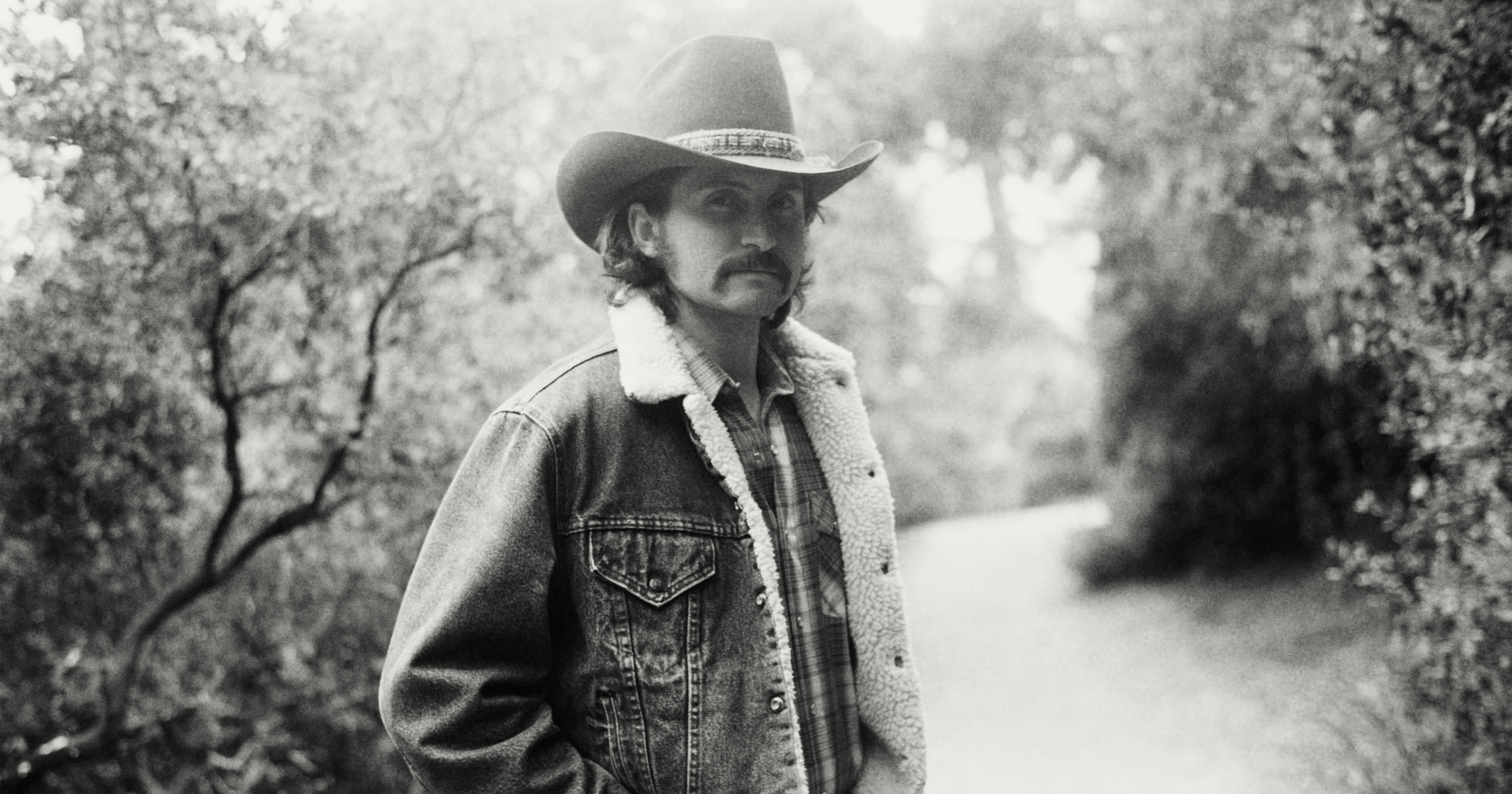
Jesse Daniel is carrying on a family tradition with his fifth studio album, Son of the San Lorenzo. As a kid growing up in Northern California, specifically in the San Lorenzo Valley, Daniel spent hours upon hours in his dad’s truck, listening to the songs that defined ‘70s rock and country radio. When the opportunity arose to create a new album inspired by those sounds, Daniel booked the Bomb Shelter studio in Nashville, recorded live with his band, and enlisted harmonica player (and Country Music Hall of Fame inductee) Charlie McCoy to add an unmistakable flourish to the new recordings.
Just as country fans have come to know their favorite singers as the Coal Miner’s Daughter, the Possum, or the Storyteller, Daniel’s hometown is enthusiastically embracing his alter ego: the Son of the San Lorenzo. Daniel dialed up Good Country to talk about how bluegrass music played a role in his musical development, the silver lining of his checkered past, and what he’s looking for in his fellow musicians when it’s time to hit the road.
