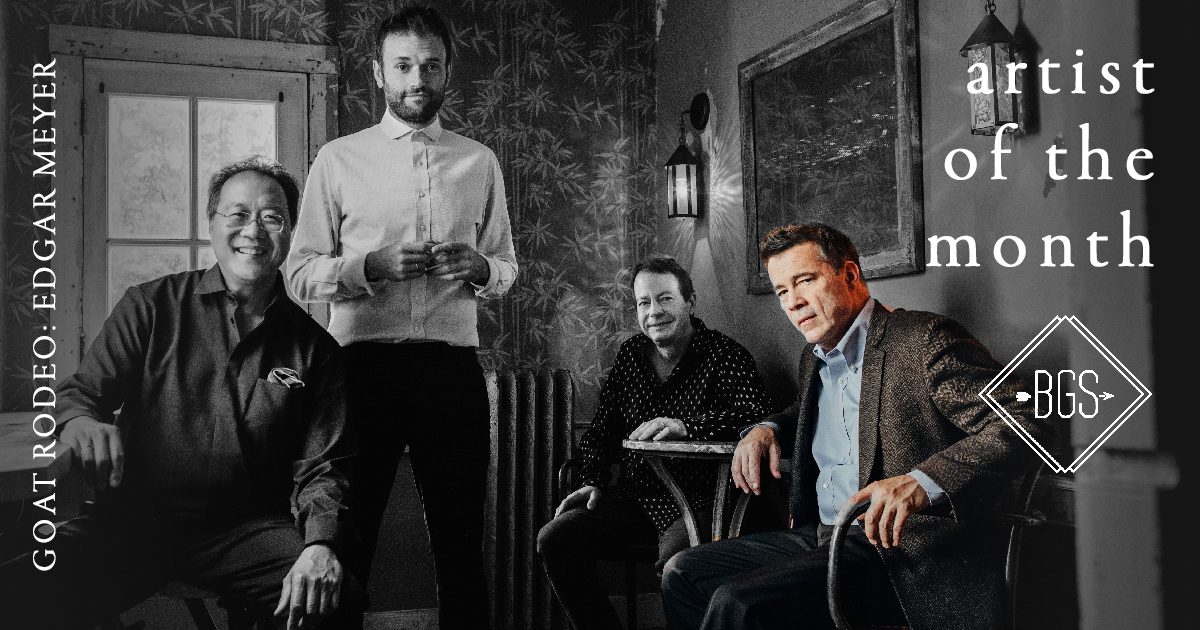
Lucky is how Edgar Meyer says he feels that he and his Goat Rodeo collaborators — Yo-Yo Ma, Chris Thile, and Stuart Duncan — were able to get together for the ensemble’s second album, Not Our First Goat Rodeo. They weren’t so lucky, however, when it came to their tour, which was supposed to start in August. “That’s not going to happen right now,” he tells BGS, adding, “We were looking forward to cherry-pick from both records.”
Along with their 2011 debut, which won two Grammy Awards, the Goat Rodeo albums represent two of the many high points in Meyers’ illustrious career. Renowned for his artistry on the double bass as well as for his compositional skills, the award-winning musician has been honored with a MacArthur Fellowship and the Avery Fisher Prize — the only bassist to have won either. Meyer also might be the man most responsible for Goat Rodeo’s existence. Having collaborated with both Ma and Thile, he introduced them to each other; later he and Thile recommended Duncan to Ma as the one to round out their quartet.
This Artist of the Month interview is the second of four installments as BGS salutes the incredible and iconic musicians of Not Our First Goat Rodeo.
Meyer: I’d say in terms of learning how to play the parts, yes. But Stuart, Chris, and I spent 20 days together writing and that’s very similar to the first one. That’s probably more important than learning how to play it. We were not particularly well rehearsed or knew the music when we [all] got together, but the important part — which is the writing — had about the same amount of effort.
How was it building these pieces together?
It’s a joy. It is a unique endeavor and we were able to go somewhere we probably wouldn’t go with another set of people.
And did songs evolve a lot once you all got into the studio?
Not much in terms of the actual notes. Maybe the feeling of it — that would evolve some. Occasionally, there might be a kind of loosely mandolin/bass improvised area that became more consistent in what it is. But there’s not a lot of that. Actually [the] music did not change immensely while recording, except in terms of it gelling. And in terms of people really understanding everyone else’s and their own roles, and making it into a whole.
