(Editor’s Note: Read part one of our series on the Dayton Bluegrass Reunion here. Read part two here.)
Working on CityFolk’s Dayton Bluegrass Reunion, I heard local terminology for the culture in which this music grew. “Industrial working-class Appalachian migrants” was rarely spoken. “Hillbilly” was said sometimes with disdain, sometimes with pride. The preferred in-group term was “briar.” Briars came from the Appalachian hills, transplants proud of their continuing organic down-home connections. I was told that the call letters of WPFB, where Moon Mullins had represented bluegrass for two and a half decades, stood for “We Play For Briars.”
Don Baker’s introduction to the second act of the reunion framed a dramatic shift of scene from Mullins’ milieu to a younger Dayton band: The Hotmud Family.
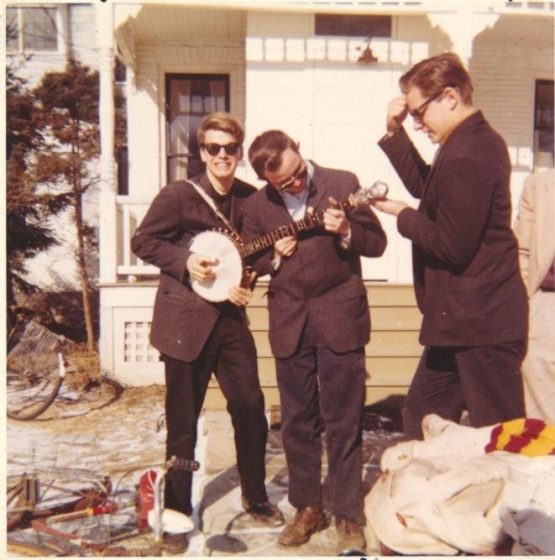
Inspired by the New Lost City Ramblers, this band began in 1970 playing old-time music based on pre-war hillbilly recordings. The band included Suzanne Thomas Edmundson, Dave Edmundson, and Rick Good, along with a succession of bassists. Suzanne, born in Dayton of Kentucky parents, was a second-generation briar. According to Jon Hartley Fox the Hotmuds were “perhaps the most significant band to emerge from the vibrant scene of the 1970s in southwestern Ohio” (Industrial Strength Bluegrass, 140-1).
They began including bluegrass in their sound during a 1974 appearance at the Mariposa Folk Festival. In blending old-time and bluegrass, they placed special emphasis on vocal harmonies, something many old-time bands overlooked. Between 1974 and 1981 they made eight albums and appeared widely at bluegrass and folk festivals. Here’s their 1975 bluegrass/old-time blending of “Weary Blues,” a song originally recorded in 1929 in Atlanta by Chattanoogan Jess Young’s Tennessee Band as “Old Weary Blues”:
The Hotmud Family came to be associated with Dayton’s Living Arts Center, described by Hotmud banjoist Rick Good in Industrial Strength Bluegrass (153-57). Established in 1967 by the Dayton Board of Education, this facility offered after-school instruction in the arts for grades 5-12 students in East Dayton.
In 1975 it began providing programs aimed at the local Appalachian-based culture. It turned to the Hotmud Family, now a nationally known band with an enthusiastic local fan base from their weekends at Sam’s Bar and Grill. At the Center, Hotmud gave lessons, ran a song circle, and led informal jam sessions. Once a week they held a live Country Music Jamboree, which was broadcast over WYSO, the Antioch College radio station. The Center closed in 1977, but the Jamboree continued with other performers at other local venues until 1986.
Act Two of the Dayton Bluegrass Reunion opened with a solo rendition of “Red Rocking Chair” by former Hotmud lead vocalist Suzanne Thomas Edmundson. Then came the group’s reunion, when Thomas was joined by the other founding Family members Dave Edmundson and Rick Good along with bassist Gary Hopkins. They did three pieces and an encore. During the 1980s the band gave occasional reunion performances. This was one of their last.
For Act Three, Baker’s stage directions began: “Beer Sign On.”
A borrowed neon sign hung onstage now lit up for the reunion of a band associated with Dayton’s bluegrass bar scene, the Allen Brothers.