For this album, you wanted to go back to the music you grew up on, which is ‘70s country and rock. How did you get introduced to that era of music?
Jesse Daniel: My dad was – and still is – a musician. Growing up, he was playing in bands and always just raised me with a guitar in my hand. Whenever we’d go on road trips, or we’d drive up to Oregon to go see family, we would be listening to Led Zeppelin or the Eagles, bands like that. There was a classic rhythm & blues influence on rock and roll, but a lot of that stuff had a very country influence, too, from Creedence Clearwater Revival to the Eagles. A lot of the bands were California bands, also.
I just heard that music growing up. That’s what was played by my dad’s band, and at birthday parties, events, and school gatherings. That was just good-time music, aside from what we were listening to as kids, when we were getting into metal and punk rock. But I guess that’s what all our dads were listening to, and the older people. So I went back to that, now that I’m in my 30s. That music has such a spot in my soul for that nostalgia, and it’s just so good.
Can you describe the experience of having Charlie McCoy on these sessions?
That was incredible. He showed up on his day to cut some harmonica and he was a very humble, unassuming dude. He told us the coolest stories about old Nashville, all the stuff he’s cut on, and all the people’s personalities back in the day that he used to know. I asked him all kinds of questions, soaking it all in. From the moment he blew on that harp and played some licks, Andrija [Tokic, the studio engineer] and I looked at each other like, “Yep! That’s the sound right there.” He just nailed it.
When I listened to “Child is Born,” the first track, I sensed you’re making a statement with this record. It’s a powerful way to open it. What was on your mind as that song was taking shape?
That song is about generational traumas or generational patterns within families and raising children. I pretty much wrote it from the perspective of trying to give some advice on how to raise a child, almost like a template. Throughout the verses, it talks about the pitfalls and what will happen if you focus on yourself and don’t raise your children right. That’s happened in my family and to so many other people. These fathers and mothers aren’t there for their kids, and when it ends up being their time to be taken care of, when they’re elderly, nobody’s there for them because they weren’t there in return. It becomes this vicious cycle that’s perpetuated. That’s where I was at with writing that one. It was an emotional one. It’s an emotional type of record in general, but I just wanted to start it off with that, for sure. A good, heavy starting place.
One of my favorites is “Son of the San Lorenzo.” I think you have had that title for a while.
Yeah, that one is a special one, too. I wrote that song in 2019 and I included it as the last song on my Rollin’ On record. I decided to re-cut it for this one and name the record after it, because since I wrote and released that song, it’s become a fan favorite all over the place, but especially where I grew up in the San Lorenzo Valley.
Whenever I would go back home for hometown shows, people would call me “the Son of the San Lorenzo” after that song. They would always sing that song. That became my nickname over the past five or so years. I thought, what better title for the record than that? With this record going back to my upbringing, to where I’m from, and identity and all that.
You’ve got references on this album to Highway 9, the Sierra pines, and the redwoods. You’re skilled at setting the scene in your songwriting. Why is it important to bring Northern California into these songs?
With my identity as a songwriter and an artist, it shaped a huge, huge amount of that. I always do things through the lens of being from Northern California. Going back to that sound, so much of the music I grew up on was from that exact area – bands like The Doobie Brothers, Larry Hosford, guys like that, who were making this country-rock and roll-blues stuff that really influenced me a lot.
Painting a picture of where you’re from, and of these things that are important to me and my music – I feel like that’s something that’s lost in music nowadays. People don’t do that as much, or if they do, it’s pretty well dominated by Appalachia or Texas. They have a lot of identity and pride in their musical heritage there and I just feel like it’s missing from California in general. And it shouldn’t be. It’s an amazing place, an amazing landscape, an amazing musical history. I see it as my cross to bear to try to carry on that legacy as best as I can.
Has bluegrass been an influence on you?
It definitely has. When I was in high school, I had a teacher for a short period of time who had a bunch of burned bluegrass mix CDs. She was the person that turned me on to bluegrass. I remember listening to that Tony Rice and Norman Blake song, “Eight More Miles to Louisville,” and I was like, “This is incredible!” The songwriting, the picking, the tempo. That made me fall in love with bluegrass. I’d been playing guitar for quite a while at that point, but that’s when I started learning the banjo rolls and trying to emulate some of those bluegrass things I’d heard and adding them into my chord progressions. Even though I don’t explicitly do bluegrass, I always have a bluegrass song on my records, or something that’s at least along those lines. For this record, it’s “Mountain Home” It’s got the banjo and fiddle and a little bit more bluegrass texturing. It’s a big part of my influence.

I was listening to “One’s Too Many (And a Thousand Ain’t Enough)” on Spotify and I couldn’t help but notice your mug shot from Santa Cruz County [as the Spotify Canvas] in the player. How did that come to be?
