[Editor’s note: All photos by Carl Fleischhauer, except publicity shot of Esco Hankins]
On the afternoon of Sunday, August 13, 1972, Carl Fleischhauer and I were in Jackson, Kentucky, at the finale of Bill Monroe’s Kentucky Bluegrass festival where we’d been since Friday. In my notes, I wrote:
We left after talking briefly with Monroe (I bought his new LP [Bill Monroe’s Uncle Pen] and latest single [“My Old Kentucky and You”] from him) and drove [85 miles northwest] to Lexington where we got a motel — the Flora — run by an 85-year-old lady who liked Bill Monroe and told us that Uncle Dave Macon stayed in the Flora whenever he visited Lexington. Dinner late on the [U of KY] campus or near at an Italian restaurant — snuck in leftover wine and had ravioli. Sure was good to bathe and sleep in an air-conditioned room.
Monday morning after breakfast downtown and some cursory hunting in record cut-out bins, we headed to the Esco Hankins Record Shop. Tennessean Hankins, a Roy Acuff-style singer, began his recording career in 1947. He settled in Lexington in 1949 and performed for years on WLAP with his wife Jackie and his band, which included Dobro player Buck Graves. He also performed weekly on The Kentucky Mountain Barn Dance, which started in Lexington in 1949 and was broadcast on WVLK.

Flatt & Scruggs joined the Kentucky Mountain Barn Dance cast that year, influencing both Graves – to whom Earl taught his right hand, three-finger roll – and young J.D. Crowe, who was a regular in the audience and often went with his dad to observe Scruggs rehearsing with Flatt for their radio shows at WVLK. In 1950, at age 13, inspired and informally tutored by Earl, J.D. got his first banjo and began practicing what he’d seen watching Earl in action.
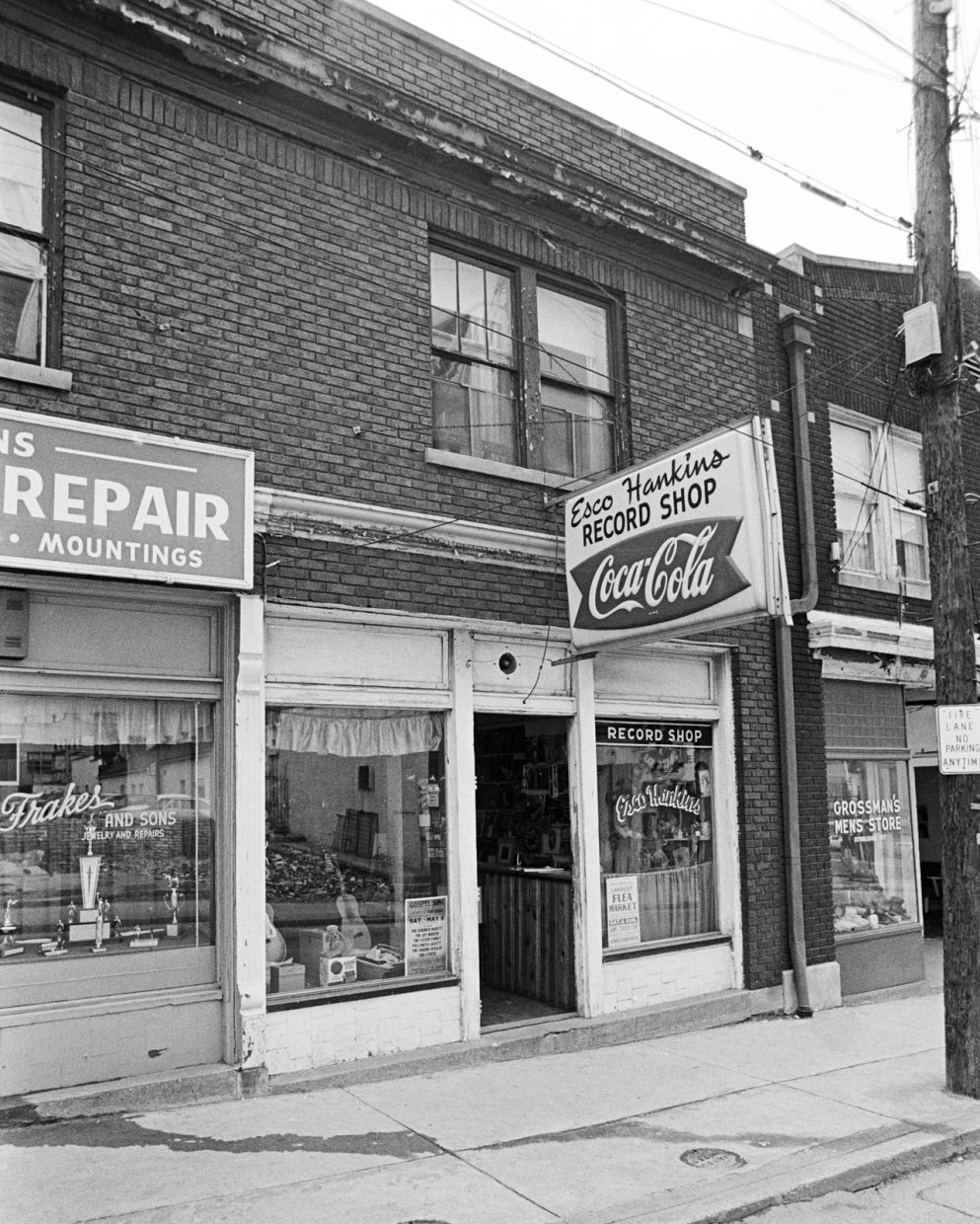

Hankins held amateur country music contests, and at one he discovered teenager Crowe, who soon became part of his band. Marty Godbey’s Crowe On The Banjo: The Music Life of J.D. Crowe (2011) is a fascinating biography that narrates in great detail much of the story I would hear in my interview with Crowe that day in 1972. Early on, Godbey quotes from one of her interviews with J.D.: “I played for him quite a bit, it was my first paying job.”
