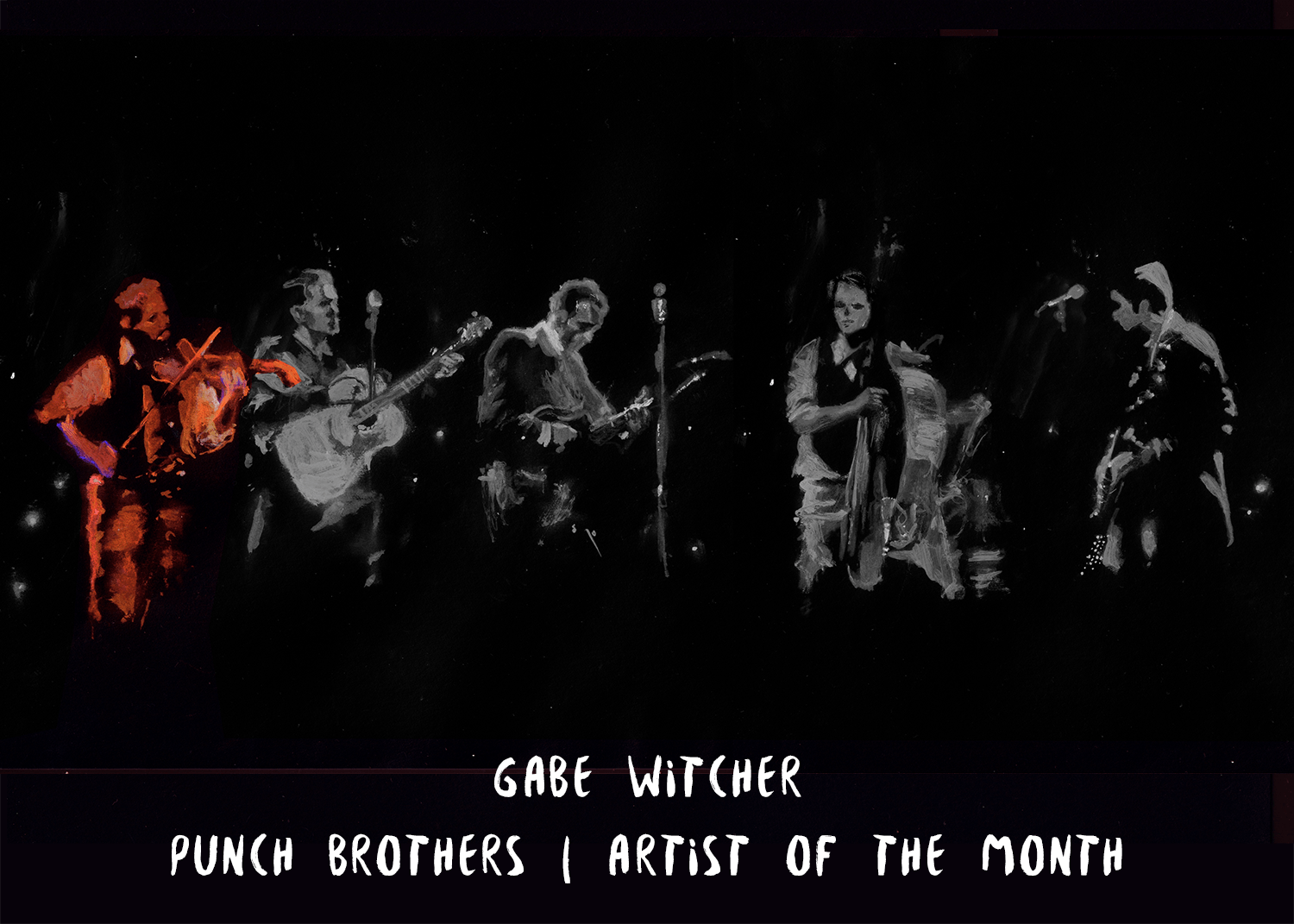
Gabe Witcher has a superstition about shutterbugs in recording sessions. “I’m a strong believer that all photos that come out of the studio must be in black and white. Color photography is too real. It loses mystery to me. Black and white has enough fantasy in it, where you can use your imagination to create the world that existed at the time the recording was captured.”
