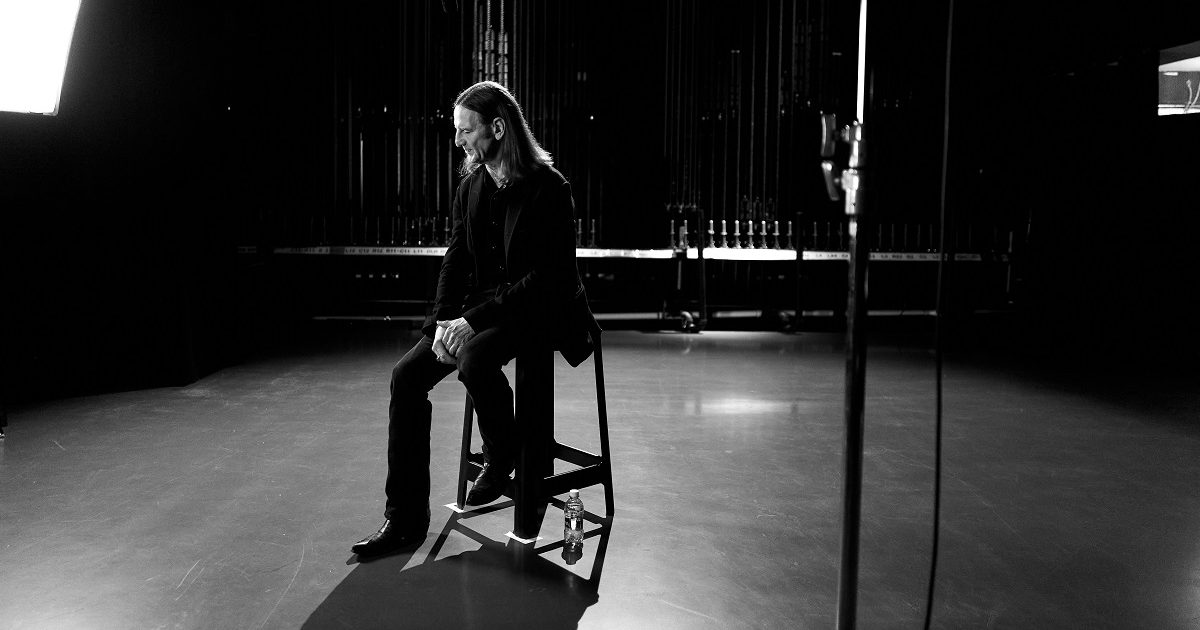
Mark Seliger has been to the Grand Ole Opry before, as a staff photographer for Rolling Stone, but this time he’s in Nashville to support the release of his country band’s self-titled album, Rusty Truck. To an empty house during soundcheck, he’s leading Rusty Truck through “Find My Way Back Home,” one of the three songs he’ll sing later that night with good friend Sheryl Crow. Meanwhile, an Opry camera crew is following him around — an ironic role reversal, considering that Seliger stands as one of the most recognizable and accomplished photographers of the last few decades, with numerous books to his name.
Within a few weeks time, he’ll shoot the Vanity Fair Oscars Party for the 10th year in a row, but for now, he’s comfortably backstage at the Opry, talking to BGS about his love for country music, the preparation that goes into photo shoots, and the turning point that led him to songwriting and eventually releasing three albums. Seliger recorded his latest project in guitarist-producer Larry Campbell’s home studio in Rhinebeck, New York.
“You’ve got to go out there and keep on reinventing yourself. You’ve got to keep on being curious, and keep your eyes open, soak up the information and be a part of the life,” he says. “I never really thought that I would make three records, right? I thought I was good with making books. But there’s something about how much better I feel when I’m making music in terms of my photography. And they work really nicely together. They complement each other. And when you go out and sing on top of that, at the Opry, I mean, come on! That’s the coolest.”
View this post on Instagram
BGS: What was that experience like for you to walk out there on the Opry stage?
Seliger: Frightening! Absolutely frightening. But what’s really remarkable is the musicianship. We usually are in rehearsals for days to try to get anything near that. And to just be able to hear the song all of a sudden come together within three notes has been incredible. And the room sounds incredible.
