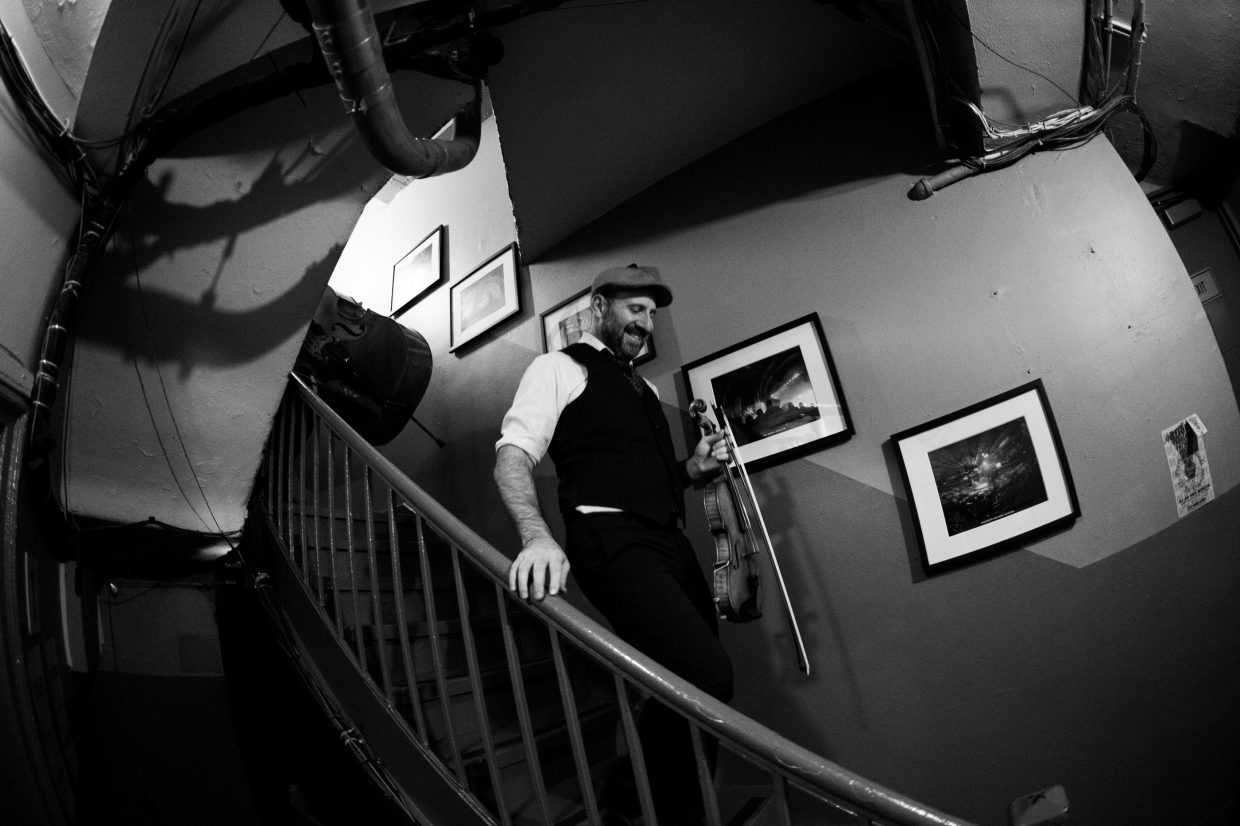
Chris Thile is walking briskly into the venue while chatting agreeably about Punch Brothers’ new album, All Ashore. He’s used to multi-tasking, of course. In addition to kicking off an extensive tour with that eclectic band, he hosts the public radio show Live From Here, and he’s also a husband and father with a lot on his mind – particularly when it comes to the state of the world.
This interview is the fifth and final installment in a series saluting the Bluegrass Situation’s Artist of the Month: Punch Brothers.
I want to ask about “All Ashore” being the first song on here. Do you feel like it sets the tone for this album?
I do! It sort of introduces, through a fog, a lot of the content that we are mulling over the course of the record. It feels a little bit like a curtain is rising. I like starting with the nebulous imagery. It felt right.
I looked up the phrase “man of war” and found out that it’s an armed ship, which is an interesting image to start that song.
Yeah, I saw that character as moving forcefully through her environment, with conviction, with authority, with purpose … brushing aside the distraction, getting straight to business. I don’t know remember why “man of war” got stuck in my head, but just that ship, if you’ve seen a picture of one, you can tell it means business. So I felt like it was a good way to introduce people to that character.
Maybe I’m thinking too much into this song, but I like that long intro to the song because it reflects a tense relationship. It’s like, “Is someone gonna say something here?” Was that intentional?
[Laughs] Oh yeah, absolutely, yeah it’s a prelude to the record. The record was designed as a whole, as a piece of music, almost like a nine-movement piece of music. And while we hadn’t originally intended for “All Ashore” to be the first movement of it, you have to go with your material as a composer – or in our case a five-headed composer. Eventually “All Ashore” just could not be denied as the opening gesture, in large part due to that kind of prelude. It felt like a beginning. It felt like a nice way to say hello. …
I think of a sunless dawn, I think it’s overcast, I think there’s fog. But one thing I love about music is it means those things to me, and those are the pictures I get in my head, but you might get something entirely different. Is it almost two minutes before any singing anything happens? I think it might be.
