March is Women’s History Month, and BGS, Good Country, and Real Roots Radio have partnered to highlight a variety of our favorite women in country, bluegrass, and roots music with our Women’s History Spotlight.
Each weekday in March at 11AM Eastern (8AM Pacific) on Real Roots Radio, host Daniel Mullins will be celebrating a powerful woman in roots music during the Women’s History Spotlight segment of The Daniel Mullins Midday Music Spectacular. You can listen to Real Roots Radio online 24/7 or via their FREE app for smartphones or tablets.
Then, we will have a Friday recap here on BGS featuring the artists highlighted throughout the previous week. No list is comprehensive, but we hope to feature some familiar favorites as well as some trailblazers whose music and impact might not be as familiar to you.
This week’s edition of our Women’s History Spotlight features musicians and artists like IBMA Award winner Dale Ann Bradley, the legendary Dolly Parton, Bluegrass Music Hall of Fame inductees Hazel Dickens & Alice Gerrard, early country hitmaker Kitty Wells, and Kentuckian-West Virginian Molly O’Day. Tune in next week for the final installment of our Women’s History Spotlight!
Dolly Parton

You knew it was coming. You can’t tell the story of country music (or American pop culture) without Dolly Parton. Growing up in Sevier County, Tennessee, she is not just the Queen of the Smoky Mountains, but quite possible the Queen of the Universe (if there was such a ridiculous title). Her rags-to-riches story will continue to be told and re-told for generations. Aside from her beautiful voice and philanthropic work (the millions of books that she gives to children through Dolly Parton’s Imagination Library is her proudest achievement), there are numerous other aspects about Dolly Parton that are remarkable.
Her business acumen is frequently praised, but it still bears repeating. Aside from her numerous endeavors (including Dollywood), it’s often worth remembering that she fought to regain control of her own career and decision-making from Porter Wagoner after her star began shining brighter than his scope of influence. (Remember, it was the ending of this business relationship that was the impetus behind Dolly writing one of her most famous songs, “I Will Always Love You.”) Call it a business decision or just genius, but Dolly’s ability to juggle embracing her role as an undeniable sex symbol and avoiding being labeled as “unwholesome” by conservative crowds has to be one of the most difficult tightrope walks in American entertainment.
Vanity Fair’s 1991 article “Good Golly, Miss Dolly“ did a deep dive into the dichotomy of Dolly’s role as a sort of clean sex symbol: “Dolly, in her openness, demystifies sex. ‘One of the things that makes the image work is that people understand that I look one way, but am another, that there’s a very real person underneath this artificial look,’ she theorizes. ‘It’s not like I am a joke. People can laugh at me, but they don’t make fun.’ … Indeed, Dolly Parton has become the billboard for sex without being the product itself.”
It is the way that she ensures that the “very real person” that is Dolly Rebecca Parton doesn’t get lost in the glitz, glamor, and boob jokes that is part of the reason why she is so endearing and universally beloved by folks from all walks of life; in a world where polarization is en vogue, Dolly is one of the few topics on which everyone agrees! She epitomizes the best of us.
Hazel Dickens & Alice Gerrard