I’m curious, what do you consider to be the golden era of country music?
Oh, that’s easy. I mean, I was pretty unfamiliar with country music when I was growing up. I grew up in Houston. And when I went to college in a small state school in Texas — East Texas State University in Commerce — probably around two months into being there, my RA loaned me his Hornet to drive to Dallas to go visit an old girlfriend. And he had the Stardust 8-track in his car. I knew the songs that were really big at that time, but I didn’t know the album. I played that and it was just like the lonesome, the phrasing, the voice… I just connected with that.
Then I started digging deep into Hank Williams. I started digging into Loretta Lynn, and into Tammy Wynette and George Jones, Merle Haggard and Buck Owens, and that whole world. It all started to make sense to me. I fell in love with the double entendres and the stories behind the songs and how there are these twists and turns. That’s what really became evident to me — that songwriting to me was the hero. It gave me a chance to take all the visual information that I had gathered in the years as a photographer, kind of pull from it, and use that in order to be able to tell stories.
When you said you were digging into these artists, how did you do that?
I would make mixtapes so I could hear different artists together, which was really interesting to hear collections of singers coming together. And then, one of the turning points for me was I had heard a Gillian Welch recording kind of in the early days. I started to follow Gillian and Dave, and around 2000, I had met somebody that was involved in their team. And I said, “You know, I’m not asking to be hired for money. I want to just work with him if I have an opportunity.” They put it out there and I met them. I ended up doing a long film for them. I also did the photography for Revelator. So, Gillian, Dave and I really connected the dots.
At that time, I was working on our first record, not knowing it was actually going to be a full album. I had asked people that I had worked with in the photography world, not to sing on it, but just to produce it. And so, after I became pretty close to Dave and Gil, I said, “Hey, I’m working on this record. I know it’s kind of crazy. It’s certainly not my field, but it’s my art form.” And I said, “Would you be interested in producing a song or two?” And they were like, “Sure. We’ll just spend a day doing it.” They booked studio musicians and they did an incredible job producing the two songs. One was called “Civil Wars” and the other one was called “Tangle In the Fence.”
How old were you when you started writing songs?
I turned 40. I was a very late bloomer. I was breaking up with Rolling Stone as their chief photographer. And I had a lull. I was also in kind of a good state to be able to write. I was probably a little bit down in the dumps about moving on. I wasn’t sure about the next move in my career and I found a lot of support in writing. The first record, I had the luxury of being able to take my time, but once I started going, I started to write pretty quickly. But, you know, writing takes me a lot of time. I have to actually sit quietly, take a phrase, start to work it through, figure out what I’m doing on the guitar. I have no idea if it’s gonna stay that way or if it’s gonna move in a different direction. Sometimes I write acapella. It’ll just be me on a tape recorder, humming it through. Probably three or four songs I played for Larry were just straight vocals, before we figured out what the what the instrumentation was going to be.
When you started as a songwriter, how did you get feedback? Did you play your songs for people?
I went to open mics. I started to go out in ’97 or ’98. I remember the first time I went out and sang in public, a buddy of mine who was teaching me guitar introduced me to a band that was playing at the Rodeo Bar in New York. And I sang “Big City” by Merle Haggard. And I got OK accolades. (laughs) I was OK with that! Then I would go out and already have half a song that I could kind of fudge to be a whole song, even though it wasn’t. I would just repeat the same verse. But what I found was a camaraderie and a friendship in musicians that was very dissimilar from the relationships I had in photography. It’s a family and I loved that. The more I played, the more I found that that’s where I wanted to spend my time off. In music. I never really wanted to make it a career, right? I like what I do. So I labeled it like, photography is my wife and music is my mistress.
When did you get interested in guitar?