It’s pretty close.
Yeah. So I love the idea that people would be in their own heads, forming their own image, and then those first lines of the lyric basically start a dance with whatever people have started to see – whatever sort of concept people are starting to get. And then basically a ship moves on the horizon, in the form of the character of Mama. You start wondering who’s telling the story, who’s the guy that comes into the song in the second verse, and what they’re all up to.

I found on this record that your stories kind of reveal themselves over time. I felt like there are narratives in these songs and it’s a pretty complete statement. Do you look at it as a concept album?
Sure, but I also think an album that is void of concept should be regarded with high suspicion. I think any album worth listening to is a concept record. You know, I understand what people mean by “concept record,” almost like a piece of musical theater, without acting or whatever. While I don’t feel like there is a linear narrative, there is absolutely a narrative that is meant to be heard from start to finish, in sequence. We wrote it that way.
We also pointedly wanted to make sure that it still made sense in vignettes, which is how most people listen to things these days. They put their phones on shuffle or whatever. Just because that’s not the way I like to listen to music doesn’t mean that’s not the correct way to do it. So we wanted to make sure that the songs could stand on their own, but I think when experienced together, they might add up to a little bit more than when they’re listened to in short bursts.
How do the instrumentals kind of factor in this? If I’ve learned anything from your Ryman show, I need to find the recipe for the Jungle Bird and Three Dots & A Dash. Tiki drinks, right?
Yeah, Tiki culture has been one of my muses for a couple of years now but this is the first record where it’s really come to the fore. There are two different rum references in the lyrics, one in “All Ashore,” one in “Jumbo.” And of course “Three Dots & A Dash” and “Jungle Bird” are a great old-school Tiki cocktails. I feel that basically the relation is two-fold. One is that Tiki culture represents one of America’s most shameless escapist gestures. It doesn’t pretend to solve anything; it just spirits you away, no pun intended.
But what I find, ironically, is that it’s in the midst of one of those escapist gestures that I find myself able to start thinking clearly about some of the things that are troubling me. And I think my bandmates would agree. A lot of people start getting to the meat and potatoes of a topic, in communion with their fellow man, right around when the second round hits the table.
You’ve made that initial escape to the point that you can actually see your life, and our lives as a society, with a little bit of perspective. You can get a little distance from it and might actually start being able to see it for what it is, and start asking yourself the harder questions. Not that you are expecting answers, but to even just ask the question, I think, and to discuss the various questions turning over in your collective minds is a worthy exercise. So all of these lyrics are the result of that kind of conversation. And so, naming those two instrumentals after Tiki drinks is symbolic of those conversations.
I like the fact that you sing in falsetto, because it can really expand where you go with your vocal, and the melody too, for that matter. Why does that falsetto voice appeal to you with the music you are making?
We’re chasing achieving the melodies we hear. If we limited the melodies that we wrote to what fits in my vocal range, my full-voice vocal range, we’d be far more limited than if we expanded to include falsetto. Something like the “Angel of Doubt” melody, for instance, we didn’t start that off going, “Yeah, you know what would be cool is if you sang about half the time in falsetto.” It’s just that’s where the melodies were headed. Also I think there’s a sensitivity and an intimacy to falsetto, to my ear. It’s almost like a request to come closer. A sort of intimacy to it that even if the melody starts taking us thither, then maybe I’ll start considering what lyrics are going to be sung in falsetto. Like if I’m going to deliver this in falsetto, then that comes in a certain character.
I find that interesting that you mentioned character. That must be refreshing to sometimes write from a perspective that isn’t necessarily yours. Is that the case?
Oh, I find it necessary to my sanity. I feel like if I were invariably seeing the world from my own perspective, it’s experientially incestuous or something. I crave seeing the world through other people’s eyes. To me, good art always lifts me out of my experience of the world and places me in someone else’s. And then I see things a little bit more clearly with each great piece of art that I encounter. That the lyric changes the perspective, even within the songs, I think that exposes a certain preference on my part, I’ll say. Or a certain hunger for multiple perspectives.
Even like “Jumbo,” for instance, even though that is satire, clearly, it’s trying to make a point. I think it’s a fairly clear indictment of the perspective from which it’s coming. Even still, part of that is an attempt to understand where that perspective is coming from.
That song went over pretty well at the Ryman. How is “Jumbo” treating you out on tour? Are people responding to it well?
[Laughs] I think so. I think it is probably difficult to get all the words, live, so it’s always amusing to see what people react to. And sometimes I think they might be reacting to something that if they were to see the lyric on paper, or what the actual statement is, maybe they might still laugh but they wouldn’t whoop and holler about it. It’s interesting how much tension is in the air right now. For us, as a society, there’s so much tension in the air you can cut it with a knife. And so a song like “Jumbo,” or “Just Look at This Mess,” and maybe “It’s All Part of the Plan” as well, it lets some of the tension out. Hopefully it can be cathartic for people who are completely mystified by the state of our country and our world right now.
Illustration: Zachary Johnson
Photo credit: Josh Goleman