (119-123).
One detail from that 1960 concert I didn’t mention: when Jeremy Foster called to invite us to open the show for the Osbornes, he said he’d booked the Osborne Brothers because they were nearby and available. We knew of this band only from the sound of their MGM album, The Osborne Brothers and Red Allen. Jeremy was disappointed that they had changed — Red Allen was no longer with them. That made their music less appealing to him. But, as I learned later, Bobby and Sonny didn’t want fancy guitar backup and didn’t need a flashy lead singer. They were focused on their trio.
In the fall of 1963, when I was managing Bill Monroe’s park, the Brown County Jamboree, in Bean Blossom, Indiana, we got reacquainted when they gave their first show there (Bluegrass Generation, pp. 224-226). With Benny Birchfield playing guitar and singing the lowest voice in the trio, they had moved from MGM to Decca. Their first single, “Take This Hammer,” had just come out. Their final MGM album, Cutting the Grass, was due out soon.
They were polishing the high lead trio they’d been working on for five years. That winter I taped them guesting on the WSM’s after-the-Opry broadcast, Ernest Tubb’s Midnite Jamboree. Their harmonies were attracting attention in country music circles.
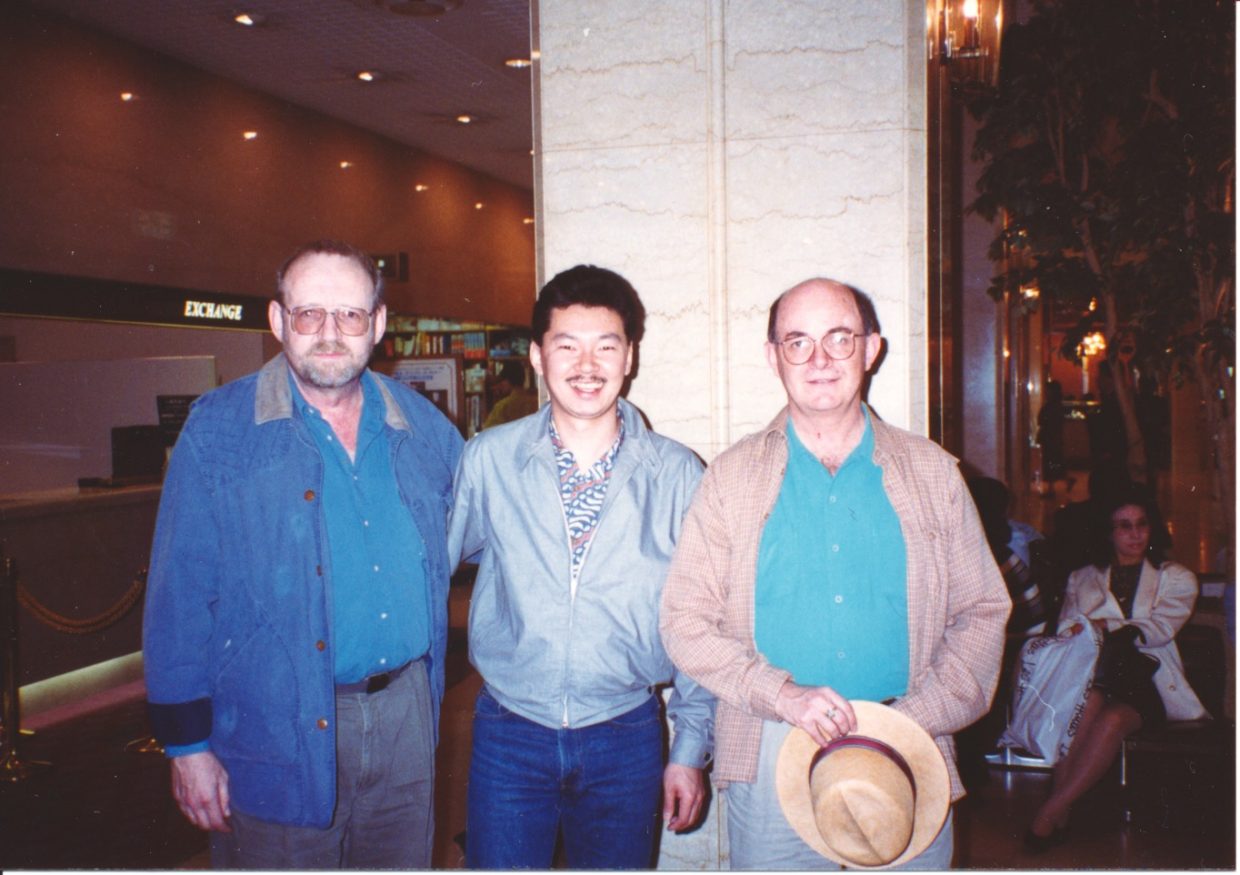
At Bean Blossom, Bobby and Sonny had told me about their regular Thursday night gigs Ruby’s White Sands in Dayton and invited me to come over some time. In May ’64, Jim Work and I took friends from California, Jerry Garcia and Sandy Rothman, to see them there.
The Osbornes joined the Opry a few months later. By then they were coming to Bean Blossom twice a year and we’d gotten better acquainted. “Banjer” talk with Sonny was always entertaining. He had experimental bridges, banjos, and capos. On stage, he had great new licks for every show.
With Bobby I shared an interest in bluegrass history. One Sunday in 1964 I invited the band back to our apartment in Bloomington for supper. While they were there I showed Bobby the work I was doing on the Bill Monroe discography and asked him if he was interested in doing something like that for the Osborne Brothers. He was. We began corresponding about their discography, and started trading tapes.
Benny Birchfield left the Osborne Brothers at the end of ’65. The following spring, in Cincinnati for an academic meeting, I ran into him at the Ken-Mill Café in Over-The-Rhine. He was playing bass in a band that included lead singer and guitarist Jim McCall, with Vernon McIntyre Jr. on banjo. Benny introduced me to the band as a banjo picker from Bean Blossom and invited me to sit in for a set on banjo. That was fun.
At that festival, my first, I finally met Pete Kuykendall. We’d been corresponding and trading tapes for several years, and he’d published bluegrass discographies in the mimeo magazine Disc Collector. Now he was promoting a new bluegrass monthly, Bluegrass Unlimited. I told him about the Osborne Brothers discography, and he agreed to publish it in BU (it appeared the following July). Promoter Haney invited me to join him, Ralph Rinzler, and Mayne Smith in introducing Bill Monroe and the Blue Grass Boys and The Osborne Brothers in a special broadcast about the festival on the local TV channel.
I saw Gabbard again the following October when he dropped in and sang bass on one cut we were recording for George Brock’s gospel album at Rusty York‘s Jewel Records in Mt. Healthy, Ohio. McDivitt’s chapter also devotes a section (pp. 63-65) to Jewel and York’s remarkable careers in bluegrass and rockabilly. Here’s Harley Gabbard with the Osbornes doing what was, as of May ’67, their new single: “Roll Muddy River.”
(Editor’s Note: Read part two here.)
Neil V. Rosenberg is an author, scholar, historian, banjo player, Bluegrass Music Hall of Fame inductee, and co-chair of the IBMA Foundation’s Arnold Shultz Fund.
Photo of Neil V. Rosenberg: Terri Thomson Rosenberg