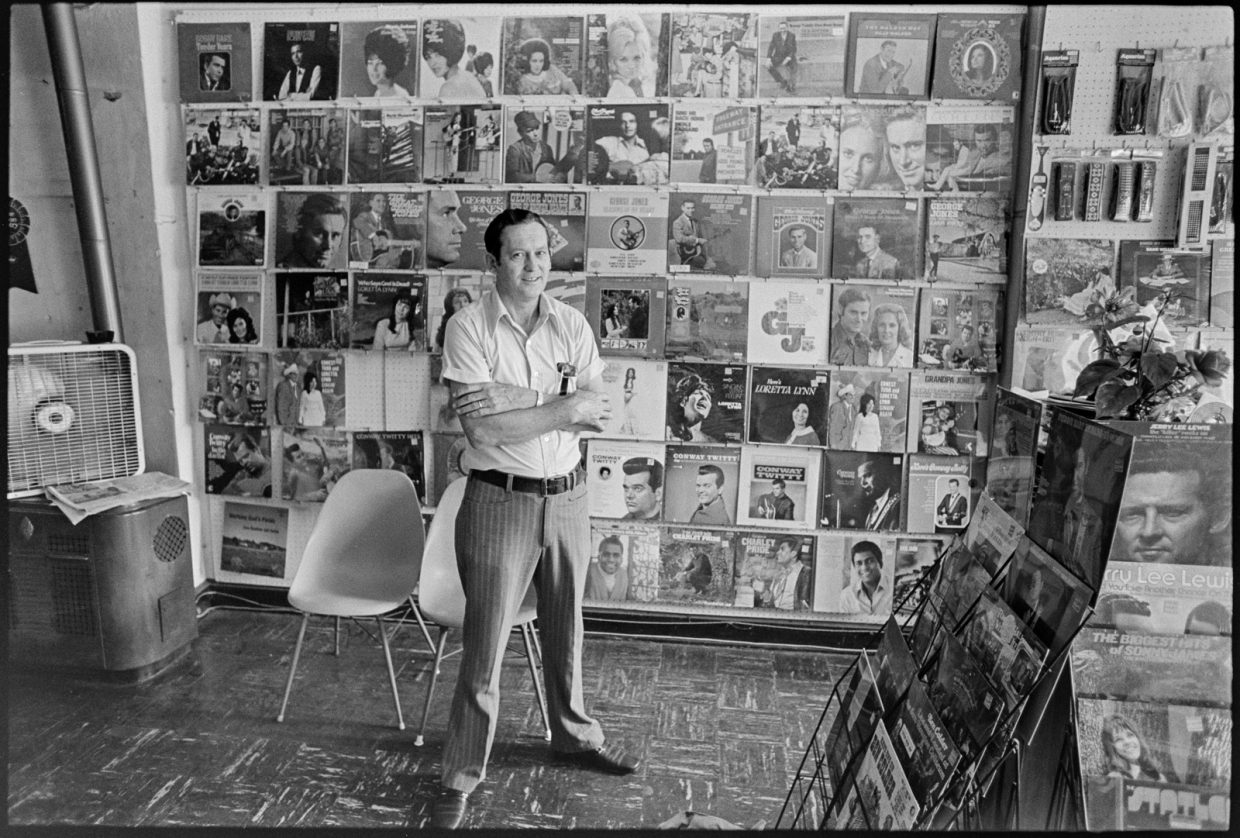

I knew nothing of Crowe’s connection with Hankins on that morning when we walked into Esco’s shop. We browsed, bought some records, and then got into a conversation with him about country music history. He generously gave me a number of old songbooks and then, when we mentioned our interest in interviewing Crowe, he phoned Lemco, the Lexington record company with whom Crowe had recently made three albums and several singles, to get J.D.’s number. My notes:
…he ended up calling first Lemco and then J.D. Crowe and then handing the phone over to me to talk with J.D. — I thought it was still Lemco and went into a long rap about my project and what I was doing and how I would appreciate if they could put me in touch with J.D. — and the voice said, “This is J.D.” and I was embarrassed but maybe it was a good thing…anyhow we made an appt. for 3:00…

Today, Crowe is best remembered as the banjo picking leader of the progressive New South, whose 1975 Rounder 0044 album with Skaggs, Rice, Douglas and Slone has become a modern bluegrass icon. He also was, in 1980, a founding member of the bluegrass supergroup The Bluegrass Album band, playing solid, perfectly timed, and driving banjo based on the style of Earl Scruggs and singing the harmony parts he’d learned with Jimmy Martin. He died on Christmas Eve, 2021.
When I interviewed him in 1972, he’d been living in Lexington, his birthplace, since returning in 1961 after a five-year stint with Jimmy Martin and the Sunny Mountain Boys. For the next seven years he’d worked day jobs (with a couple of brief stints back with Martin) while playing in local taverns with his group, The Kentucky Mountain Boys.
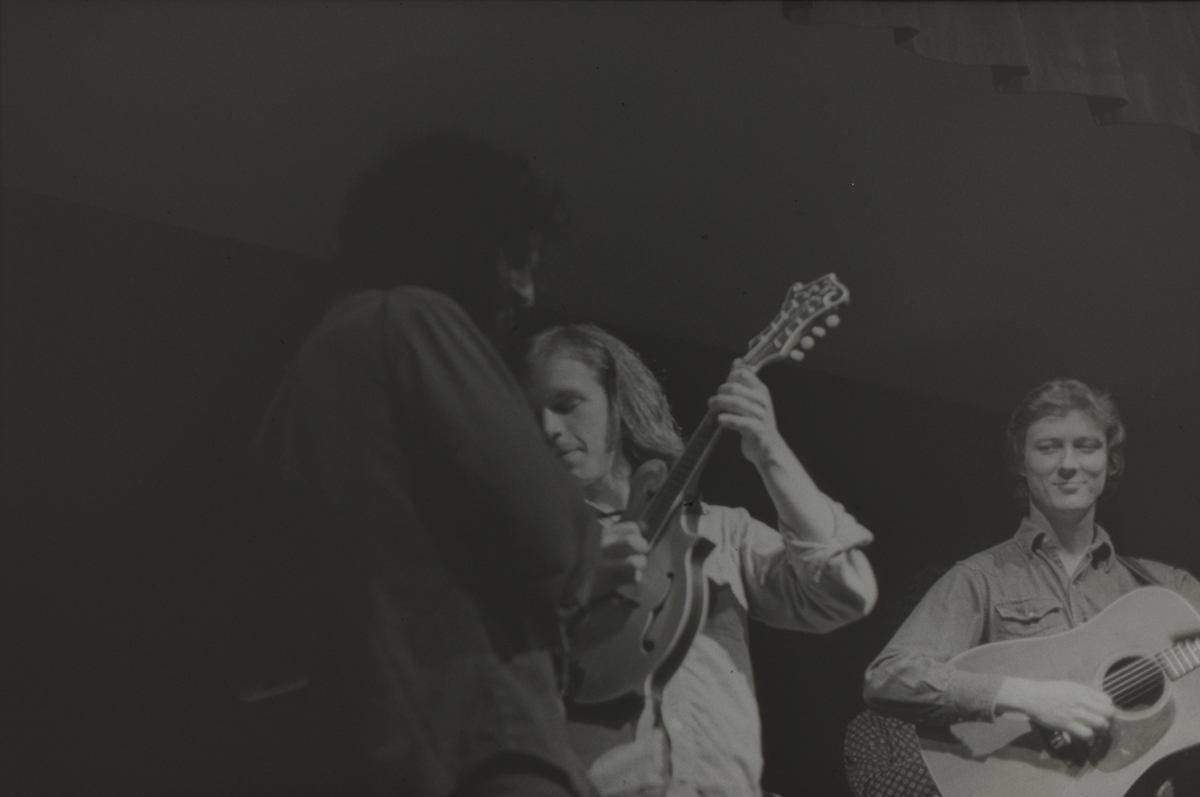
In 1968 they began appearing six nights a week at the Red Slipper Lounge in the Lexington Holiday Inn. It was a change from his former blue-collar tavern milieu – lots of young college students in the crowds. This gig was going strong when Carl and I visited him.