Formed in the late ’60s to back their father Red Allen, they began performing without him and were touring in 1974 when brother Neal died. After a brief hiatus, the three other brothers (Harley, Greg, and Ronnie) carried on into the early ’80s, recording Rounder and Folkways albums. The new Smithsonian/Folkways album Industrial Strength Bluegrass — which just won Album of the Year at the 2021 IBMA Bluegrass Music Awards — includes Harley Allen’s “Suzanne,” first recorded by the Allen Brothers in 1982, here recreated by Mo Pitney and Merle Monroe:
They continued to play together in the Dayton area into the mid-’80s, but by then Harley had begun a solo career, first joining banjoist Mike Lilly in a band Jon Hartley Fox calls “one of the best bluegrass acts Dayton ever produced” (Industrial Strength Bluegrass 136). In 1985 the Allen-Lilly Band closed a set at the Berkshire Mountain Bluegrass Festival. Harlan County native Lilly led the way into “Little Maggie” with coon dog and motorcycle as Frank Wakefield watched:
Harley went on to a Nashville career as a singer-songwriter, winning two Grammys and singing on the O Brother, Where Art Thou? soundtrack hit “I Am a Man of Constant Sorrow” before dying at the age of 55.
At the Reunion, the Allen Brothers put together a band with Harley on mandolin, Greg on banjo, and Ronnie on bass, with Wendell Barrett on guitar, and David Harvey on fiddle.
Here’s how they sounded with a similar band (different fiddler and mandolinist), with Monroe’s “Uncle Pen” enlivened by guitarist Harley Allen’s transformation of Jimmy Martin’s “G run” and a fancy ending, followed by a bluegrass trio rendition of the Paul Siebel’s classic “Louise.”
At the Reunion, they did three tunes and an encore. Then it was intermission time.
The second half began with Baker introducing Act Four, the Dry Branch Fire Squad. This band was led by mandolinist Ron Thomason, a Virginian who had migrated to the region as a child. Around since the mid-’70s, it’s still active today. Thomason came up in Dayton’s regional scene in the ’60s, working in bar bands and on the road with Ralph Stanley.
Committed to traditional bluegrass, Thomason, now living in Colorado, has had many talented musicians in his band. He is famous for his emcee work, which regularly grows into humorous monologue. Baker’s directions for this act listed two pieces (including one gospel song), separated by:
“Rap — Ron Thomason”
Here’s a sample of Ron’s “rap” — a comic speech from a 2007 California festival:
At the time of The Dayton Bluegrass Reunion, Dry Branch had four albums on Rounder, the start of a long string with that label. Like the Hotmud Family, they were folk and bluegrass festival regulars.
The band this evening consisted of Ron on mandolin, John Hisey on banjo, Mary Jo Leet on guitar, and Charlie Leet on bass. In 1987 a similar lineup recorded “Aragon Mill,” a Si Kahn song that Ron had learned while working at coal miner’s union rallies with Hazel Dickens:
Act Five brought on another performer still active today, Larry Sparks and the Lonesome Ramblers. Sparks had come up in the Dayton bar scene at about the same time as Ron Thomason. He worked with the Stanley Brothers and Ralph Stanley at the end of the ’60s and made his first album on his own in 1970s. He became a member of the Bluegrass Hall of Fame in 2015 and has a new album out on Rebel.
At this concert his Lonesome Ramblers had a reunion dimension. Mandolinist and singer Wendy Miller, who’d played on Larry’s earliest recordings and was with the band through most of the ’70s, was back for this evening’s concert. Also in the band were banjoist Barry Crabtree and Larry’s son, Larry Dee, on bass.
They did three songs: “Dark Hollow,” “Face in the Crowd,” and “Kentucky Chimes,” all regulars from his albums and concerts. He closed with an eight-tune medley of his other hits. There are many videos of Larry’s great singing and lead guitar work. Here’s one of my favorites:
Acts Six and Seven dramatized the transformations of Dayton’s foundational 1956 band — The Osborne Brothers and Red Allen.
Act Six was all reunion. Red Allen had been officially retired since 1984, although he’d recently recorded four tracks on Home Is Where The Heart Is, David Grisman’s new Rounder album, joined on these tracks by son Harley and banjoist Porter Church, who’d been in his band The Kentuckians.