Yeah, that’s my mug shot from one of the times I went to jail. During that period of my life from 18 through my early twenties, I was a heroin addict, a methamphetamine addict. I was in a vicious cycle of addiction I had gotten into in high school. Once I was out of high school, it accelerated and I became a full-blown junkie, a full-blown drug addict. So that took me on frequent trips to jail for a week here, a week there. I never did any serious time, thank God. I should have, but I didn’t. I was constantly in and out of jail or rehab programs.
That mug shot is a reminder of that past and of that period of my life I wrote about in that song. That song is comprised of all the advice I had gotten from older people who had gotten their stuff together over the years, including some of my own family members who have been sober. They would tell me all these little bits of wisdom and try to help me, and I was just too deep in it to really see. But that song is basically the advice I’d give to somebody now, made up of all the advice I got back then when I was in that position.
Do people who know your story approach you for advice when you’re out on tour?
Quite a bit. There’s a cool, cathartic element to it for me, because I get to put my story and struggles into these songs and they help me. Then it becomes that for other people. I had a woman come up to me at a show, and she told me that my song “Gray” helped her mother get clean. She sent this song to her mother and it broke her down so much that her daughter was sending it to her, saying, “Hey, listen to the lyrics of this song. I care about you and I want you to get help.” And she did. She’s been clean for a couple years now and she says it’s because of that song.
I’ve had a lot of people reach out with similar stories, that they’ve gotten their stuff together after hearing my story or listening to my music. That’s the ultimate form of redemption for me, that I could take my destructive past and turn it into something constructive in helping people. That’s my whole mission. Aside from making the music I love, that’s my mission in my contribution to music.
That’s interesting to hear your mission statement, because you’re the head of your own organization now. I don’t know if you think of yourself that way, but you’re a businessman.
Yeah, more recently I’ve started to think of it that way. And it’s true, especially doing it independently like we have for so long. We’re just now starting to work with a bigger booking agency, a bigger management. We’re stepping things up. But my fiancée Jodi and I really built this together ourselves, brick by brick.
I’ve often heard you shouldn’t get in a relationship with someone until you know you travel well together. What do you remember about those early years with Jodi on the road?
In the early years, even before we started touring in a band together, I would play regionally and Jodi and I would go on road trips together, camping trips, whatever. We just wanted to keep going. That was always part of our relationship. We traveled really well together. We had similar interests. We’d just listen to music and talk and go pull off at roadside swimming holes up in the mountains. We loved that sense of adventure and going places. It was one of the main things that drew me to her when we first got together. She had just as big of a sense of adventure as I did.
So, in the music aspect of it, that’s really helped because we both have that wanderlust and we’re just down to be on the road and to go play new places. When one of us gets tired and burnt out, or maybe sick of being on the road, or something’s not going right, we have the other one to put it in perspective and help balance things out. You lean on that person, which not a lot of people have. A lot of times, your wife or your husband or whoever is at home and you’re out there, alone, missing them. So, I do have the luxury of being with my person out there.
What did Jodi think about the song “Jodi” when you played it for her?
She loves the song. Just like I say in that first line, “To write a love song for you was not an easy thing to do.” It really was a hard subject to tackle, because it’s so vulnerable and true. I had to sit with that one and try to make it as meaningful as possible, so it didn’t come off as a corny love song or too cryptic. I wanted it to be straightforward, but really meaningful.
What do you look for in musicians as you start to put together a band for a tour?
First off, they’ve got to be a great musician. That’s number one. They’ve got to understand the styles and the stylings that I like to go for with my music. I know it’s not for everybody. Sometimes the guitar style is a little bit outside of their bubble, so the playing has to be there.
On top of that, personality-wise, it helps to have people with good attitudes. That’s a huge one I’ve learned over the years. If somebody isn’t there for the right reason, or if they’re halfway in, halfway out, or maybe they’re partying a whole bunch on the road. I’m clean and sober on the road, I don’t do anything, but my guys will go out and have a beer or whatever. That’s totally fine. But if guys are going out and doing drugs or drinking and having it affect their performance or attitude… That is something that happened in the past, so I have a pretty strict policy with that. If you’re going to be in my band, you don’t have to be a teetotaler, but just try to keep it pretty mellow. It’s about the music. That’s what the focus is.
When you listen to Son of the San Lorenzo front to finish now, what goes through your mind?
I see a pretty complete body of work. Sometimes I’ll listen to some of my earlier records and I’ll look back and think, “Oh, I’d change this,” or “I’d do this a little different,” or “Maybe I would have put this song here…” I think that’s easy to do, to pick things apart, especially when you’ve grown as an artist and a songwriter. But when I listen to this record, I put so much time into the song arrangement and into each lyric and each part of the production. I wrote all the guitar licks. Well, ninety percent of the ones you hear on here are ones that I wrote, and then I showed them to the guitar player and he played them better than I was able to play them. [Laughs] All these little things, I put so much effort into this record that I listen back and I’m just really proud of it.
Want more Good Country? Sign up to receive our monthly email newsletter – and much more music! – direct to your inbox.
Photos courtesy of Lightning Rod Records.