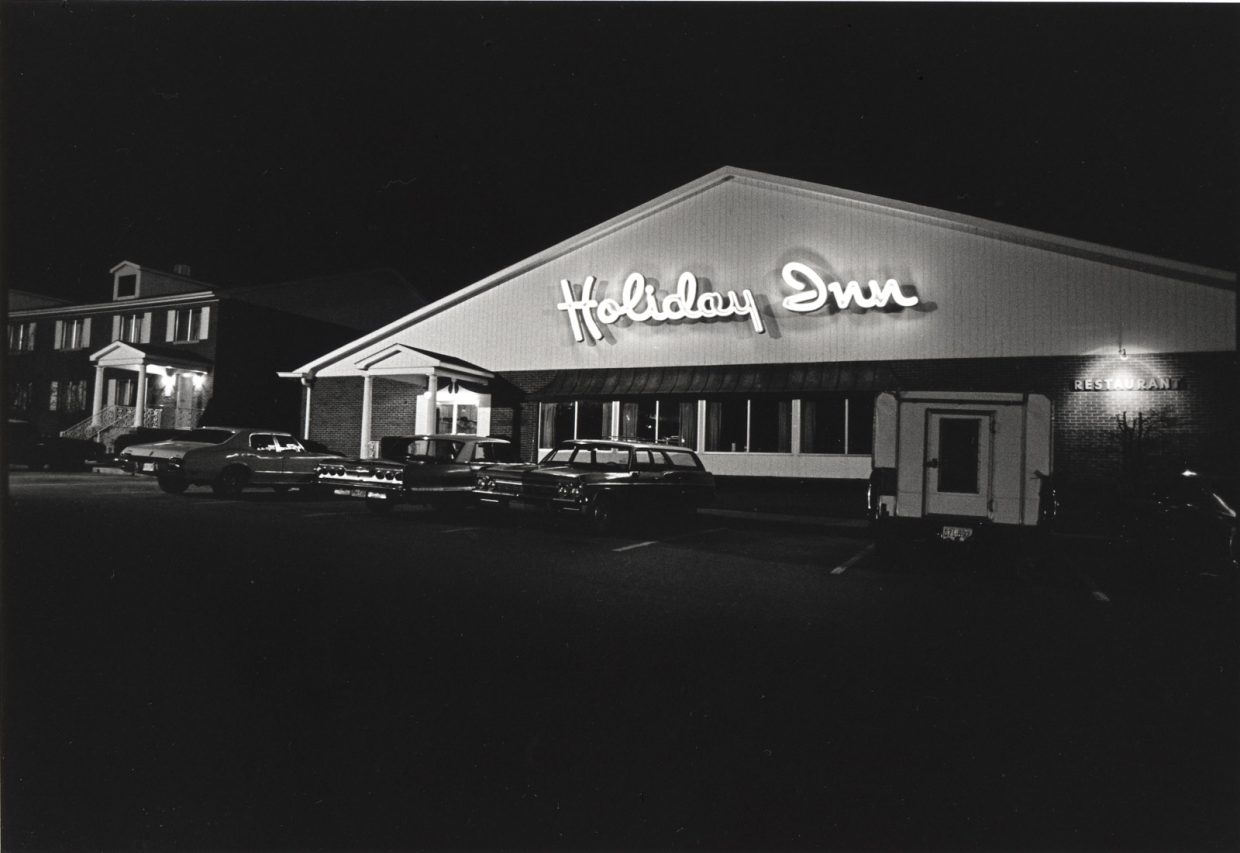
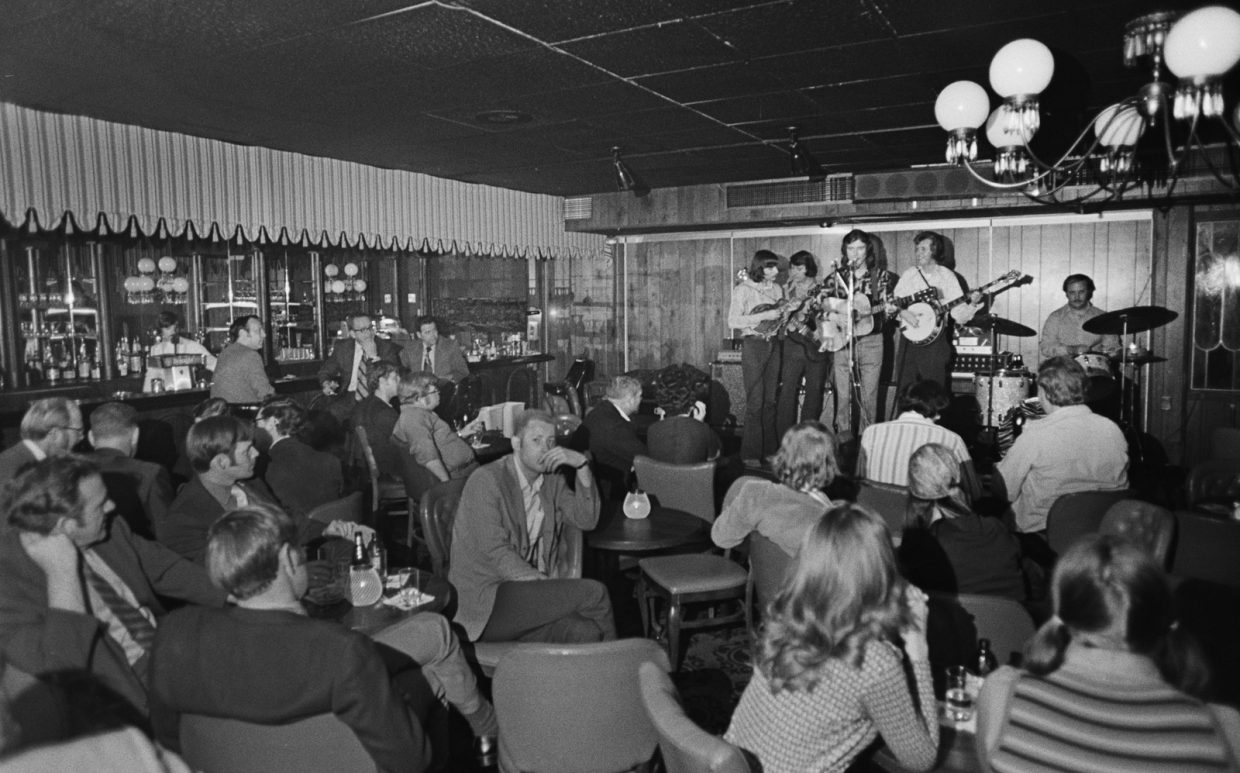


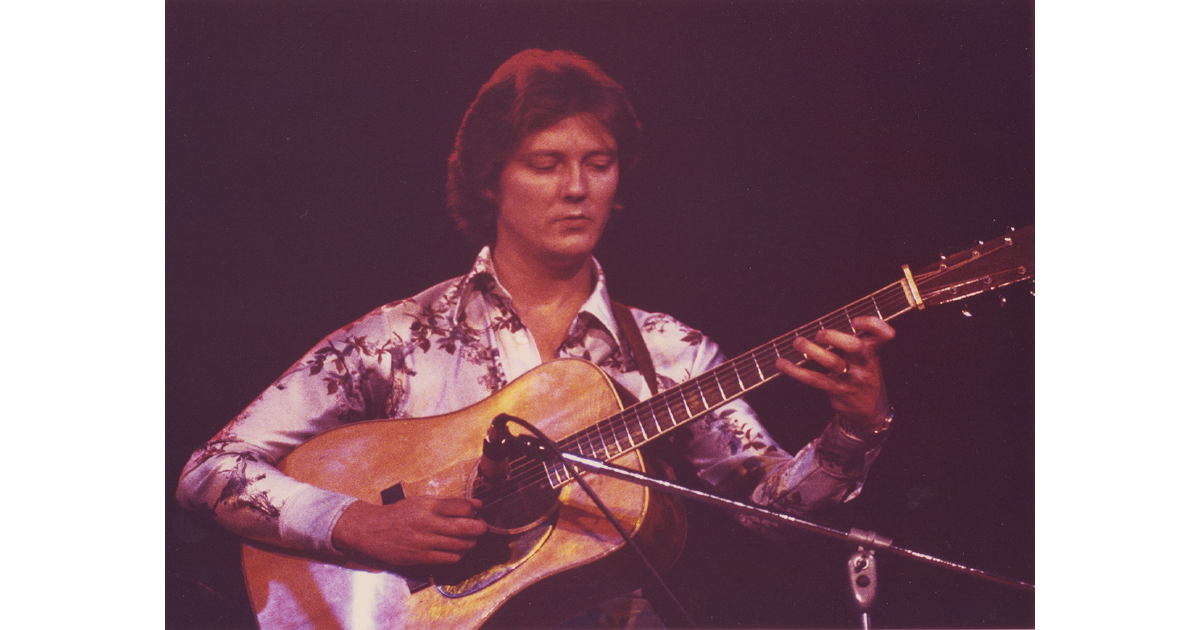
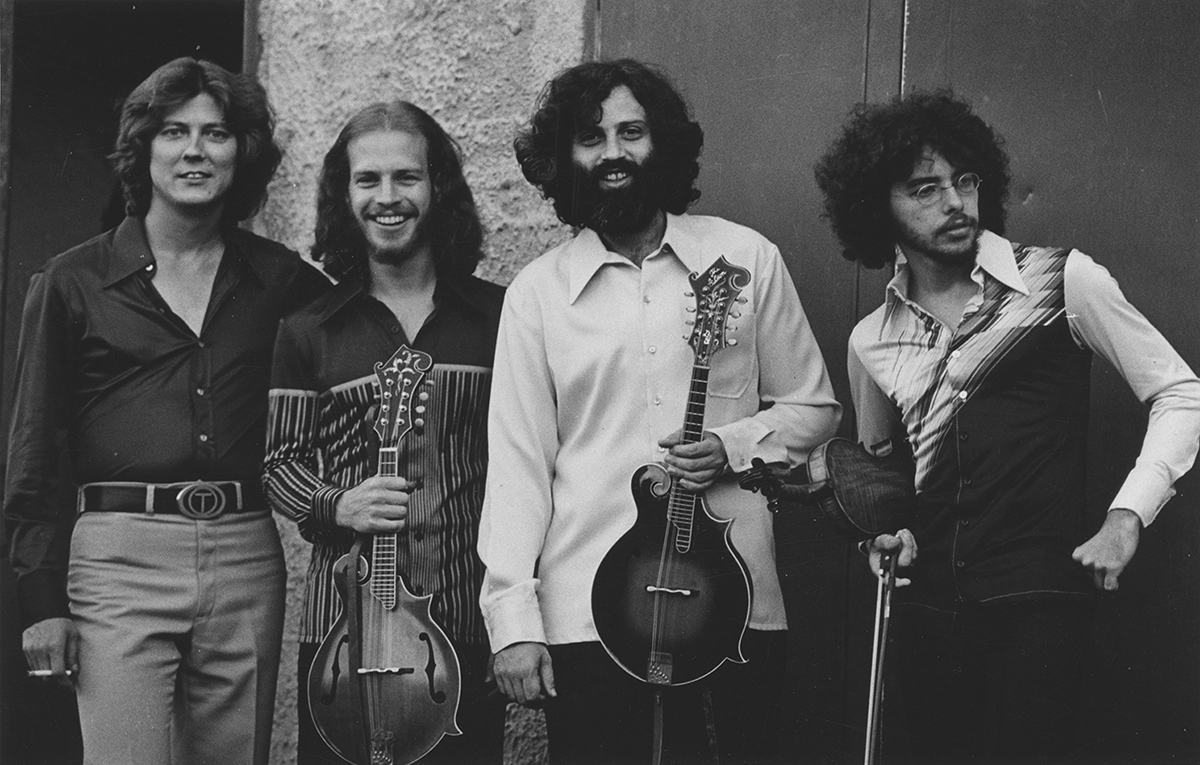
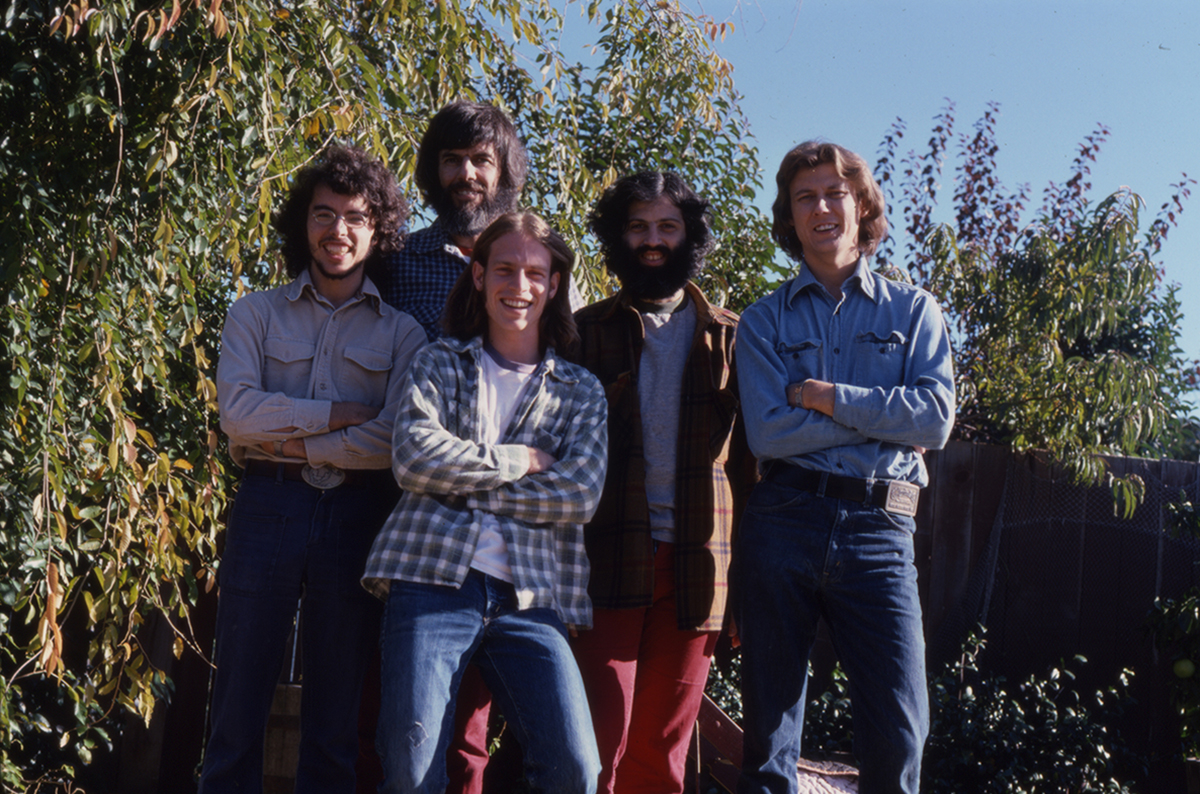
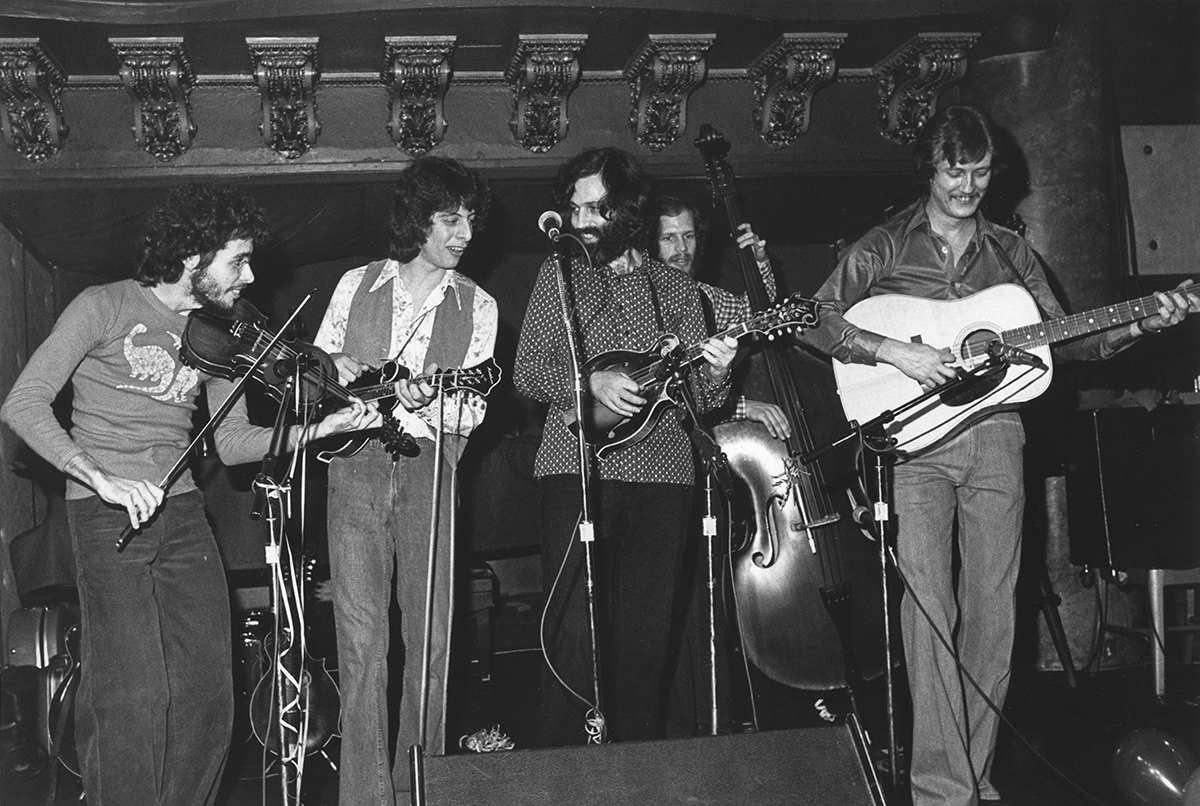
J.D. was now working full-time at his music. A number of notable musicians had worked for him in The Kentucky Mountain Boys, like Doyle Lawson and Red Allen. At this point, in 1972, his band consisted of Larry Rice, mandolin, Tony Rice, guitar, Donnie combs, drums, and Bobby Slone, bass. He had just changed the name of the group to the New South.
