Charlie Parr and Gina Clowes both have a thing for banjos and dogs.
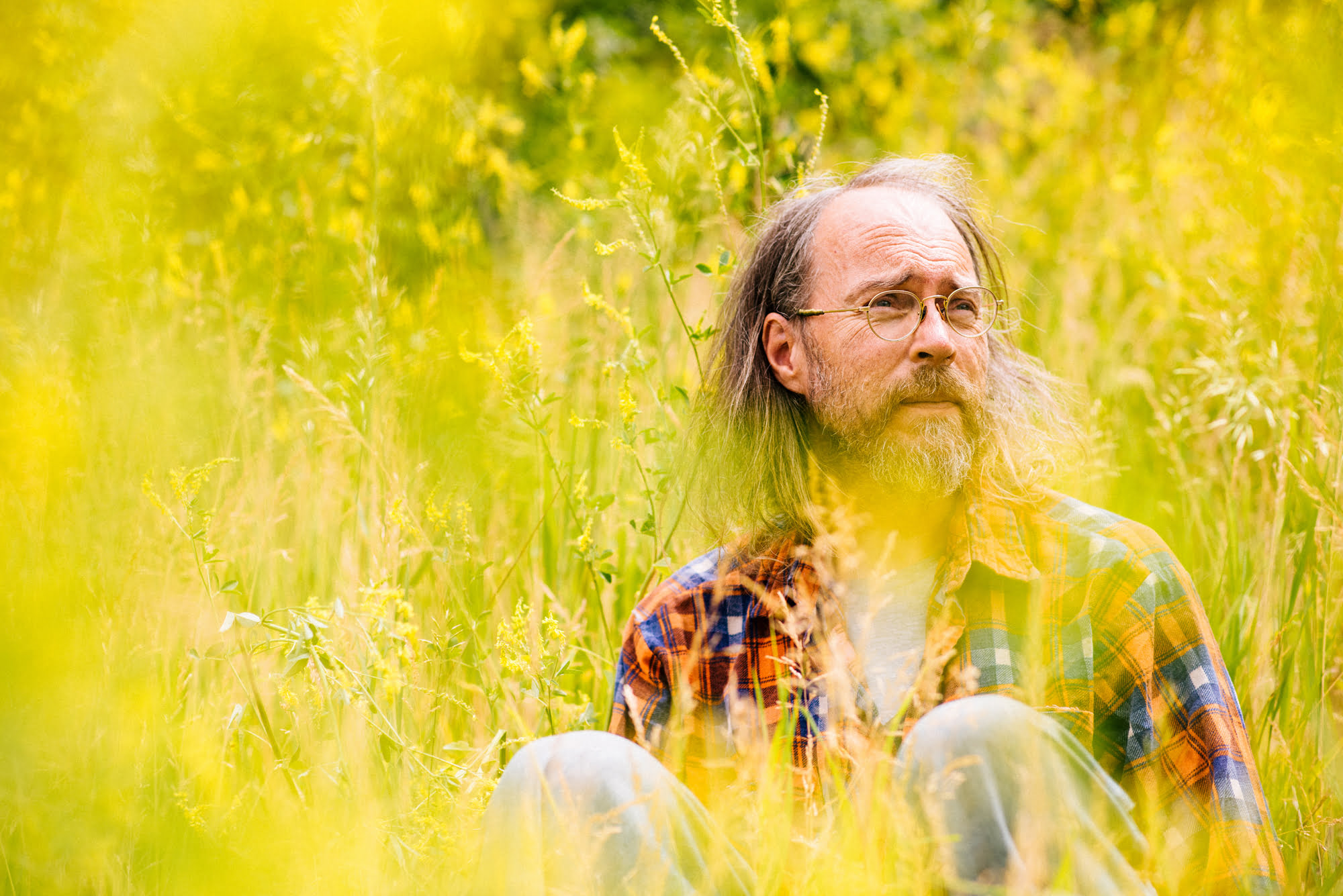
Parr’s new album is actually called Dog, and the title track argues that even man’s best friend has a complex inner life: “A soul is a soul is a soul is a soul,” insists the furry one as the Minnesota human picks out an acrobatic acoustic blues riff. Parr is an especially deft and intuitive player who jumps from old-time to bluegrass to blues to folk faster than a greyhound, but Dog is first and foremost a songwriter’s album. Parr inhabits various points of view — a dog, a hobo, another dog, a hoarder — as useful projections of his own depression.
