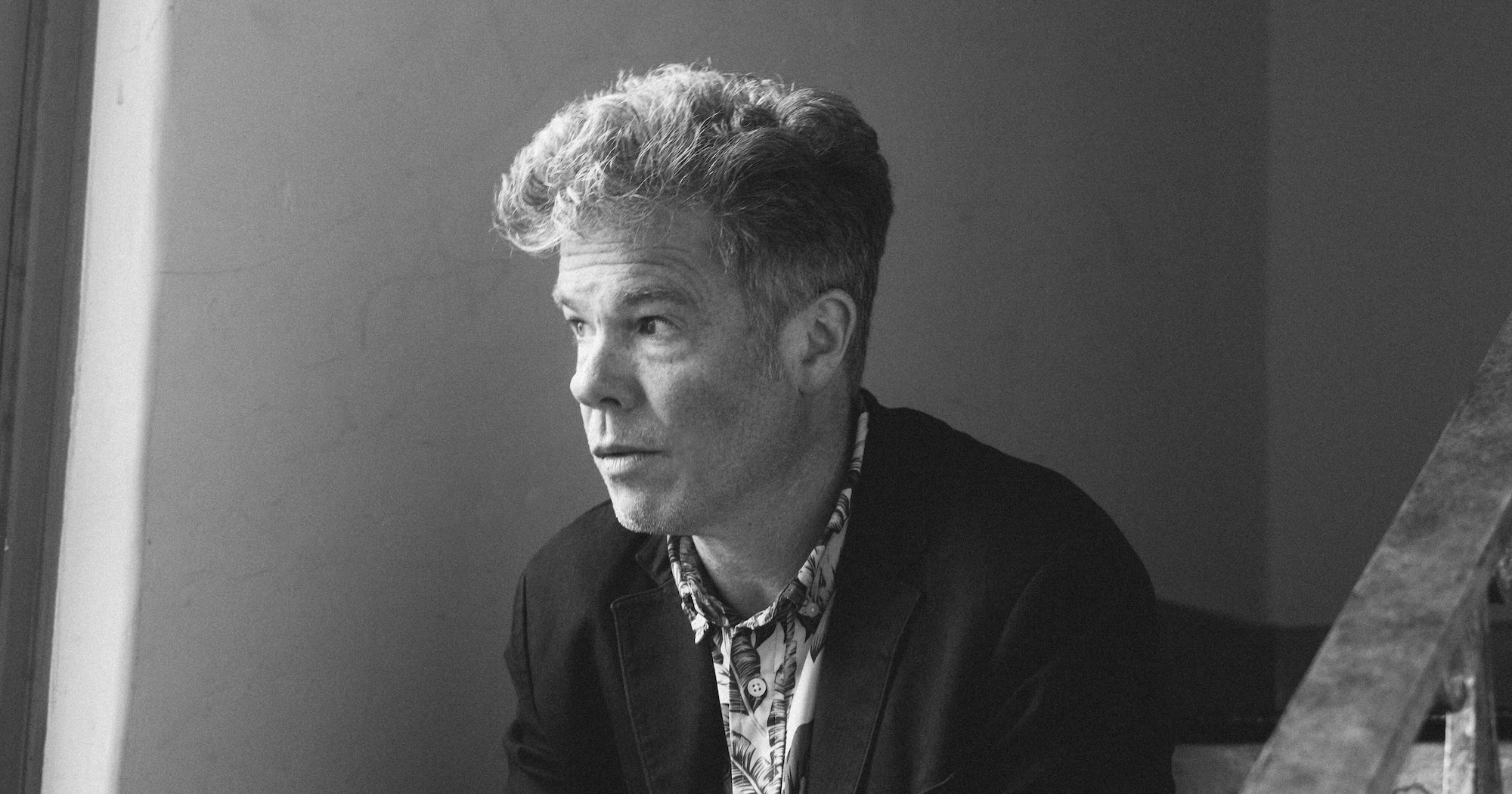
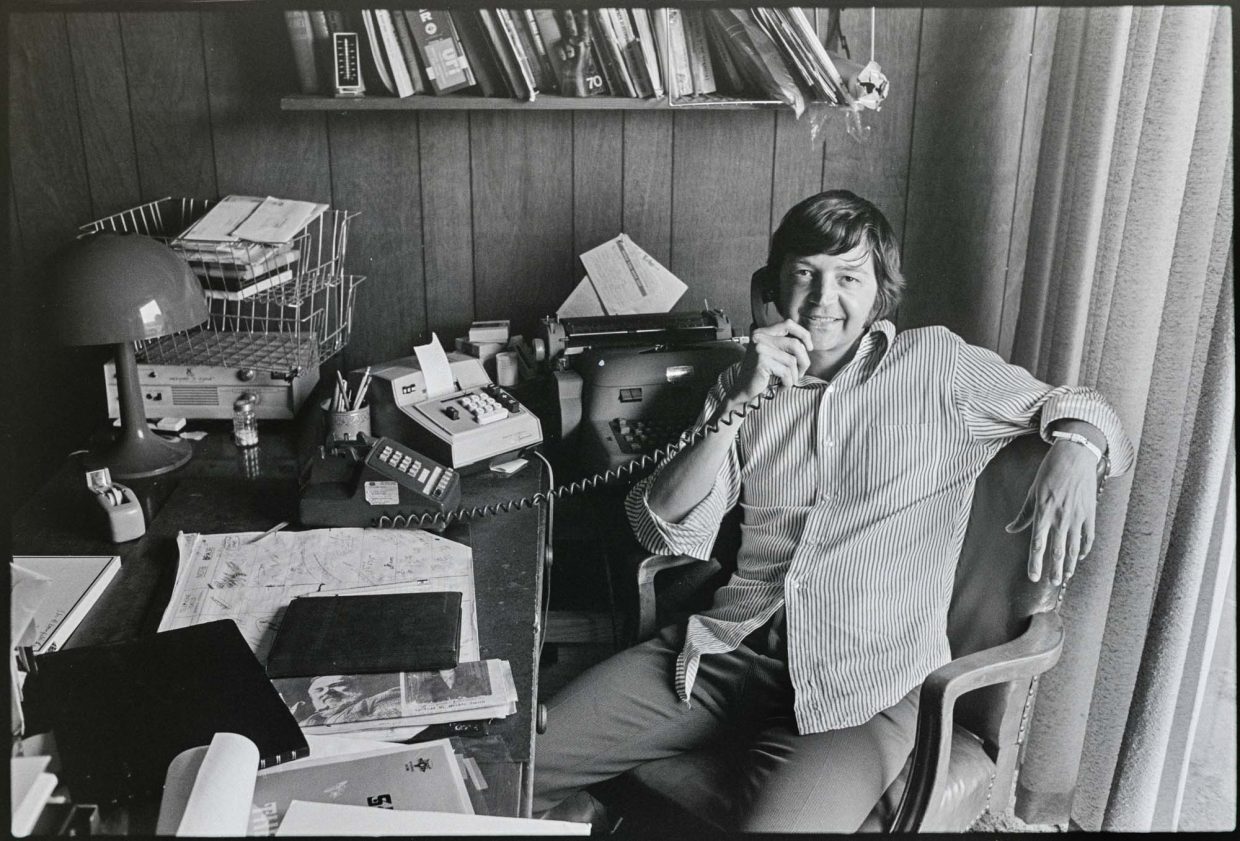
Idaho-born singer-songwriter Josh Ritter has released a dozen studio albums over the past quarter-century, crafting an elegant body of work. A few years back, he earned the ultimate compliment in tunesmith circles when Bob Dylan covered one of his songs, “Only a River,” co-written with Bob Weir.
By now Ritter is well-acquainted with the wisdom of following the muse wherever it leads. Recently, however, he was moved to take a step back and focus more on the muse itself rather than the destination. That inspiration began with “Truth Is a Dimension (Both Invisible and Blinding),” a visionary song from his latest batch of compositions. Beautifully simple and unadorned, it’s just voice and guitar as Ritter summons up myths and memories surrounding “the one who got away.”