It is, he admits, a “weird little thing that I think about,” but he’s not wrong. Most iconic music photos — whether it’s Paul Simon smashing his bass onstage or Johnny Cash furiously flipping the bird — need no other hues beyond black and white. Anything else is a distraction: too flagrant, too revealing, too matter-of-fact. Witcher would rather let the creative process retain some sense of fantasy and wonder.
Thirty years into his career, he has yet to tire of the mystery. Something like a child prodigy on the fiddle, he paid his dues in the Southern California bluegrass scene, appearing on Star Search in the 1980s before joining Herb Pederson’s band, the Laurel Canyon Ramblers, as a teenager. Witcher has recorded with Béla Fleck, Dave Rawlings, Eric Clapton, and many others, but he’s best known as a founding member of the renowned prog-grass group Punch Brothers. Comprised of superlative musicians, they’ve recorded four albums of adventurous acoustic music with such producers as T Bone Burnett, Jacquire King, and Jon Brion.
Throughout his career, Witcher has gravitated toward the other side of the glass, gradually accepting more production responsibilities within Punch Brothers and without. He helmed Sara Watkins’ breakout third album, Young in All the Wrong Ways, in 2016, and this year he produced two new records by his Punch Brethren: Universal Favorite finds banjoist Noam Pikelny going truly solo, just his voice and banjo in a variety of styles and settings, and Witcher ensures it sounds both intimate and expansive. For Mount Royal, the second collaborative album by guitarists Chris “Critter” Eldridge” and Julian Lage, the producer emphasizes their masterful technique as well as their subtle and insightful arrangements. They’re representational albums, he says, but full of verve and skill and even a little mystery.
How did you gravitate toward this particular role?
I had a band with my dad when I was young called the Witcher Brothers, and we made a record when I was 11. That was my first foray into the studio, and I remember having so much fun. Back then, it was all tape. I remember the feel of the machines, getting the microphone set up and coming into the control room for the first time and hearing the sounds of the instruments coming back at me through the speakers. It was a thrill. At that moment, I was hooked on recording. I got a four-track machine, and I spent a lot of time at my cousin’s dad’s house — I guess my mother’s cousin. His name is Don Was, and he’s a huge record producer. He had a bunch of recording gear, and I was always in the studio, setting up equipment and recording for fun. It was something I loved to do in my spare time. When I was about 14, I was asked by someone I didn’t know to play on their record, and that started my career as a session musician in Los Angeles. I got asked to play on other things and, little by little, I managed to build up a reputation. So I’ve always felt at home in the studio.
Were there any particular albums where you started to notice the production?
One of my earliest musical memories was listening to Abbey Road on my parents’ turntable. I couldn’t have been older than two or three, and especially as I got a little older, I remember listening to that record and realizing that there were only four guys in the band, but the sound they were making was much bigger than that. This guy plays the drums, these two guys play guitar, and this guy plays bass. How are they able to get all this other stuff going on? That really opened the door to figuring out what the technology was and what overdubbing was: “How does that work?” I started to think about how they were building tracks and, from then on, a world of possibilities opened up.
When Punch Brothers started making records, I was already an old hand at it and could instinctively take on the role of producer with those guys. Everybody finds his own role within the band, and that became mine. For the last record, Phosphorescent Blues, we had the amazing T Bone Burnett to produce, and I had already been working with him as a co-producer on a bunch of projects — and as an arranger. When you work with T Bone, it means you’re going to hear him say something like, “I’d love for you to write a string arrangement or a horn arrangement for this song.” So you’d do that and, “Okay great, now go record it.” He’s giving you the keys to the kingdom. Sometimes he would show up for sessions and sometimes he wouldn’t, and to have him place that level of trust in me gave me the confidence to think of myself as a producer.

How did that affect the sessions with Punch Brothers?
He was there for all the tracking and he got all the performances out of us, but when it came time for all the editing and mixing, I knew what the band wanted and I knew what I wanted, so he let me take the reins. I was there with the engineer, Mike Piersante, and we finished tracking all the guys. When everybody else had left, I was sitting there with a bunch of hard drives with hours and hours of music — and it’s up to me to edit and oversee the mixing. It was a natural extension of all the things that I’d already been doing.