Clowes’ new solo album, titled True Colors, isn’t canine-themed, but it similarly presents her as an exceptionally well-rounded artist. After dominating banjo competitions for 20 years, the Virginia native (perhaps better known under her birth name, Gina Furtado) joined the ace bluegrass outfit Chris Jones & the Nightdrivers last year, so it’s no surprise that her songs would showcase her swift and graceful picking. But songs like “Good Old-Fashioned Heartbreak” and “The Wayward Kite” reveal a graceful singer and an insightful songwriter.
And she has farm animals.
Gina Clowes: I’m battling my frisky little goat. She’s been jumping all over the place and following me around as we talk. Charlie, I think with that song “Dog,” you’re asking the question we all have in our hearts. I grew up with a border collie by my side all the time. Now I have a boxer mix. It’s actually my son’s dog.
Charlie Parr: Reuben is a miniature schnauzer, so she’s not a very big dog, but she’s an enthusiastic walker. One of our cats died, and we ended up getting this little dog, and she’s just an amazing addition to the family. She’s very dedicated to the notion of not taking walks that have much to do with where you, the human, want to go, but with what she’s interested in and the smells she smells. My idea of a walk is very different, and I used to make her take the routes I wanted to take. Suddenly it occurred to me that it’s cruel if the only time you get to go for a walk is when somebody else lets you and then they make you do what they want to do. I felt like, “Oh my God, that’s so terrifying.”
What did you do?
CP: I started following her around town and letting her stop and do whatever she wanted to do. And the walks took on this epic strangeness where I would find myself in parts of town that I had no idea existed. She would take me to these odd places that I’d never seen before. I live on the shore of Lake Superior, and she would take me to new parts of the shore I had never seen before. You think you have a handle on where you live, but you don’t at all. I felt like I owed her a debt of gratitude for reminding me that it’s not about me. It’s not even really about her. It’s about something else. We did this together, not to sound too crunchy about it.
GC: Growing up with my border collie, Maggie, I feel like I came across so many more adventures than I ever would have without her. We spent all of our time out in the woods. She would find these injured animals. She had a very different view of the world that we don’t have.
 Is the time you spend with these animals good for writing?
Is the time you spend with these animals good for writing?
CP: The way I write songs is weird, because I end up writing stories and distilling them into songs. Those walks with Reuben are always good for that. Some weird story will come out of them, and I jot down stuff when I get home. Three-quarters of the time I throw it away, but that last little bit of time, it will turn into something that I think is not too bad.
GC: Part of it, too, is getting away from listening to music. You get out in nature and your brain has a chance to put together whatever influences it’s been absorbing when you’ve been in the car or in the kitchen listening to music. It’s a quiet time, and that’s when I come up with some of my better ideas.
CP: I listen to a lot of music. Obviously you do, too. But I have to spend a certain amount of time each day deliberately not listening to music. When I’m walking with Reuben, I never listen to music, partly because I don’t like things in my ears. When I do long drives, I listen to music. I’m a child of the ‘70s. We’re album-oriented people, so I will listen to a record and then I will stop for about the length of a record. I listen to music and then not listen to music about as much time.
That seems like an interesting idea. It gives you time to absorb and think about what you’ve heard, rather than just cramming even more notes into your ears.
CP: When I was growing up, I had my father in the front of the house. He grew up in the ‘30s, so his primary listening was around songs. He was interested in songs. His record collection was weird and shambolic, and he had a lot of 78s and old LPs from the ‘50s. He wasn’t into album-oriented anything. My sister, on the other hand, was listening to album-oriented rock from the ‘60s and ‘70s. The Grateful Dead and Captain Beefheart were playing in the back of the house. So I got interested in both of those things. But I find it hard to stop listening to an album after I’ve started. I have to let them play through, because you feel like you haven’t finished it somehow.
GC. It’s like an opera. You miss part of the story. I’m the same way. I’m just behind the times, and I would rather just pop in a CD rather than listen to Spotify.
CP: I’m part of that generation that was not raised with that technology. We had just enough technology to be spoiled, but not enough to be weird about it. I hate to be that way. I end up being that way around my son a lot, starting a lot of sentences with, “In my day …”
GC: So, Charlie, I noticed you’re using a slide on your left hand. Are you doing that with the banjo, too?
CP: Sometimes I do. I play a fretless banjo, so it can be hard to tell. But I do like using a slide. When I started playing, I had an interest in slide guitar, so the very first thing I did, when I was eight years old, was try to play slide guitar. I’m completely self-taught, so I’m doing everything upside-down and backwards. The slide adds something like two tones to every fret space, so it becomes really interesting. I’ve played a lot of slide on the banjo. Lately I haven’t been playing much banjo, but I’m trying to get back into it.
