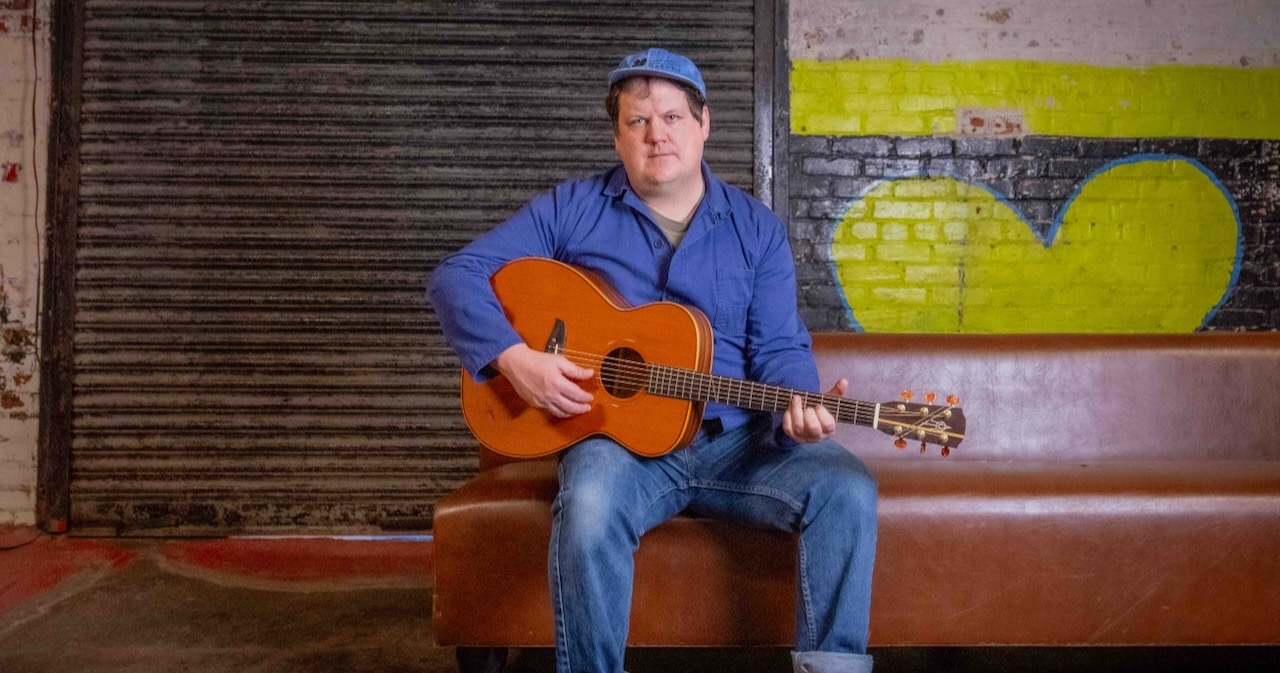
Two weeks before the release of his new folk album, When I’m Called (available today via Fat Possum), Jake Xerxes Fussell’s sister, Coulter, who is a quilter, had a show of her work in Oxford, Mississippi. In this show, Coulter patchworked 24 small quilts with fabric sourced from her friends and fellow quilters. There was one quilt for every hour of the day.
Though Fussell has said that he and his sister do not talk about her work very much, there are some profound resonances between her quilts and his music – the idea of updating tradition by the use of unusual materials and freer forms, for example, or the idea of using old material to make new texts, but also something deeper. The songs and the quilts mark time, but not in conventional ways. Instead, they track time in a looping, stuttering fashion. Time is both abstracted and made concrete, as a quilt can appear like midnight and a song can be both a work song and a travel song; but also how a quilt or a song can be a mark of a 19th century technique using 21st century material.
The sources for these records and quilts are a network of people. They include those as close as their parents or close family friends, but also as wide as academic song catchers from the 1950s and 1960s, the folk revival of the same era, the careful annotaters of 1990s web forums, or 2020s Instagram accounts. In the time I spent talking to Fussell, he was careful to note these networks, where and who he learned from, the songs he picked up, but also the methods.
These methods were not only adapted from family and friends, but also professional contacts and music legends who pursue a similar ambition to extend what “folk” means. They include Blake Mills, who has been a session musician for everyone from Bob Dylan to the Avett Brothers; or Robin Holcomb, the avant garde vocalist and multi-instrumentalist whose estranging 1992 album, Rockabye, provides a conduit from artists like Bill Frissell and John Fahey to contemporaries like Blake Mills or Daniel Bachman.