I had first seen Crowe in April 1960 when I went to Wheeling, West Virginia, with a couple of college friends. A month earlier we had opened for the Osborne Brothers at Antioch College. Bobby Osborne had urged the audience to come see them at the Wheeling Jamboree at WWVA. We took him up on it at spring vacation.
We drove down from Ohio and took a cheap room in a hotel close to the Virginia theater where the Jamboree was held. That evening we saw the Osborne Brothers as expected, but just the two of them were there. Bobby played guitar and sang “Down The Road” while Sonny picked the five. Good music, but no band! We enjoyed some of the country acts like Rusty and Doug and the fiddling of Buddy Durham. But we weren’t expecting any more bluegrass when Jimmy Martin and the Sunny Mountain Boys were introduced. It was the most memorable moment of the evening for us.
The four-piece band – Jimmy Martin, Crowe, mandolinist Paul Williams, and fiddler Johnny Dacus – bounded up to the mic from backstage and opened with Crowe’s the up-the-neck single-string banjo intro to “Hold Whatcha Got,” Martin’s latest single.
The audience, which included a bunch of young women seated up front who had cowbells and knew how to use them, went bananas. It was a tight band, thought by many to be Martin’s best, and we were very impressed. Crowe’s banjo break was amazing. It marked him as a unique stylist.
Thereafter, when talking with fellow banjo pickers, I identified this single-string work as “J.D. Crowe style.” The success of “Hold Whatcha Got” led Martin to record several more using the same rhythm and banjo break style.
Following our experience in Wheeling, we began listening to Martin’s late Saturday night show, after the Jamboree, on WWVA. The live sound of new songs like “My Walking Shoes” – driving, up-tempo stuff with Crowe’s banjo out front – caught our ear.
J.D. told Marty Godbey about watching Earl rehearse: “I was more interested in trying to learn the breaks to songs and backup than instrumentals.” His work on Martin’s Decca recordings was definitive; Martin’s banjoists were told to play it like J.D.
He began to record on Lemco with the Kentucky Mountain Boys in 1969 when the band included Doyle Lawson and Red Allen. This was the most recent Crowe recording I’d heard at the time of our August 1972 interview.
That afternoon Carl and I drove to his trailer park home. We set up my cassette recorder and mic, and I began the interview with a few ethnographic questions: “Let me ask you just some of the basic things, like how old you are and where you were born and so on.”

He was 34 and told of childhood with country music on a farm six miles outside of Lexington. Then he described how his musical calling emerged in the fall of 1949 after Lester Flatt and Earl Scruggs came to town.
I saw them in person before I ever heard their records. Cause, the first record I heard of them was one called “Down The Road.”
“Down The Road” was Lester and Earl’s newest record release in October 1949.
His family were regulars in the audience at the Kentucky Mountain Barn Dance.
And I saw, they came here — fact, I never heard of ‘em!
They was there one night, and they was so well received that they was hired.
His first banjo was a 39-dollar Kay, but within a year he’d moved up to a Gibson. Scruggs was his informal mentor. At fifteen he was playing dances and at sixteen Jimmy Martin hired him after hearing him playing on the radio with Hankins. “Hankins?” I asked.
Yeah, I guess that was the first person I worked with professionally.

After five years working full-time in Martin’s band – in Detroit, Shreveport, and Wheeling – J.D. quit. It was 1961, he was twenty-four.
I think I just, a, kindly got tired, I mean, you know, wanted to try something different.
This was a phrase he used several times in the interview: I just wanted to try something a little different, he said later, speaking of the band he started. Moving back to Lexington, he got a day job, and formed The Kentucky Mountain Boys, who played five nights a week in local clubs until 1968. Then the Holiday Inn gig came along:
I give up my job and I’ve been doing it full-time ever since.
As a bandleader, he stressed the hard work involved in building a career:
…you know how the music goes, unsure, you know. Which anything is, really when you get down to it. It’s just what you want to make out of it, and how hard you want to work… And a, believe me, it’s, it’s rough. A lot of people, you know, think it’s a lot of, a bowl of cherries, you know, just have a good time, but it’s not like that.
“I suppose the picking is only the small part,” I said.
That’s just the smallest part of it, really.
J.D. explained how his full-time band operated – fall, winter, and spring they played six nights a week at the Holiday Inn. Then they took the summers off:
Work road shows.
He told me about his band members — mandolinist Larry Rice, his brother Tony, and Bobby Slone — and explained about the Rices’ California connection:
They were born in Danville, Virginia, but … they went to California when they were just little shavers and they lived out there I guess ten or twelve years in Los Angeles. And that’s where Larry came from, he was living there at the time… Bobby Slone, our bass player, he’s been with me I guess about six years. Well, he used to live in California also, and he had worked with them when they was growing up and so he told me about them. And of course, Tony I met after Larry joined me. He moved back to North Carolina and he came up.
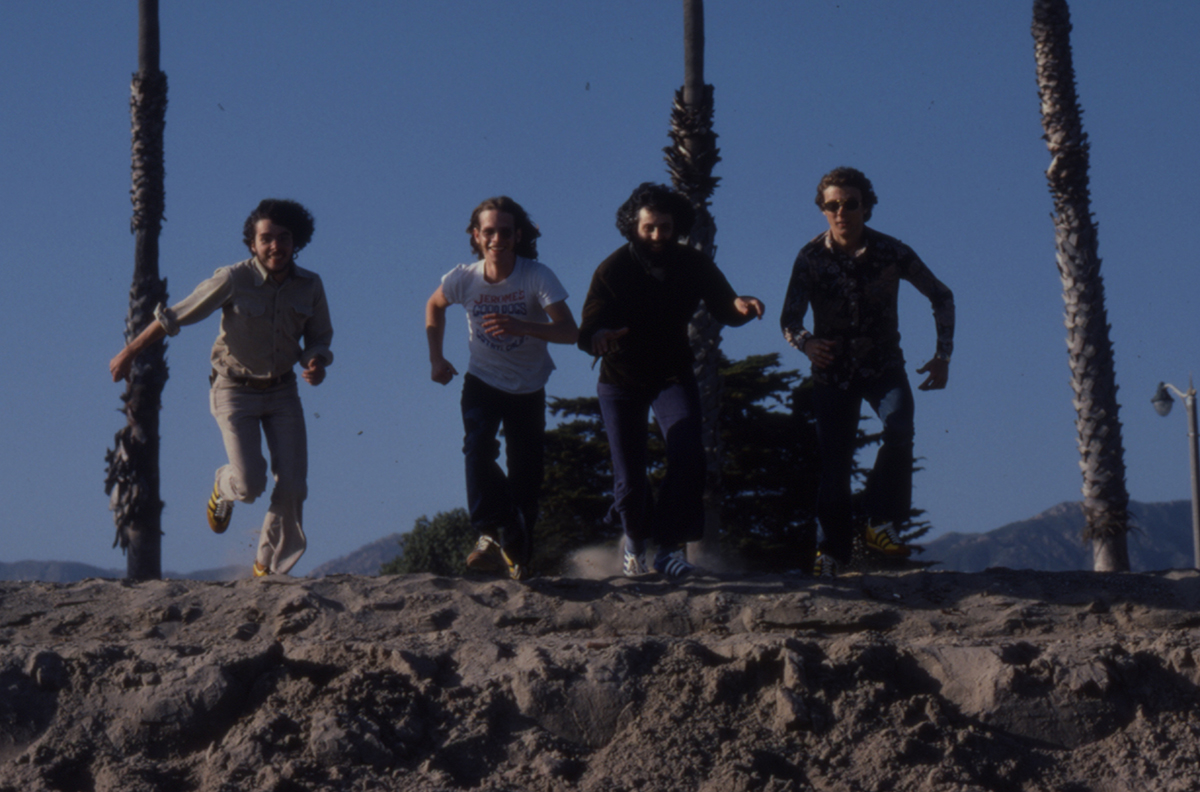
His band were all veterans of the late ’60s LA scene where folk-rock and country-rock had blended with bluegrass. That musical mindset had a kind of creative vision that Crowe could empathize with.