“Truth…” turned out to be one of the 10 songs making up studio LP number 13 for Ritter, the whimsically titled I Believe in You, My Honeydew, which releases today followed by widespread touring well into next year. Along the way, he’ll be posting regularly on Josh Ritter’s Book of Jubilations (one of the better artist Substacks out there) and at some point he’ll get back to working on his in-progress third novel. Fiction writing has turned out to be yet another thriving subset of Ritter’s career.
“I have a rough draft done,” he reports. “My wife Haley reads all my first drafts because she’s my best reader, so she’ll tell me the problems I need to fix. I’m excited about this one. I’ve written two other full novels since the last one came out, but they don’t have the spark this one does. It’s nice to have an ongoing project you can work on a little at a time, take a break and let it marinate.”
In the meantime, there’s lots to be excited about regarding I Believe in You, My Honeydew. BGS caught up with Ritter by phone from his home in Brooklyn.
You recently wrote a Substack post about first drafts, which you likened to a sculptor’s “acquisition of the stone” that will eventually be carved into a statue. An elegant way to visualize the slog of writing a book.
Josh Ritter: My true writing journey began through songs, which was the first form I really connected with. Writing songs, you can edit very quickly and on the fly. But after years and years of that, I was really struck by the different pace of editing when writing a novel. It takes no big effort to change things in songs. But with a novel, there’s just no getting around that you’re heaving big lumps of stone around – paragraphs that you have to haul from one place to another.
That makes it a lot heavier, but it can also be a joyful act. Pulling the rock is so exciting, that initial spark of inspiration and desire to heave this impossible stone. It’s beautiful when the story is exposed for the first time, all these rich characters. Same as a song.
Your first novel, 2011’s Bright’s Passage, actually started out as a song. Does that happen often, where a piece of writing starts as one thing but becomes another?
As a writer, what I have is water that will fill whatever container I put it in. Songs have a shape that can hold a whole story that could be a novel – like Springsteen’s “The River,” that could be a novel. At the same time, it’s fun to have novels as a different mountain to climb in your mind. Songs are something you can get to quickly, but you might also want to do this other kind of writing that takes a long time and a lot of love. Then you have to decide the economy of that: Is it important enough to you to be worth it?
I’ve always thought songs are like corridors where there are doors but not rooms. Turn on a song, listen to it, and you’re walking down that corridor. And off the corridor, the rooms are your own thoughts and memories, wondering about everything from what to make the kids for dinner to the nature of God. You can hear stuff on the radio that leads to profound questions that are not about that moment, but would not happen without the song. It’s really beautiful. Sometimes you just want to follow songs behind the door, wherever they go.
From your new record, “Truth Is a Dimension (Both Invisible and Blinding)” is such a beautiful, heavy, heartbreaking song. Listening from the outside, it feels like the heart of I Believe in You, My Honeydew. Does it feel that way to you, too?
There are certain songs I feel fortunate to receive, which is what that one felt like. It unfolded in such a quick and finished way, with such clarity, and it gave me so much to draw from. Not just the subject matter, but this idea I became obsessed with about truth becoming changeable. There’s a metaphysical aspect, but also more physical than we give it credit for. And as I was writing it, I realized I was writing this with a muse. Had to be.
Afterward, it occurred to me that this was not something I could’ve done by myself. Hemingway used to say that we all get lucky sometimes and write better than we can. But it all depends on who you’re writing with in your mind. Helps to have a third party in there, between the head and the heart.
That was the first song I wrote for this record, and the rest unfolded out of the same general idea. What I hoped to do was perceive a muse as something fuller than what I had appreciated in the past. To assume that a muse is a spiritual acquisition, that didn’t feel right. And to have “lost” one’s muse implies you had it to begin with. No one likes to be “had,” you know?
The bittersweet vibe of that song reminds me of one of my favorite songs and videos of yours, 2010’s “The Curse.”
That’s another one I fell into. A lot of the story songs are like a trance, with the song unfolding as it’s happening. The song is only as long as the trance lasts, and when it’s over it’s really done. I’m almost glad it doesn’t happen all the time. That sense of revelation is so powerful, and I don’t want it to wear off. I imagine it’s the same feeling as hitting a golf ball really, really far.