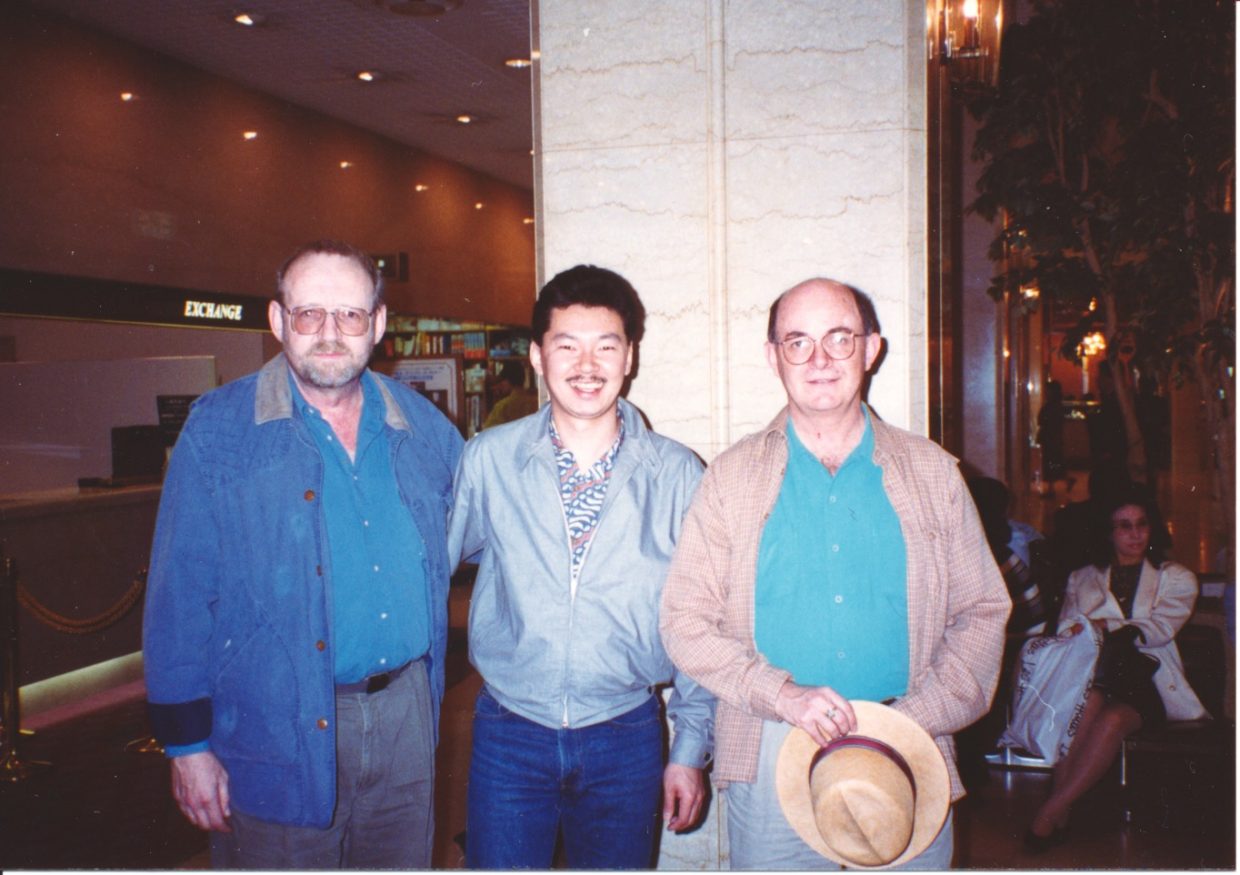
Red started this band in 1959 with mandolinist Frank Wakefield. In November 1961, in Nashville for the D.J. Convention, they cut six classic tracks at Starday with top bluegrass musicians of the day: Don Reno on banjo; Chubby Wise on fiddle; and John Palmer on bass. The whole great session is on YouTube:
Sierra Hull reprises Wakefield’s “Mountain Strings” on the new Smithsonian/Folkways album Industrial Strength Bluegrass. The track was nominated for IBMA’s 2021 Instrumental Recording of the Year.
In the early ’60s Wakefield and Allen worked out of the D.C. area, with a radio show in Wheaton, Maryland. In 1964 they did a Folkways album in New York, produced by David Grisman and Peter Siegel.