I used to be, if it didn’t have a banjo in it, then I’d cut it off. But now, with the exception of rock and roll and blues. I’ve always liked it. I used to listen to blues, just all the time. I like the style of B.B. King, of course he’s still going, you know, and, a Fats Domino, Little Richard, you know … they was in the fifties. And there’s just a lot of ‘em, and of course the rock changed you know, course what they call country rock, which is good, I like that. In fact, we do quite a few numbers of that ourself.
I asked: “When you were leaving Jimmy Martin, were you thinking of putting some of that into your music?” He explained:
That wasn’t out yet … I didn’t have too much choice. You (could) only do country, do bluegrass, or you just do hard rock. But now there’s so much new stuff’s out that it’s just endless, to what you can do, and take over songs and adapt them over, your own little thing, in style.
You can take with what you had and combine it with a couple other forms of music and come up with a little different gimmick, a little different style. That’s the whole thing, that’s what you got to have.
Perhaps the most novel aspect of the New South sound at this time was the fact that since the prior September – almost a year before – they had been playing electrified instruments.
I had the idea, you know a, maybe that might be the answer, because, like I say, like we couldn’t get any records played on country stations.
The Osborne Brothers had gone electric in 1969; J.D. said their example had influenced him “a little bit.” Also in 1969, Earl Scruggs had begun playing an electrified banjo with his sons in the Earl Scruggs Revue. Jim & Jesse had done an electric album in 1971. I asked J.D. if he’d recorded with his electric group.
The latest single is. Course I use a steel and a piano and a drummer, the whole works on that. In fact I didn’t play too much banjo, on account, if there’s a lot of banjo, some things, they won’t even, some stations won’t play it.

We’d just been at a festival; I wanted to know what he thought about festivals. Had they helped his music?
The festivals have helped to a certain extent. You know. Right now, they’re trying, they’re getting too many of them, in my opinion. Cause you can over do a good thing, you know and, which I know we worked some of ‘em that didn’t turn out so good … most of ‘em, though, we’ve worked this year have all been great big ones, I mean a lot of people. And I figure they will probably continue having that kind of a crowd. And I think that it’s, it’s helped.
“Is it a different kind of crowd than the country music crowd?” I asked.
A, not really, I’d say a people that go to bluegrass festivals would also go to see Porter Wagoner and Conway Twitty and Merle Haggard — Nashville, you know. They like it, course they like bluegrass too. A lot of your country people, you know, like other types. There’s — they like it, but they won’t come out to see it, you know, they don’t like it that good. They can take it or leave it, in other words. That’s what you got to get to, those people, the general public. You know, cause there’s a lot of people come to the festivals and — but you know if you figure, the population of the world and you know, don’t look, it’s not too good a’ odds, so…
An experienced observer of the ongoing bluegrass scene, J.D. was keenly involved in his music business. He spoke of recording studio dynamics, record company practices, broadcasting politics, fan magazine reviews, and other factors in running a band.
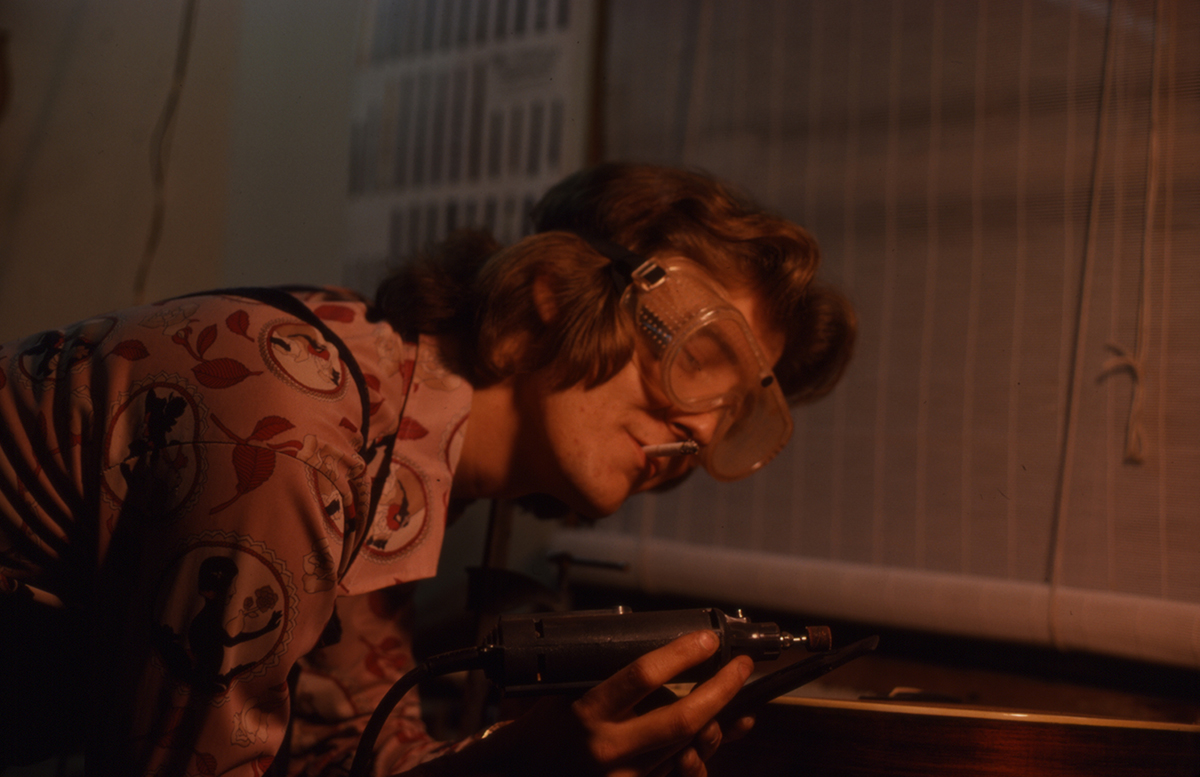
At that point I turned off the recorder and asked if he would show me his electrified banjo. When I turned the recorder on again, he was giving me the history of his banjo, starting with the neck:
This, this is original here, this part as you can see was pieced from a tenor, you turn it over and it’s a great job — see, that’s been pieced.
(N:) Oh, yeah.
(J.D.:) From there up. They matched it perfect, see, you can tell, right there, it starts up on the neck, go right in there, or right here, you can see its smaller up the neck.
(N:) It’s a splendid job.