For Fussell, the creation of a drawing, painting, quilting, or song-making can come from the same geographical site, the same kinship network, or the same historical records. His parents were academics who painted, sang, wrote, and quilted, but he also had friends like Art Rosenbaum, who painted, gathered songs, taught them in and outside of the University of Georgia, and won the 2008 Historical Recordings Grammy.
Rosenbaum died in 2022 and the songs on this album are in his memory, absorbing captured Scottish songs from the 1970s. The track “Feeling Day” is both bright and mournful, moving in the body of Rosenbaum from Georgia to Scotland and back, where it was taught to Fussell and then captured here. The intermingling of technology, memory, curiosity, professional competence, and ancestor work all made contemporary by skill and memory. (Like the quilts.)
Fussell talks about reclaiming and re-interpreting these songs, versions of versions, updated for contemporary listeners. The album includes the work of Rosenbaum, but it can also be seen on the very first track, about the Mexican painter Maestro Garry Gaxiola, whose decades-long (and most likely one-sided) feud with Andy Warhol centered on questions of what populist art is and what folk art is.
It can also be seen in how Fussell sings “When I’m Called,” a song partially composed from a found paper scrap (again, the quilting) containing a child’s to-do list. It reminds me of the folk anthologist Harry Smith, who spent a long time cataloging paper airplanes he found on the street. It can especially be seen on Fussell’s version of “Gone to Hilo.”
Depending on who you ask, the song’s original title is either “Johnny’s Gone to Hilo” or “Tommy’s Gone to Hilo.” For most versions, those who sing “Tommy” think that the song is about Ilo, Peru and those who sing “Johnny” think it is about Hilo, Hawaii. Fussell sings “Johnny.”
The song is not really a sea shanty, because they require a stronger beat to function as a work song; but it was intended as a song for sailors, a kind of lament, and the gap between forms here has deepened as it has moved further from the sea. The work quality dropped, and the lament quality ratcheted up. It has been sung by dozens of people, one of those tracks that criss-crosses the Atlantic with the folk – Peggy Seeger sang it when she was in England with Ewan McColl, for example.
Perhaps the saddest version of the song is by Paul Clayton. I think maybe three people in the world care about Paul Clayton, and Fussell is one of them. Clayton grew up in New Bedford, Massachusetts, and collected songs about that town’s whaling history since before he was 20. He went to UVA and studied under the legendary song collector Arthur Kyle Davis, traipsing through Appalchia finding songs and then moving to the East Village, integrating himself with Van Ronk and especially Dylan. Fussell claims that his version of “Hilo” is directly in the tradition of Clayton – that how he weaves a song is how Fussell weaves a song.
Between 1954 and his too early death in 1967, Clayton made almost a dozen records of revolutionary war songs, sea shanties, timber shanties, songs of marital discord, songs which Dylan ripped off, and songs which are only remembered by enthusiasts. Fussell is an enthusiast, his version is the lament that Clayton created from the work song and the interweaving of the lament and the work song – the doubling down on the historical memory, the absorbing of a technique renewed in the knowledge of history – is key to the whole enterprise.
Listen to how Clayton emphasizes certain words – for example, “bully boy” – but also listen to how it’s just Clayton; a clarion voice, and a melancholy one. Listening to Fussell’s, with Robyn Holcolmb singing harmony, the sadness is still there, but the tradition is too. The tightness of the version traps tradition, that it is in the middle of the album, that it’s a single, marks a network of relation, an aesthetic about public choices, and a wrestling with tradition.
Folk music asks again and again, “Why are we making these choices?” and, “Whose choices are we making?” Fussell, at his best, makes choices that are smart, open, generous, and mark a time and place – be it Georgia or Hilo or Oxford, Mississippi or a room where Clayton and he can have a conversation with all those 19th century sailors.
Thinking again of Coulter’s quilts, they both mark time in an abstract sense – the idea of what noon or midnight looks like – but they also mark the time it takes to create a work. There is this idea that time is linear, that it marches forward relentlessly. The quilts mark the history of their creation, the actual moments that Coulter made them, but they also weave together the stories of those who gave her their scraps, the interlacing of decades of commercial and domestic enterprises intended to make an object which shows its sources/seams.
Everytime someone sings a traditional song, this kind of citational practice renews the song, the text, the material. Like a quilt, when Jake sings, time bends and loops, inviting other people’s time, other people’s lives. In a worst-case world, this could be greedy, or wolfish, consuming without respect; in Jake’s work, a much better world, this is a kind of kinship network, sharing and consuming mutually.
Photo Credit: Kate Medley