GC: I love the slide on the banjo. You don’t hear it very often, but one of my favorite players, Tony Furtado, does that sometimes. Last week, I went to the music store to pick up something really small, just a button for the guitar strap. When I tried to pay, they said, “Sorry, we can only accept a credit card if it’s over five bucks.” So I grabbed one of the bottle slides because it was sitting on the counter there. Might as well. Somehow that makes me more inspired to give it a try.
CP: It’s a unique sound. Banjos are a lot like resonator guitars: The attack isreal swift and the delay is real swift. So you have to do some stuff to keep your tones going, and bottleneck is a really an answer to that. I borrowed a friend of mine’s banjo that had a magnetic pickup installed in it. I wasn’t really into the sound of the pickup, but what I was into was the fact that I could take an E-bow and play it on the banjo. It works on the magnetic pickup, and the tones I got out of that were otherworldly. I was completely fascinated. I really like a lot of experimental music. Paul Metzger plays a 23-string banjo and used a lot of electric manipulations with it.
GC: I feel like the banjo has been boxed in, maybe because it’s relatively new to be doing it three-finger style.
CP: I think you’re right. It has been boxed in. People have decided that there’s only one tuning that’s associated with the banjo. I asked Dock Boggs about that. He would re-tune his banjo for almost every song, and I asked him about it. He said something to the effect of, “The song comes out of the tuning.” I thought that was fascinating.
GC: Yes. If you listen to a lot of old-time banjo playing, they change their tuning so much more, and it really does open up the spectrum of moods you can get out of it.
CP: I use a lot of open C, except I end up pitching the D string all the way up to E. I really like that a lot. It’s a little tight, but it’s a cool chord.
GC: Just make sure you point it away from your eyeball when you tune that one!

Is that something you’re actively pursuing? Are you always looking for new ways to play this instrument?
GC: For me, it’s not so much about trying to find a new sound. It’s more about just trying to find a better way to evoke a particular feeling. I like Scruggs-style banjo playing. Earl was awesome and he created this super-cool style that was him expressing something. It works out as a great template for players to use now, but I’m looking more at trying to figure out different methods of explaining the mood that I’m going for. There are many more ways to do that.
CP: It’s a bit of a mixture, sometimes, between manipulating the mechanics of the instrument and manipulating the technique. In 2006, I developed a brain disorder called focal dystonia, which completely destroyed my picking hand. I had to re-learn everything from scratch because I could only use my index finger. I used to use my middle finger a lot, but now it’s like a trigger finger — it just sucks up into my palm. I spent about a year looking at players like the Reverend Gary Davis and Elizabeth Cotton and Roscoe Holcomb to get some inspiration for how to do everything with just thumb and index finger. I had never had to do anything like that in my whole life, but at the end of the day, it turned into … well, it had to turn into a good thing or it was going to turn into a truly bad thing. It forced me really rapidly to change things about the way I played, even the way I sit and the way I hold the instrument. I found some places that I didn’t think I would ever find, and I had a little more power in my picking than I had before. Some of the frilly stuff had to go away, but I found other things to replace it and developed some self-confidence I didn’t have before.
GC: I can’t even imagine going through that. Is it physical or psychological?
CP: It’s repetitive stress syndrome in your brain. That’s what I’ve been told. I started playing guitar when I was eight and became very quickly obsessed with it. I tried to play all the time, but I didn’t have any lessons. No one every told me, “Don’t do that or you’ll end up with a problem in your future.” I did everything wrong for a long, long time. Now I’m 50 years old and I’m playing a little catch-up to get things to sound right. But it’s made me develop some different ways to look at things. When I want to get certain sounds, I have to work within the parameters of what I have. Sometimes that means manipulating instruments. I’ve added strings to guitars or taken strings away. I’ve put snares on the banjo head to get that buzzy sustain out of it. I try to do whatever I think needs to happen to get where I want to go. Half the time, I don’t even know what I want, and then something will come out that I like and I’ll amplify that a little bit more.
You’re both playing in traditions that can be very conservative, very restrictive. But on these new records, it sounds like you’re very consciously trying to find new ways to play.
GC: I love bluegrass. I was raised on it. I’ll always love it. But it does put you in a small box. There’s a specific form to every song — two A parts and two B parts and so on. That’s part of what makes it so great. It’s easy to get up on stage and jam. There’s a big repertoire that everybody knows, so you can all play together. But I don’t like the idea of genre, because it’s always going to be too small for all the ideas you want to use. You can’t use them all, if you’re trying to stick them all into a very small box.