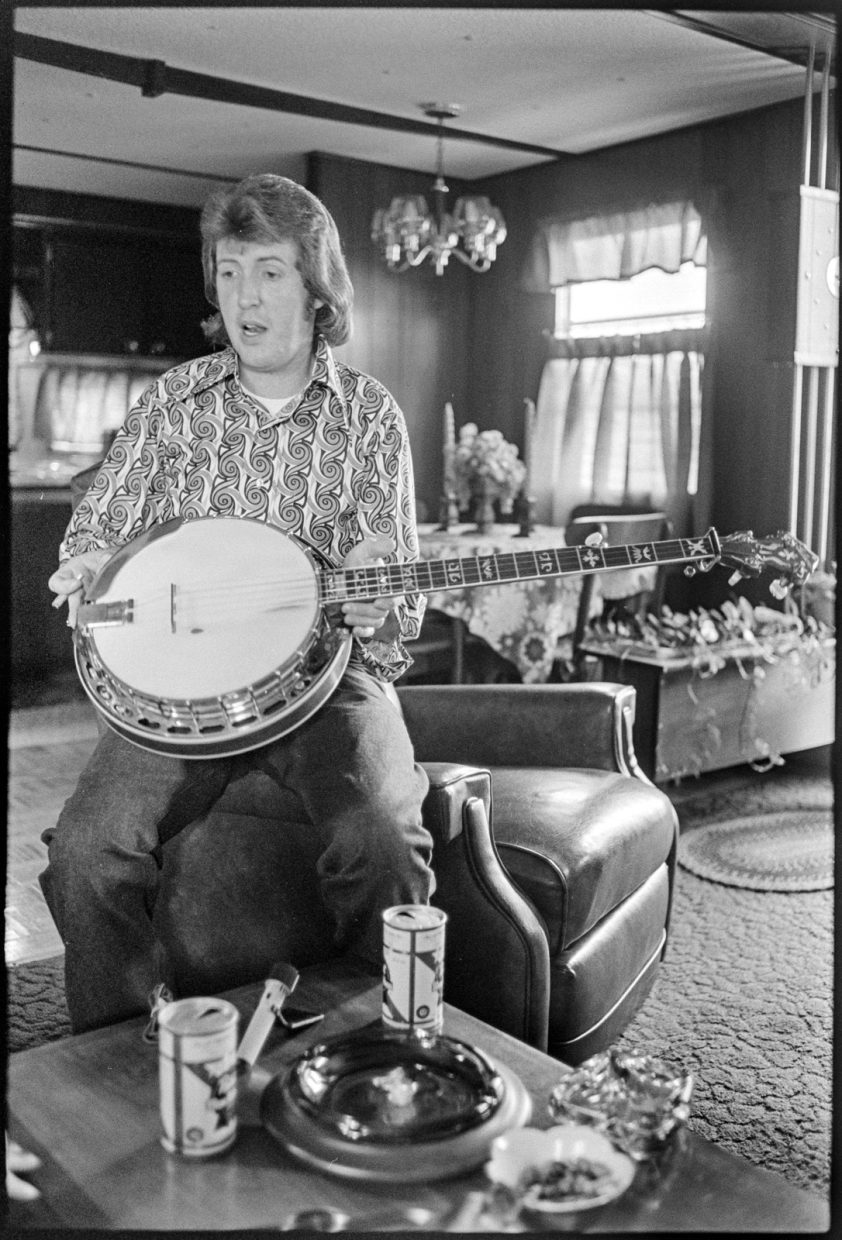

J.D. had seen a lot of old Gibson Mastertones over the years. He knew chapter and verse about wood types and design details. But I wanted to know about his electric setup. I knew nothing about electric instruments, which were anathema to the ’50s folk revival I’d grown up in. He spent some time showing and explaining the details of his still-experimental pickup system (Godbey describes it well, p. 110). Carl asked if he could take a picture, J.D. politely told him no.
He told me what it was like to be playing electric, with the strings closer to the fretboard (“low action”) than on an acoustic:
(N:) Can you do licks that you wouldn’t otherwise do?
(J.D.:) Yeah. You can do a lot of stuff that holds, you know, you can get a sustain. That’s what nice about it.
Then he announced what he was hoping on for the future:
I’ve got a six-string ordered.
In 1970 Sonny Osborne had added a sixth bass string to his five-string; it was part of a lush sound – string sections, twin steels, etc. – on their latest recordings. J.D. liked the possibilities the added string would enable, especially because he, like Sonny, was playing an electrified instrument. He’d even had to cancel a contract for a bluegrass festival that didn’t allow electric instruments. He told them:
Hell no! We’re gonna play electric…. We played up here electric for nine month and [then] we played acoustical; I sounded like I was playing a two-dollar Kay. Cause your hearing gets accustomed to that volume. And it’d take me three or four months to get back on the acoustical route.
Our interview ended there. Afterward I evaluated it in my notes:
Interview with J.D. Crowe — nothing spectacular, your hr.’s worth of history, but attitudes and early learning gone into pretty carefully. Very friendly but reserved in a reassuring way. Carl busy snapping away.
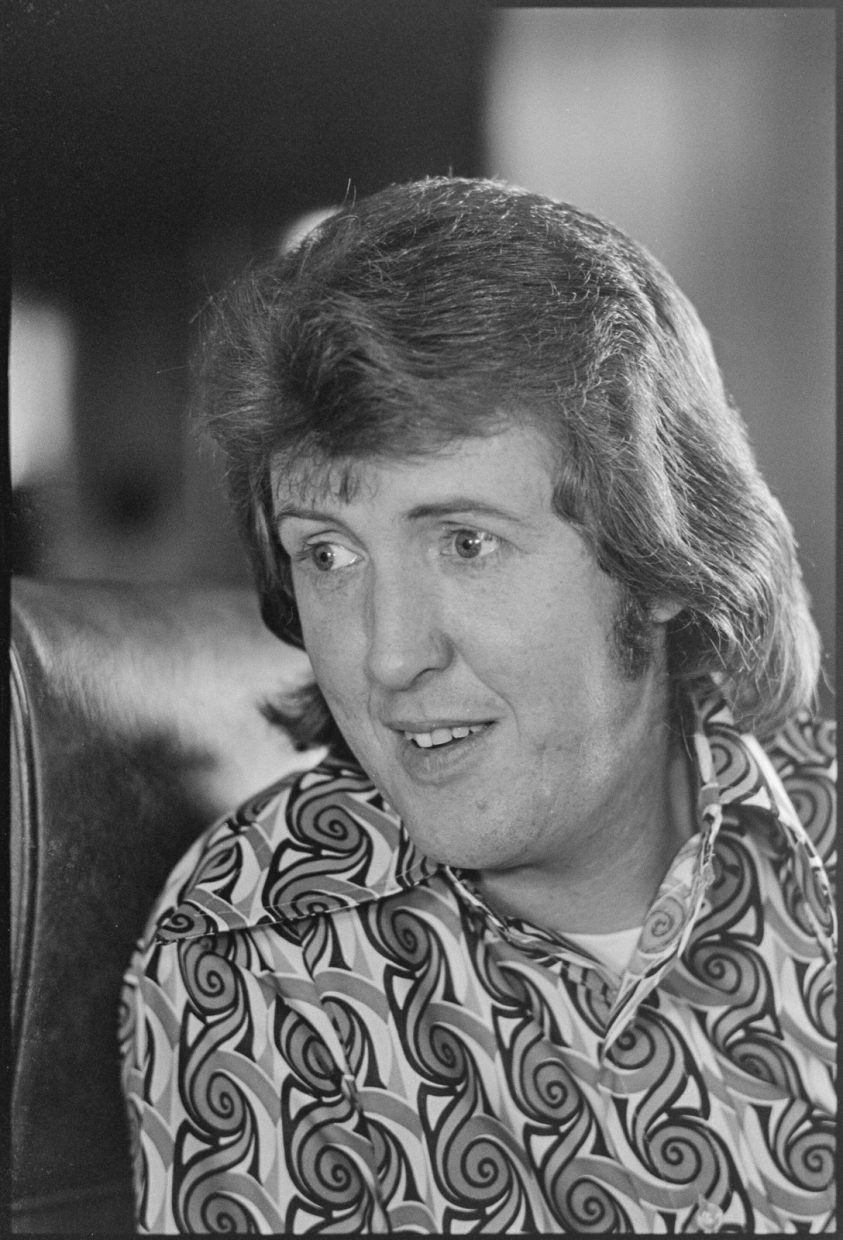

We left Lexington immediately, heading for Louisville, where we were to stay with friends of Carl’s. Consequently, I didn’t get a chance to see J.D. and his New South in action at the Red Slipper Lounge.