The band has worked with a different producer on each album. How were those experiences different?
Each producer brings a different aesthetic and a different worldview to the proceedings. Early on, we were very idealistic and dead set on making only representational documents. With The Blind Leading the Blind, we knew it was an ambitious piece, but we wanted to make sure we could actually perform it live. We were very stubborn about capturing it all live, so Nonesuch recommended we get a classical producer. Because that’s what we were doing: We were making a classical piece, so we needed to record it in a classical way with a classical producer [Steven Epstein]. Looking back 10 years later, was that the best way to present that music? I don’t know. If we had to do it over again, we would probably play most of it live and overdub harmony vocals, but you learn.
Jon Brion had a different method on Antifogmatic. He set us up in a semi-circle because he wanted to capture the energy and interaction of what we do. We played all of the music live, but he was able to get a better vocal sound by overdubbing the vocals. I understand that, but it’s very hard when you have five people imagining trying to play based on what they imagine the vocals are going to sound like. We had to learn on the fly how to do that. We had to learn to listen in a different way, and I think it was successful in its own way.
Jacquire King was a lot of fun. He was down for a lot of experimentation on Who’s Feeling Young Now? By that point, we wanted to utilize the studio as another sonic tool instead of just something take a snapshot. We wanted to use the element of fantasy that the studio provides. We dipped our toes in a little bit with that record. We experimented with sounds and overdubs — anything to introduce new things, but always dependent on the song and what it needs. Jacquire really helped us figure out what works for our instruments, and he had us thinking about ways to capture sound that I had never really thought about before.
And the thing with T Bone is, he’s wide open. He wants to do whatever is going to make the best end product. We had different set-ups for different songs. It was a fun process because he’s a master and keeping the bigger picture in mind. The Punch Brothers have a tendency to overdo things and try to squeeze so much perfection out of everything that we squeeze the life out of it. So it was a real education to see how he worked.
What did you take away from those experiences that you’ve applied to your own sessions as a producer?
The most important thing you can have in a producer is trust. You trust that they’re going to understand your vision and you trust that they’re going to help you achieve your goal. It’s such a deep relationship with the rest of the band, and we understand each other so well, that it made sense that I would be the one sitting on the other side of the speakers telling them if they’ve gotten what they want. And I know what they’re capable of doing, so I’m in a unique position to push them. Someone else might be like, “Hey, that was great.” But I would be like, “Hey, that was great but I know you can do better.”
That seems like it would be crucial, especially on these records where there’s nothing to hide behind. It’s just one banjo or two guitars.
Those are very, very representational records without many studio tricks. You approach that kind of project as though you’re making a document. There’s not a lot of fantasy involved. Your job as producer is to put them in a position where they’re comfortable and playing their best, then you have to make sure you capture the sound they’re making as fully as you can. That all sounds very simple, but you become something more like a psychologist at that point. You’re talking a line between keeping people happy and creative, but also trying to find positive ways to shape what they’re doing, to get the best possible results. It helps that the Punch Brothers guys have been working together for so long that we know how to speak to each other in a way that avoids any bad clashes or setting each other off and making them freeze up.
For instance, Noam is extremely thorough — more thorough than I think he needs to be. There’s an interesting dynamic where we’ll work on a song for a couple of hours, and I’ll be very happy with what we got. I’m confident in what we got, so why not come in and take a break before we start working on the next song. But he’ll say, “Let me just do one more. One more time.” Three hours later, he’ll finally feel okay about it even though we have three times as much material as we actually need. He’s familiar with me, but he might not feel as comfortable with someone else to sit there for hours on end. He obviously does feel comfortable: It’s just Gabe. He can’t get mad at me.
As a producer, you have a couple of jobs. One: You’re a proxy for the artist. You’re basically in a position to say, “If I was an audience member, would this be reaching me? Is this going to impact me emotionally?” Two: You have to make sure there is some underlying theme that ties it all together and makes it work as a whole. All the best records tell a story of some kind. It’s all just storytelling. Even though one song is about one thing and the next song is about something else, you can still construct some kind of narrative out of them, even though it may not be a linear story. That’s a big part of the producer’s job: to make sure everything fits together in a satisfying way.
Is telling a story easier or harder with instrumental versus vocal tracks?