On that song and others, you really have an affinity for waltz time.
Oh, I love it. Waltz time is such a beautiful architecture that feels like a Viennese street, really fundamental and blocky. It’s a stone you can build on, a lot of melody can go on top of a waltz. So sweet and dark. If I could do it every time, I probably would.
So with the muse, do you have an actual mental picture of what it looks like? A visual manifestation?
It’s not something I can anthropomorphize, but the closest I’ve found is honeydew. It’s familiar and weird, almost self-luminous. Cut it open and it’s this mess of wires and biology in there. It tastes strange but also good when you eat it, unearthly but also familiar. Music is my way of exploring the euphoria and unexplainable elation of experiencing that vision. Sometimes it seems like ideas and feelings from other worlds are fearful, and I’m comforted by the idea that they can be communed with.
So, how to communicate with this thing? Because when you come right down to it, I couldn’t even assume it knew English. It could read my mind without knowing the language. So I had to teach it about things I love, invite it into this experience of being a 48-year-old man who writes songs for a living and lives with his family in Brooklyn. I had to be open to this other life force, show gratitude and offer it a place at the table.
The songs came out of that and I like playing these songs we worked on together. I wanted this record to be fun. I liked the idea of it being high-flying but also earthy. Like seeing something celestial at a Friday night bonfire party with Solo cups, one of those occasions with friends listening to music together and looking up at stars. That’s as holy a moment as can be found. I wanted to write about that moment as the setting for a soundtrack of that liminal passing as dusk comes on.
What other songs on this record do you like best?
I’m proud of “Noah’s Children,” which I remember as just a marvelous fun time to make in the studio. You could just feel it develop. I brought it in with that strum and quickly realized that Rich Hinman’s amazing guitar-playing really gave it the percussive slink I wanted it to have. It became something I really wanted to be singing at that moment.
“Kudzu Vines” was fun as well, just turn everything way up. And starting the record with “You Won’t Dig My Grave” was intentional. Records are about a moment in the time and life of an artist, and that song’s definitely about surviving bullies and forces that seem dead set against humanity, dragging us downward from our potential. Sometimes the only way to defeat someone like that is to outlive them.
You mentioned that this record was fun to make. Have some of your other records been more of a struggle?
In different ways, every record is never separate from the lives of the people making it. I’m sure every member of my band would have a different answer but [2023’s] Spectral Lines was very difficult to make. It was during the pandemic and also following my mom’s death – like [2013’s] The Beast In Its Tracks followed my divorce. Those were moments of personal crisis, living in that moment and what came out of it. Often there was not joy. But there was need and there’s some joy in that.
So yeah, some records are harder to make than others, but that almost doesn’t make it into the equation as soon as it’s done. You’re proud of it and that bad feeling goes away. I guess there’s a reason we do things twice. Whatever mountain you climb, the hurt is forgotten if you love it enough.
Now this one was all recorded in a way that’s the most fun for me, everybody together in a room, just a great time in Minnesota way out under the stars. No reason for it not to be a good time. I’m very proud of the story and its conclusion.
Long ago, you started out intending to follow your parents into the field of science – until taking organic chemistry in college at Oberlin. Maybe they were disappointed at first, but given your successes they must be pretty sanguine about your career choice.
I always say, never let college get in the way of your schedule! On the one hand, I was really disappointed not to be whatever idea I had at that time. At the same time, I was profoundly impressed with how many of my peers were doing things of just magical intent of purpose. And I was left there thinking, “Okay, this is going to change some things. I have to think about this because I’m not going to be who I thought I was.”
But my parents took it well. My mom died a few years ago and my dad is living in Minnesota with his new wife. It’s been fun, he comes out to the shows. When your mom dies, suddenly you don’t have someone to show your booboos to. I’ve been fortunate that he has become that for me, someone to share both victories and griefs with. Seeing parents go on to new lives and loves is a beautiful thing. It’s one reason why this is such a happy record.
Photo Credit: Jake Magraw