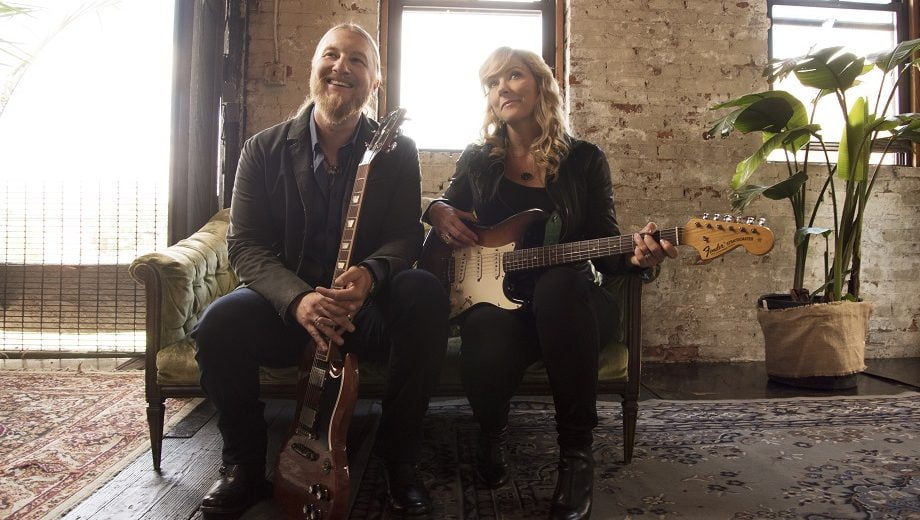
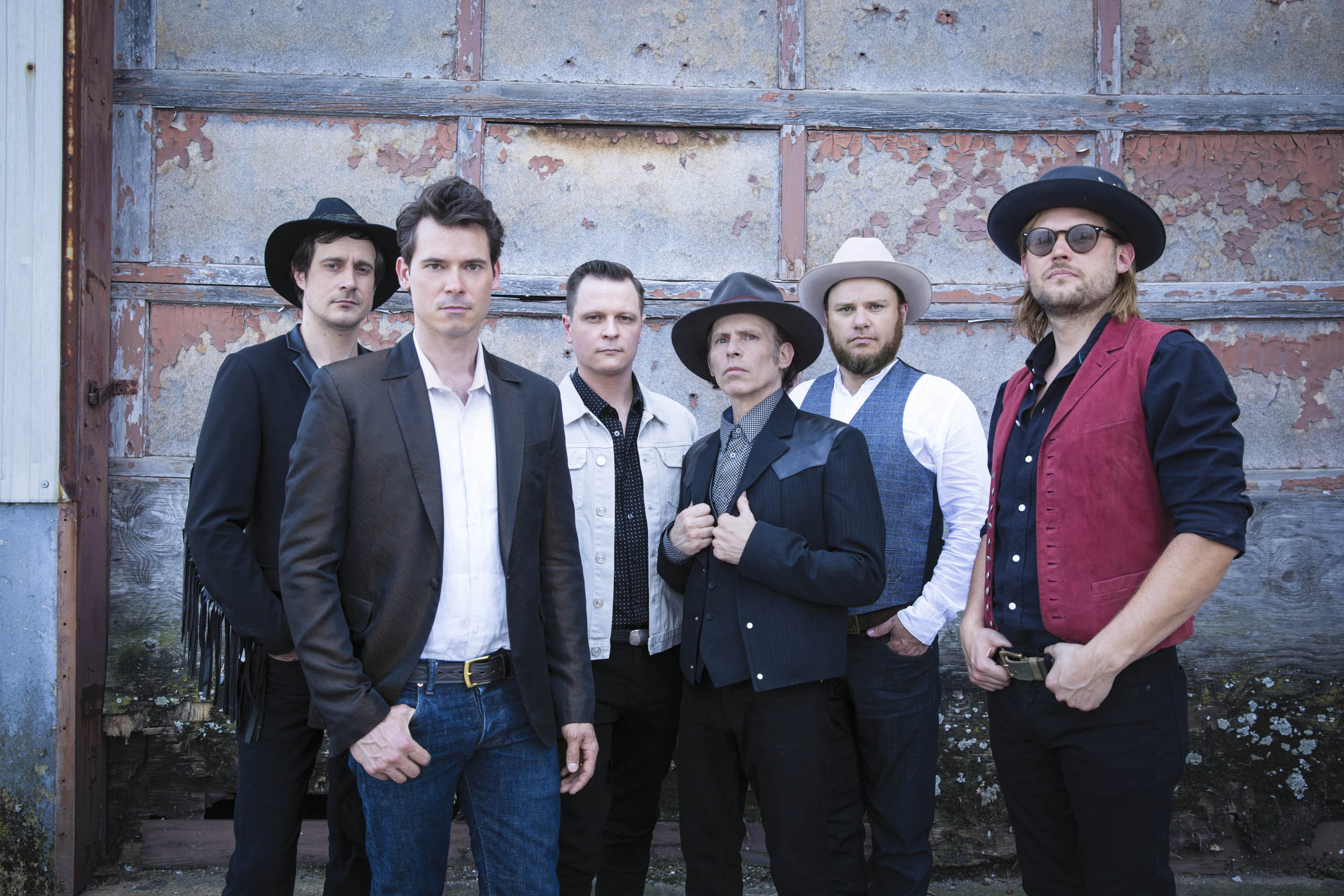
With Tedeschi Trucks Band, you get a partnership. That impressive ability to divide and conquer serves them well on stage, with Susan Tedeschi nailing the vocals and tearing up the guitar, along with Derek Trucks calmly proving his own guitar proficiency. That’s not to mention the other 10 musicians that make this one of the most potent groups on the road right now, as evidenced by their newest album, Signs. (Incidentally, the conversation took place shortly before the death of longtime keyboard player Kofi Burbridge, who passed in February.)
To begin our Artist of the Month interviews, Derek took the phone first — yet frequently praised Susan throughout the conversation, especially her ability to captivate a crowd. Before passing the phone over, he also dug into his preference for analog recording, his history with the Allman Brothers Band, and the reason why age doesn’t really matter.
BGS: I know you recorded this album on two-inch analog tape and you have that Neve console. Why is it important for you to use that vintage gear?
Trucks: I think every time you record, you’re searching for that sound you hear in your head, and what you hear live on the floor. I feel like the more analog we go, the closer we’re getting to that. This is definitely the warmest recording we’ve done to date. You know, I think the beauty of having a studio is that you’re always working toward that and you don’t have to reset and start from scratch every single time.
And there’s something about recording to tape that focuses everybody a little bit differently. You don’t have unlimited tracks, you don’t have unlimited space, and it becomes a little more performance-based. Everything seems to mean a little bit more. Every reel of tape is important! You don’t have a hard drive to fill up, so it’s a different feel all the way around. And it slows things down in a good way. I think it really does put everybody’s head in a different spot.