CP: Musicians didn’t make up genres, anyway. It was record companies and radio stations and furniture stores that decided what the genres were. I don’t like them, either. All of the most exciting music that I’ve heard — including bluegrass music — has come from that weird in-between space where somebody did something slightly different, like Bill Monroe or Captain Beefheart. It’s happening now with a lot of groups, like Megafaun, for example. They blended a lot of electronic sounds with accordion and clawhammer banjo and came up with a couple of brilliant records before they stopped. It’s hard to say what genre they’re in because they’ve added so much stuff. I think that’s brilliant.
It gets back to an idea we were discussing earlier of how you listen to music. You don’t just listen to one style of music. You listen to a lot of different stuff. So why would you play just one narrow kind of music.
GC: Something I latched onto early: When I was learning to play the banjo, I was told I should imitate my banjo heroes. But someone else told me, “Why don’t you imitate other instruments? Why not imitate the guitar or the saxophone or whatever? Try different forms of imitation.” That opened the door for me to try new ideas and come up with new things.
CP: I had a conversation with Dakota Dave Hull, a player in Minneapolis who told me, “Don’t listen to so much guitar music. Listen to piano music. Listen to horns. Listen to jazz. Listen to a lot of different stuff.” You end up taking those voices back to the instrument you’re playing, and it adds a lot. I was also inspired by Spider John Koerner, who was constantly messing with his own songs and with other people’s songs. At one point, I was talking to him about an older song, and he pointed out that we wouldn’t be talking about that song if people had messed it and forced it through that folk process. Without that, it would have died. We’re only talking about it because people loved it enough to screw with it.
GC: Everything I put on True Colors turned out to be so very personal that it was a little uncomfortable. I had this idea that I could blame it on a friend: “Oh, a friend of mine went through that experience, not me!” But those songs are based on real feelings that I had, real experiences, and it was therapeutic for me to write about them. It helps to process everything that I go through. It’s what we talked about earlier — spending some time in quiet and working things out. Last summer, when I was writing everything for the album and getting ready to record, I stopped writing in my journal and I stopped listening to music. I just stopped cold turkey. My husband was worried, but I was just processing things and writing about them. And there they are now.
CP: That sounds familiar. I had a lot of bad internal stuff that kept getting recycled and regurgitated and, after a while, I needed to write the songs and get them away from me. I only really broke loose of them when I got other people involved. I was going to make this a completely solo record, but then I thought that would be devastating. The songs are already horrifying and way too personal, so I need to bring in other people and let them become an influence on the music. It changed stuff a little, but it also didn’t sound so dark anymore, I guess.
GC: I know what you mean about bringing people in. I was nervous showing my songs to people, but they came in and they’re happy and they played the living daylights out of the songs. Everybody just got the mood. It helps to get out of that space in your mind.
CP: There’s a certain amount of lightness that’s created by playing with other people. I’ve played mostly by myself, but when I play with friends, it’s a massive relief, just the amount of joy it creates. It’s hard to explain that kind of lightness that comes into even the darkest music, when you have other people there.
You both talk about getting these songs out of you and away from you, but then you record them and take them out on tour. You have to live with them every night. Is that difficult?
CP: I don’t ever regard songs as being finished. I’m not writing a book or painting a picture. I’m creating something new every time I sit down to play a song. In a weird way, I’m rewriting the song, which is now influenced by the audience and their energy. It’s not the same song as it was when I first came up with it. Now it’s something different. It’s not a song about A or B. It’s a song that includes something else. It becomes easier to deal with, because it’s no longer my burden alone. I’m sharing it with a lot of people who have all these different interpretations.
GC: That hits the nail on the head, Charlie. I write to distance myself from something. I write to let it be free and do whatever it will, so it doesn’t feel very personal when I share the song with somebody. It doesn’t have the same sense of being a deep, dark secret anymore. Now it’s out in the world. I’m free from it.
CP: Exactly. For me, it’s all about process. When a song feels finished, I just quit playing it. It’s not interesting to me anymore. You can’t work on it anymore. It reminds me of Simon Rodia, a folk artist from Los Angeles. He created the Watts Towers out of cement and junk, broken pieces of porcelain. He took 34 years to build them. He would come home every day from his job and he would cement little bits of pottery on these weird sculptures. Then, one day, he came home and there was no more room to add anything else. So he went next door to his neighbors and gave them the keys to his house and then he left and never came back. You can go and visit those towers, and there’s a sign out front that reads, “Art achieved and abandoned.” His art was all in the process. It’s not the finished product. That’s what the song is. It’s a process. When a song is finished, I have a tendency to just leave them behind. Even if I’m just learning a song, I usually won’t ever play it again because the process of learning is over.
Charlie Parr photo credit: Nate Ryan










 Is the time you spend with these animals good for writing?
Is the time you spend with these animals good for writing?