They’re challenging in different ways. To create a narrative on an instrumental record, you have to make sure there’s enough variety to feel like you’ve gone somewhere. When you’re making a record, you’re making a 40- or 50-minute piece of music. It might be divided up into 10 or 12 or 15 segments, but you’re making a piece of music that’s roughly the same length as most symphonic music, so you have to approach it that way. You have to piece it together in a way that gives the material shape and keeps it interesting. For a record with singing on it, you have the added difficulty of that extra layer of words. You have to have the musical narrative and then you have to have the lyrical narrative. There’s some wiggle room in there, but you also have to keep in mind the artist and what they’re trying to say. On the Critter and Julian record, they brought in a bunch of vocal songs that were all great, but I just didn’t believe Critter when he sang them. I had to figure out why, which was tricky, but it came down to what I knew about him — where he comes from and what kind of music he has made in the past. The material had to fit within the story of him as a performer, as an artist, and not just within the context of an album.
How does that work with someone like Sara Watkins? What I love about Young in All the Wrong Ways is how it plays against what we know of her as an artist and takes her story in a new direction.
Absolutely. What makes it work with her is that she acknowledges that it’s something different from her. People change and evolve and grow, and this is where she is right at this particular moment. I really felt the honesty of what she was singing to me in those songs. It all made sense. There was a weird incident in the studio with her. All of the songs that ended up on that record were her original songs, but early in the process, she had brought in a song that Benmont Tench had written. It was a new song of his and we had permission to record it. I thought it was good, so we put it on the list. We were about three-quarters of the way through tracking her record when we got to that song. It was just her singing and Benmont playing. The song is dark, about a relationship that’s past its prime and she’s struggling to break from it. She started singing, and the mood in the studio shifted. It had been very happy and positive and constructive, but it turned really dark really quickly. It had been easy-going up to that point, and I watched everybody get very frustrated.
The next day, Jay Bellerose, who plays drums on the record, was talking to me and asked me what happened. The only thing we could come up with was that the song just wasn’t her voice. Nobody believed it, when it was coming out of her mouth. It was a case of the wrong song for the artist, and it’s the only song that didn’t make the record. Don’t get me wrong: It’s a great song, when Benmont sings it. It’s his experience. It wasn’t Sarah’s experience. There was just something about the vibe of the song that wasn’t right for her.
It’s extremely hard to explain that kind of thing, and everybody feels it in a different way. The studio is such a vulnerable space, especially for the person who’s being recorded. It’s such an intimate setting that interpersonal dynamics become the thing that makes or breaks a record. You’re going for an indescribable feeling — something way beyond playing in time or singing in tune, all the technical aspects that make a good performance. When you achieve that next layer, it’s hard to describe. There’s an energy that comes from getting the right people in a room together. Sara’s record was successful because we got the right people playing the right music, which becomes a positive feedback loop. Good things start happening, which inspire more good things, which inspire more good things, and then you have this wonderful document of that time and those people. This kind of thing never happens, especially when you hire a band, but for Sara’s record, people were hanging out in the studio after the tracking was done. We would play for hours and hours, then we would do overdubs in the evening and people would just hang out. We’d open a bottle of wine and people would just hang out in the studio. It was beautiful.
I feel like people sometimes fixate on gear — finding the right pedal or using a certain kind of microphone. That seems much less important to these sessions.
That’s exactly right. People can get caught up in the technological aspect of the studio — at great detriment to the music. At least in regard to the music that I’m interested in making, we have way too much ability to manipulate sound. I hear so much recorded music that has no vibe, no human quality to it. It sounds like the people weren’t even in the same room and maybe not even in the same country when they recorded it. It’s all been pieced together very carefully, but it’s missing an essential element: There’s no interaction. Some people can do beautiful things that way. For what Radiohead does, it’s great. They’re able to use those tools in a musical way. But the music that I want to make has to feel, in some way, like it’s being passed from person to person. It’s interesting because, when you nail it, it’s the kind of thing that sinks into the background. It becomes so effortless that you don’t think about it. It’s the same with movies: You know a director has done his job right when you can’t tell that they’re even there. The goal is to get lost in the storytelling.
Photo credit: Brantley Gutierrez