Overall, yes. It’s tricky in that we attempted to try to find things that were wholly different from the first one. I wouldn’t say that we entirely succeeded in that, but I don’t think we were disappointed either. We just felt obligated to try and find brand new places to go. At the end of the day, it still sounds exactly like that same set of people — and I don’t think we were able to deeply change it. I think it is nine years later and I think we are all a little bit different. It is a different record, but very recognizable from the first one.
Were there musical territories that you all were specifically interested for this album?
For each piece we do, there’s always something that we are trying to explore that is new in some way for one or all of us — that’s almost a baseline. An esoteric example would be… I relate to harmony most centrally as a three-voice thing. For me if there’s more than three voices usually, no matter what the type of counterpoint is, most of these things are not going to track all four at the same time. But it is possible with good three-part writing to have the listener track all three voices almost all the time. That’s just what I find. Obviously somebody with enough skills will try to turn that on its head.
Depending on which way you count, there are either 19 possible three-note chords or there are 12. The modern music guys like to say 12, but their way of counting says that the major chord is the same thing as a minor chord. So, I prefer to count 19 and make those redundancies separate chords.
So, for “Not for Lack of Trying,” we experimented; there’s a chorale that it’s kind of built around — a three-part chorale. It has a repeated phrase. I think we tried to get one of each kind of chord. And maybe it’s a 24-note chorale [because] the last five chords are the ones that were used in the beginning. But there’s at least one of each of the 19 kinds of three-note chords in that chorale. That’s not something we did on the first record.
But there’s always some kind of something that somebody or all of us are trying to explore. And it’s not going to usually be something like, “Oh, we wanted to see if we could mix some bluegrass with some Caribbean music.” It’s going to be much more melodies, rhythms, harmonies — very specific musical questions.
I think mainly good… it’s a little more even than the first one. Maybe it doesn’t have some of the crazy highs, but it is a little more consistent. It’s more like somebody’s doing it for the second time.
This time everyone was a little more consistent with what instruments they played. Was that a conscious choice?
It’s just how it went down. The truth is on that count we were trying to emulate the first record. I probably like the variety of the first one slightly more. What we knew before we started the project was that an instrumentation of mandolin, violin, cello, and bass is not a very good instrumentation, and we knew the three of us would have to switch instruments in order to make the textures really work. Then when we are all on our main instruments, you can hear the comfort. You can hear all of us doing what we do best, but if you had to listen to those four instruments for a whole recording it wouldn’t work as well.
Song titles on both Goat Rodeo albums are very fun, like “Waltz Whitman.” Does one person tend to come up with the titles or are they batted around and one title rises to the top?
Chris and I had a session on the phone for about a half an hour the day before we turned in the album. “Waltz Whitman” was Chris’s, and he didn’t like it when he said it. I liked it a lot and made him stay with it. And, of course, he likes it now.
A lot of projects that Chris and I’ve done, and that I have done in general probably, have a lot of titles with useless meanings that the listener will never know about. Because we don’t put a lot of stock in titles. And so we could slap almost anything on there. This one actually didn’t have anything that we wouldn’t be afraid to have on the front page of the paper. There’s no hidden stories behind these titles. That’s unusual. Maybe it’s a new trend for me.
It’s a tough one because I will start by rejecting the question. What has had bigger impressions on me are particular pieces of music, and not particular recordings of them. The set of my favorite Beethoven, Bach, and Mozart pieces have had a bigger influence on me than single recordings have. My primary method of browsing in my formative years was less recordings than sitting at the piano and going through those composers’ scores. Although my list of influences is broad, at the top of it is Beethoven, Bach, and Mozart, and my primary way of knowing them is not through recordings.
So it’s their compositions overall?
Yes, that is exactly right. And the scores themselves. Because that is what we have from them. Whereas with Stevie Wonder, the way I know him is through a recording; so that’s how I’m influenced by him. But with these classical composers, it is not through the recordings. Like I’ve said that’s the most important. It probably depends primarily on the vintage. It’s a tough one, because some people who lived during the times of recordings are not well-documented. Anyway, that’s a true answer though. That’s how it works for me. The essence of what moves me is the writing.
(Editor’s note: Read the remaining installments of our Artist of the Month interview series here.)
Photo credit: Josh Goleman