What does that room look like?
We designed it visually thinking about Levon Helm’s band up in Woodstock. It’s a few hundred feet from our house in the swamp down here in Florida. It’s barn-shaped and the main recording room is a pretty good-sized room. When we rehearse with the 12-piece band, everyone’s set up in the main room. But it’s a bunch of vintage gear and old Fender amps. There’s a few drum kits in there and a B3 set up at all times. You know, it’s ready for action!
Speaking of those drum kits, I noticed at your show that you tour with two drummers. What’s the benefit of that?
There’s something special about that sound, man. It’s a powerful thing when you get those guys playing. The pulse gets really, really thick. When the whole band is firing, it feels like a freight train behind you. I think after years of being on stage with my uncle [Butch Trucks] and Jaimoe [the Allman Brothers’ drummer] and the Allman Brothers, when it really works and it’s really good, there is nothing quite like it. So when we put this band together, I was certainly thinking about those guys and that sound.
The chemistry really has to work when you have two drummers. It can be a freight train or it can be a train wreck! [Laughs] It can be really bad. I’ve been in situations where there have been two drummers and it’s a “less is more” situation sometimes. But Tyler [Greenwell] and JJ [Johnson] have a special chemistry. They really listen hard to each other and complement each other well, and they have a sound that is completely unique to the two of them. It’s a big part of what makes the band unique, I think.
At risk of being too heavy, what’s that experience like when you don’t have Gregg on stage, or knowing that you aren’t going to play with Butch anymore? Was that hard for you to process?