In 1973, the electric edition of the New South recorded an album in Nashville for Starday. Titled J.D. Crowe and the New South, it was issued on CD in 1997 under the title Bluegrass Evolution. Crowe played his 6-string on two of its ten cuts. Here’s one, “You Can Have Her.”
The album wasn’t released until 1977, two years after they stopped playing electric. In 1975 when Larry Rice left the group, J.D’s new mandolin player, Ricky Skaggs, had insisted on “acoustical.” By then J.D.’s vision of “something a little different” was working just fine without the extra electricity; Rounder 0044 came soon after.
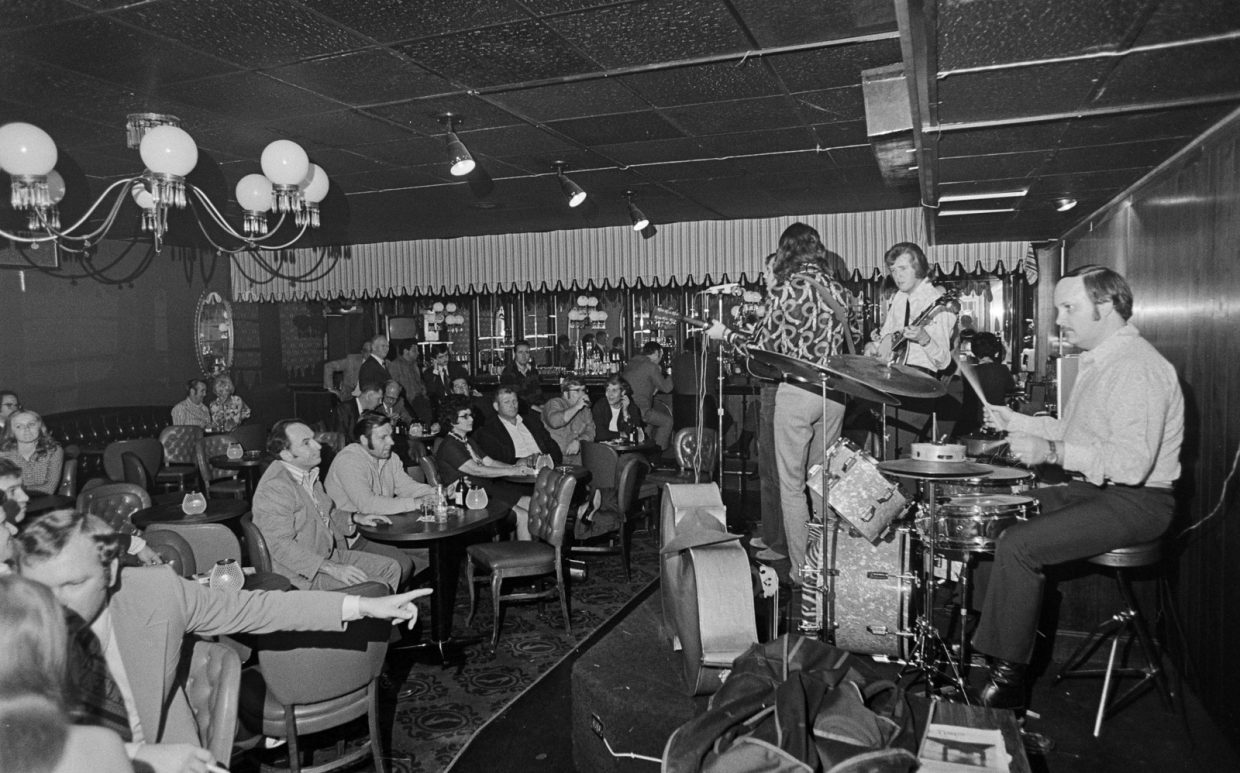
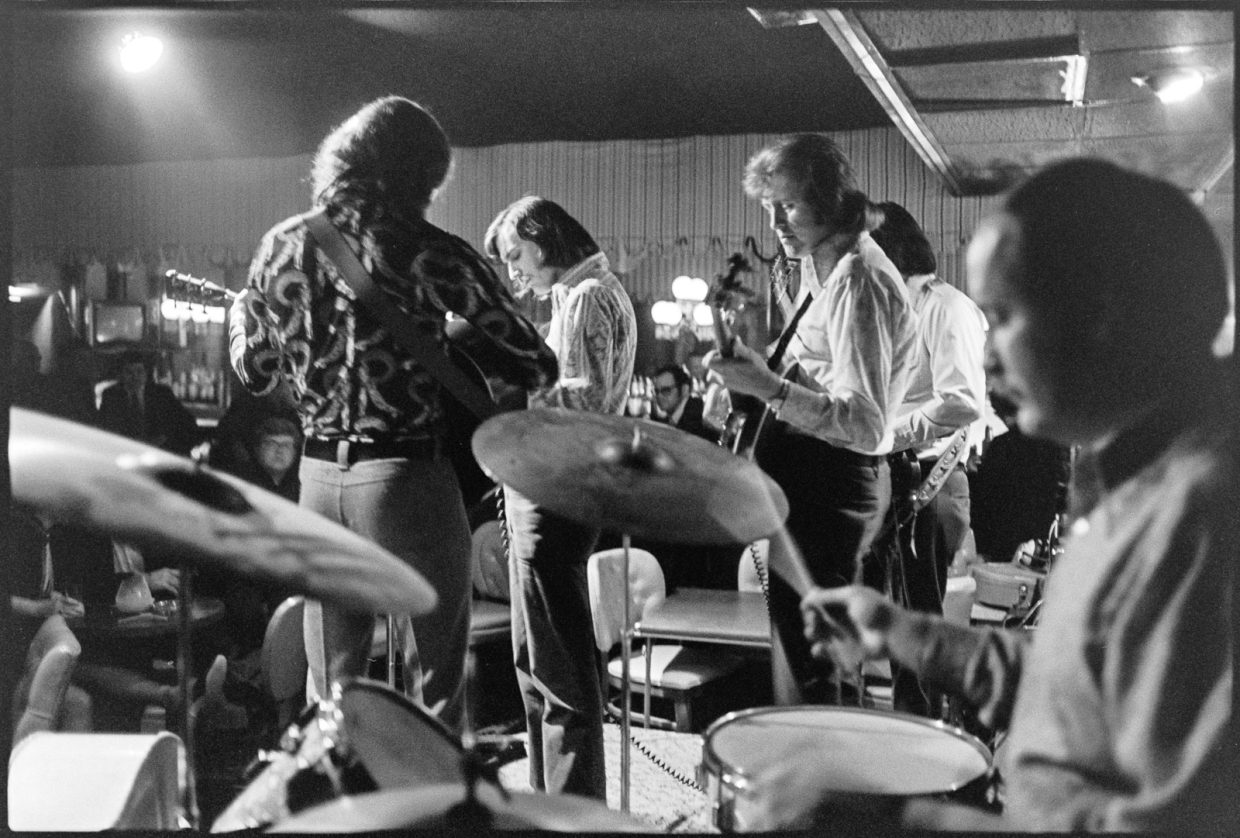


That day I wished we’d taken the time to catch the band in action, but we had only five more days for our bluegrass field trip. Kentucky was just the start; our next planned stops would take us to Ohio, Indiana, and Illinois. Recently, a recording of an evening at the Red Slipper was uploaded to YouTube. Here’s the 1972 sound of the electrified New South (with drums):
Thanks to Tim Stafford and Carl Fleischhauer.
Neil V. Rosenberg is an author, scholar, historian, banjo player, Bluegrass Music Hall of Fame inductee, and co-chair of the IBMA Foundation’s Arnold Shultz Fund.
Photo of Rosenberg by Terri Thomson Rosenberg.
Edited by Justin Hiltner