Members of the Bluegrass Music Hall of Fame, Hazel Dickens & Alice Gerrard were an unlikely pair who blasted down doors for women in bluegrass. Hazel hailed from the mountains of West Virginia, while Alice was from across the country in Seattle, Washington. Alice attended Antioch College in Yellow Springs, Ohio, where she was exposed to folk and bluegrass music. While a student there, she helped coordinate bringing The Osborne Brothers to the Antioch campus, making history as the first major bluegrass concert held on a college campus! After college, she wound up in the D.C. area, becoming active in their flourishing bluegrass scene, where she became friends and musical partners with Hazel Dickens – who had moved to the region with her family to find factory work years earlier.
Hazel & Alice became some of the first female bluegrass bandleaders and recorded some classic albums for Smithsonian Folkways and Rounder Records before embarking on successful solo careers by the mid-’70s. With Hazel’s mountain sound and Alice’s more folk-oriented sensibilities, their music appealed to both traditional bluegrass fans and those who were being introduced to the genre via the Folk Revival. Their original material which highlighted a woman’s perspective were critical in bringing a voice to women in the bluegrass canon. Decades later, their music and legacy is still rippling across American roots music, with artists as diverse as Rhiannon Giddens and Dudley Connell still celebrating their influence and impact.
Molly O’Day
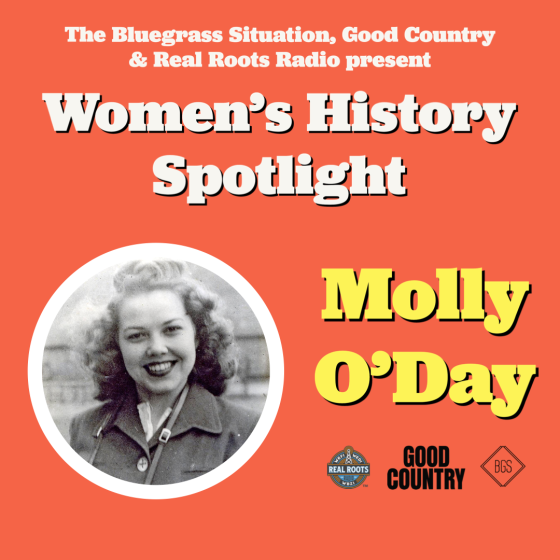
Born Lois LaVerne Williamson, country pioneer Molly O’Day was born in Pike County, Kentucky. She would become a popular radio star in West Virginia by the early 1940s, eventually leading Molly O’Day & The Cumberland Mountain Folks. Her band crossed paths with Hank Williams on the radio circuit and Molly even sang quite a few of his songs on radio and later in the recording studio. Molly learned “Tramp On The Street” from Hank Williams and it would land her a recording contract with Columbia Records. (Fun Fact: Her band at the time of her first Columbia recording session featured a young Mac Wiseman on bass!)
In an era when the term “hillbilly music” was still commonly used, Molly’s music, retroactively, could have country and bluegrass labels applied to it. Her powerful voice felt just as at home on an ancient balled like “Poor Ellen Smith” as it did on soul-stirring gospel songs like “Matthew 24.” By the early 1950s, Molly and her husband grew weary of life in the limelight and essentially retired from the music business, both dedicating their life to ministry. She would record a few gospel albums for some small record labels in the ensuing years, but her final album was released in 1960. She would pass away in the late 1980s, but she left a mark on country music and earned the respect of her peers at a time when the list of female country pioneers was relatively short.
Dale Ann Bradley

Revered as one of the most heartfelt bluegrass singers of her generation, this Kentucky songbird’s career started in earnest as a member of the Renfro Valley cast in her home state of Kentucky. The Renfro Valley Barn Dance was an extremely popular barn-dance style radio program in the 1930s and it spurred the creation of Renfro Valley as a country music entertainment destination in Kentucky. This helped kickstart the careers of folks like Steve Gulley, Jeff Parker, Dale Ann Bradley, and more by the 1990s.
While at Renfro Valley, Bradley would eventually join The New Coon Creek Girls, one of bluegrass’s only “all-girl” bands at the time, and aptly named after The Coon Creek Girls, a pioneering female string band of the 1930s who also started on The Renfro Valley Barn Dance.
Dale Ann’s soulful voice, largely influence by the Primitive Baptist tradition which she grew up around, quickly gripped the bluegrass world, leading to a successful solo career for the last three decades. In addition to recording songs that hearken to those familiar with mountain people and mountain ways, the appeal of Dale Ann’s voice has led her to adapt songs from outside of the genre to her style of bluegrass, tackling tunes from Tom Petty, Bobbie Gentry, The Grateful Dead, Jim Croce, and everyone in-between! Her diverse material has led me (and many others) to the conclusion that no matter the material, if Dale Ann is singing it, I already know I’m going to like it!
Kitty Wells

Hailed as the original Queen of Country Music, Kitty Wells hit a massive reset button on the role of women in country music after the massive success of her breakthrough hit, “It Wasn’t God Who Made Honky Tonk Angels.” Written by J.D. Miller, it was penned as the antithesis of Hank Thompson’s hit, “The Wild Side of Life.” After writing the song, the search began for a woman to sing it. Kitty Wells had pursued a country career, to little avail, and had essentially consented that maybe it wasn’t in the cards for her, when she was contacted to record the song. “It Wasn’t God Who Made Honky Tonk Angels” would become the first Number One hit by solo female in country music history, and its status as one of the most iconic country songs of all time only grows.
This explosion of success led to many other hit records by Kitty Wells, and opened the doors for those who would follow in her wake like Jean Shepard, Loretta Lynn, Dolly Parton and more! You can’t celebrate Women’s History Month without honoring the gal who famously sang the line, “It’s a shame that all the blame is on us women!” (Still kind of bummed that Margot Robbie didn’t sing that line in Barbie. Seems like a missed opportunity to me!)
As an added bonus, here’s another cool version from 1993, where Dolly Parton, Loretta Lynn, and Tammy Wynette recruited Kitty Wells to join them on a new version of this country classic on their collaborative album, appropriately entitled Honky Tonk Angels.