I don’t know if I ever thought of it that way so much. I played with them for so many years and I was always doing my solo groups and other things at the same time, so there were always a few different streams. I knew it wouldn’t be forever, so that part wasn’t a shock, but more recently we started playing a few of those tunes from time to time, and it definitely hits me now. Especially when we’re playing the Beacon Theater or some of these rooms I’ve played with [the Allman Brothers Band] so many times. You certainly miss them, and you miss that sound and that spirit. When we’re making records, there are certain times when for some reason I’ll be thinking about them. They were family, they were friends, and they were musical heroes, too. Those are big losses and I think it takes a while to unpack that stuff.

I’ve heard you and Susan both talk about being “a lifer.” How would you describe what that means?
I was thinking about Del McCoury this morning when I knew I’d be doing this article. It’s the people that you just know are going to be playing and touring and making people feel good as long as they’re on the planet. The Allmans, B.B. King, Willie Nelson –there are thousands of musicians who play in small clubs that are that way. You just know once you start doing it. I knew when I started in my pre-teens. Once I got serious about it, I always got that feeling like, ‘This is what I’m going to be doing. Whether it’s successful or not, I don’t think it’s going to matter.’ [Laughs]
And the beauty of what we do is that we can do it forever. I think about professional athletes sometimes and how they give everything to their sport — and by the time they’re 30, they’re washed up. We’re incredibly fortunate. We can play into our 90s. There are guys out there doing it.
What is it about Del McCoury that you admire?
He’s one of those personalities, man. You just see him and you immediately love him before you meet him. Then you meet him and you love him more. [Laughs] And there’s something to a guy who keeps his family with him. It helps that his family members are incredibly talented too. It says a lot about somebody when music and family intersect like that, and it becomes a way of life. There’s something that really speaks to me about that.
And his sound — I don’t think there’s anyone alive who’s doing it better. Every time I hear those guys, it just makes you feel good. It gives you a little hope. It is authentic and really, really good on every level, and that dude has it in a headlock. We love him. He’s fearless, man. He’ll jump up with anyone. He’s sat in with our band. He’s not a guy that won’t go outside of his genre. Del will step on in.
That’s an interesting point because I don’t think your band can be categorized as one certain thing — you fit in a lot of places, too. That must be a great feeling to not be locked into a certain style.
Yeah, I’ve always appreciated that about this band, and my solo band as well. We were always kind of half-accepted and half-shunned by every genre. They’d put us on a blues festival and we’d hear ‘You all aren’t blues enough.’ Or in the early days, the jam band festivals, but we weren’t jam band enough. Or jazz… they let us in all of them a little bit, but no one would fully accept us, which I appreciate because that’s where my tastes have always been. I think it’s what I naturally come from, so I never minded it.
In the early days, it was a little more difficult because when you get accepted by a certain scene, it makes it a little easier to tour, and there are certainly benefits to that. But I like being able to bounce around, and in the course of a month, play a festival for four or five different genres of music. It makes you a better player because everywhere you go, you hear things that you wouldn’t have heard or known. You see incredibly talented musicians that maybe you weren’t aware of. That makes you double down on what you’re doing when you see somebody new.
I remember the first time seeing Jerry Douglas and thinking, “All right…” [Laughs] “Well, there’s that!” I think it’s important to listen wide.
It’s remarkable to me how poised you are when you play guitar. You make it look easy while some guitarists put their whole body into it. Is that the way you’ve always played, just stand and deliver?
Yeah, and at different times, especially early on when I was a kid playing, I would get people almost every night coming up and asking, “Why aren’t you smiling? Aren’t you having fun?” [Laughs] It’s like, “I’m taking this shit serious, people!” I’ve never had a stage presence that’s going to bring people to the show. I’ve had to do it another way. I don’t know… some of it is just your personality, mainly.
But I remember seeing pictures of Duane Allman as a kid and I always imagined him standing there, getting it done. And I remember seeing footage of John Coltrane when I was in my early teens, just black-and-white footage around the Kind of Blue sessions. He was stepping up and taking a solo, and the look on his face — it just felt really important. It hit me, like, “That’s what I’m after.”
Editor’s Note: Read our Artist of the Month interview with Susan Tedeschi.
Photo credit: Shervin Laivez
Illustration: Zachary Johnson