Soon after, Wakefield, whose innovative music is discussed by Ben Krakauer in Industrial Strength Bluegrass (182-183), began working with New York band The Greenbriar Boys and later he relocated to Saratoga Springs, New York. Here’s how he sounded in 2008 — still pushing the boundaries:
Red kept the Kentuckians going in the mid-’60s with a succession of great sidemen, among them banjoist Porter Church and mandolinist Grisman, who produced two albums of the Kentuckians on the County label.
In 1967 Red worked briefly for Bill Monroe and took Lester Flatt’s place in the Foggy Mountain Boys when Flatt had heart surgery. The next year he was in Lexington working with J.D. Crowe and Doyle Lawson.
By the early ’70s he was back in Dayton, working with his sons and playing locally what Rick Good calls “bargrass” (Industrial Strength Bluegrass 156). For tonight’s concert Red and Frank’s Kentuckians included Porter Church on banjo, Buddy Griffin on fiddle, Ron Messing on Dobro, and Larry Nager on bass.
During Red’s four-song set, Red Spurlock and Noah Crase, banjoists who’d played with Red during his early years, sat in for choruses with the band. A reprise of Wakefield’s famous “New Camptown Races” brought guest David Harvey, son of Dorsey Harvey, another influential mandolinist, to play harmony.
The final segment, Act Seven, featured Dayton’s Grand Ole Opry stars, the Osborne Brothers. Two days before the concert the Dayton Daily News said the Osbornes had “achieved the greatest fame of those taking part in this tribute to the flowering of bluegrass music in Dayton.” It would be hard for anyone to follow them. After joining the Opry in 1964 they’d moved from Dayton to Nashville. During the late ’60s and early ’70s, a string of country hits (“Rocky Top” is the best known today) led to industry awards for their vocal work.
With this success the Osbornes’ recordings moved toward a contemporary country radio-friendly sound, mixing pedal steel, piano, fiddle, drums, and electric bass alongside their bluegrass banjo and mandolin. Their live sound also changed. In 1967 they added electric bass; in the early ’70s, a drummer. Next came electric pickups on banjo and mandolin. They did this to make themselves heard in the big country package shows they were playing, where all the other acts were highly amplified. Their “going electric” was viewed with alarm in the acoustic-oriented bluegrass festival world, but it only lasted for a few years.
Throughout these years, their unique vocals remained a constant. They continued to record and tour. Their repertoire drew largely from decades of recordings along with newer material. They now carried a straight-ahead bluegrass band including fiddle and acoustic bass.
This evening, playing with the Osborne Brothers were Paul Brewster on guitar and third voice in the trio, Terry Eldredge on bass, and Steve Thomas on fiddle. They did four songs, all favorites from their earlier recordings, including a version of “Kentucky,” the Blue Sky Boys hit of the ’30s that they’d recorded for Decca in 1964 and which remained in their repertoire right up until Sonny’s 2005 retirement. Here’s an early ’90s Opry performance of it, introduced by Bill Anderson. The band includes future Grascals member Eldredge on guitar and third voice and Terry Smith on bass, along with second guitarist (and bus driver) Raymond Huffmaster, Dobroist Gene Wooten, and fiddler Glen Duncan.
According to Baker’s stage directions, the closing act consisted of:
“Music — Medley”
An earlier draft reads:
“[medley in B natural: each unit from each of the 7 segments chooses a song which they play when their turn comes]”
My memory of this is vague, but I think that’s just how the Dayton Bluegrass Reunion ended, in B natural. But it wasn’t over quite yet. In that day’s Dayton Daily News columnist Nick Weiser had announced:
“Following the Dayton Bluegrass Reunion at Memorial Hall, the Canal Street Tavern, located at 308 E. First St., will have a reception for the audience and the participants of the Bluegrass Reunion Show. Mark Bondurant will open the show at 9:30 with a reception to follow after the show. Many of the musicians from the Memorial Hall show are scheduled to get together and jam at the Canal Street Tavern reception. Admission is $1 at the door.”
I went with my camera… Next time!
(Editor’s Note: Read part one of our series on the Dayton Bluegrass Reunion here. Read part two here.)
Neil V. Rosenberg is an author, scholar, historian, banjo player, Bluegrass Music Hall of Fame inductee, and co-chair of the IBMA Foundation’s Arnold Shultz Fund.
Photo of Neil V. Rosenberg: Terri Thomson Rosenberg.
Neil would like to thank Tom Duffee, Rick Good, and Al Turnbull.