I took piano lessons when I was a kid. And I continued to play piano all through junior high school and a little bit in high school. And I traded in my Vox mini organ for an Alvarez guitar, which is now signed by pretty much anybody I’ve ever worked with. It was really about learning guitar, fingerpicking, everything from Eagles songs to Cat Stevens. You know, the usual suspects of early guitar playing. I wasn’t a huge Americana fan when I started in that world, but my older brothers turned me on to different phases of Dylan. They turned me on to the Band. They turned me on to things that were heading that direction. But it wasn’t until I started to write songs that I found my voice. I’m not really a guitar player. I accompany myself on guitar in order to sing my songs. My instrument is really my voice, and that’s the thing that I’ve been working on over the years — to be able to learn how to sing properly and to develop a style to where it really feels like what I consider to be Rusty Truck.
View this post on Instagram
When I was listening to this record, I heard the fiddle and banjo on “Ain’t Over Me.” Do you like bluegrass? Do you have any bluegrass influences?
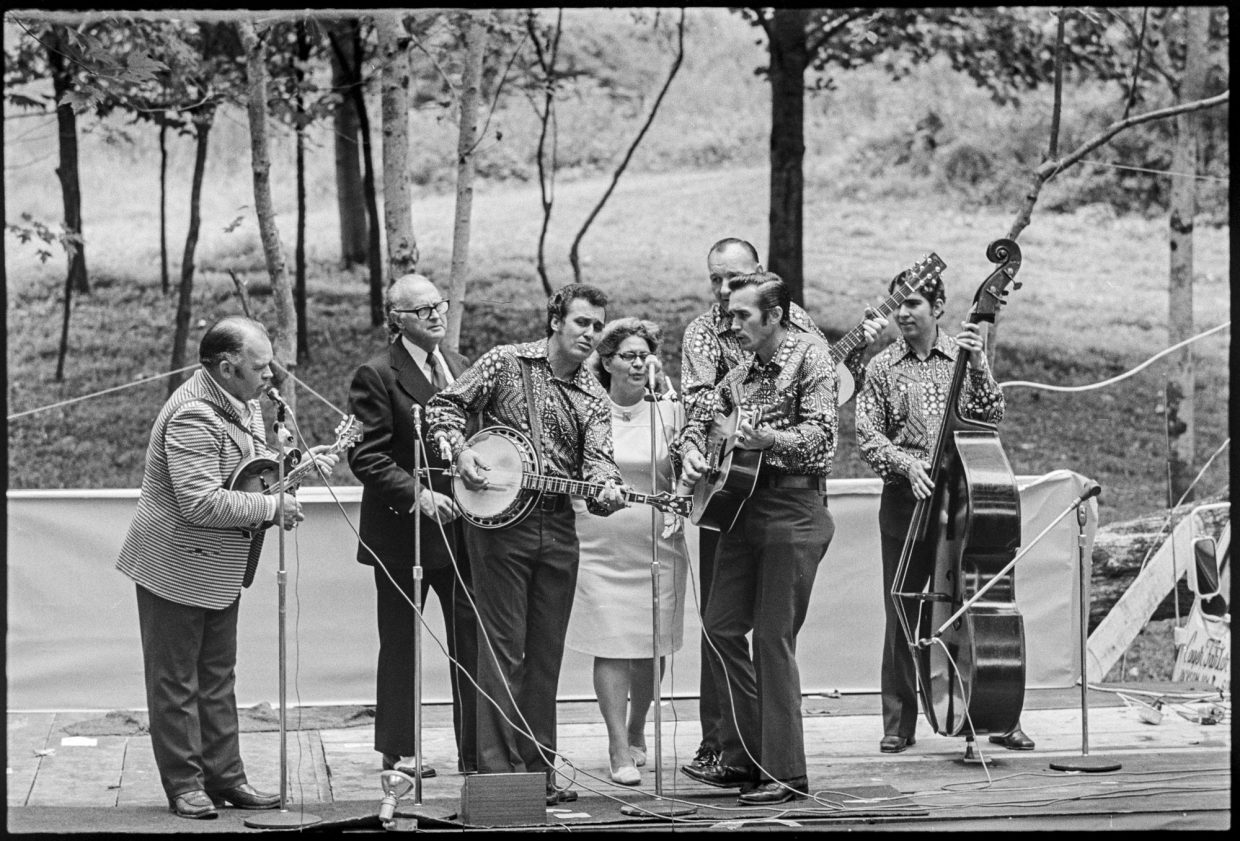
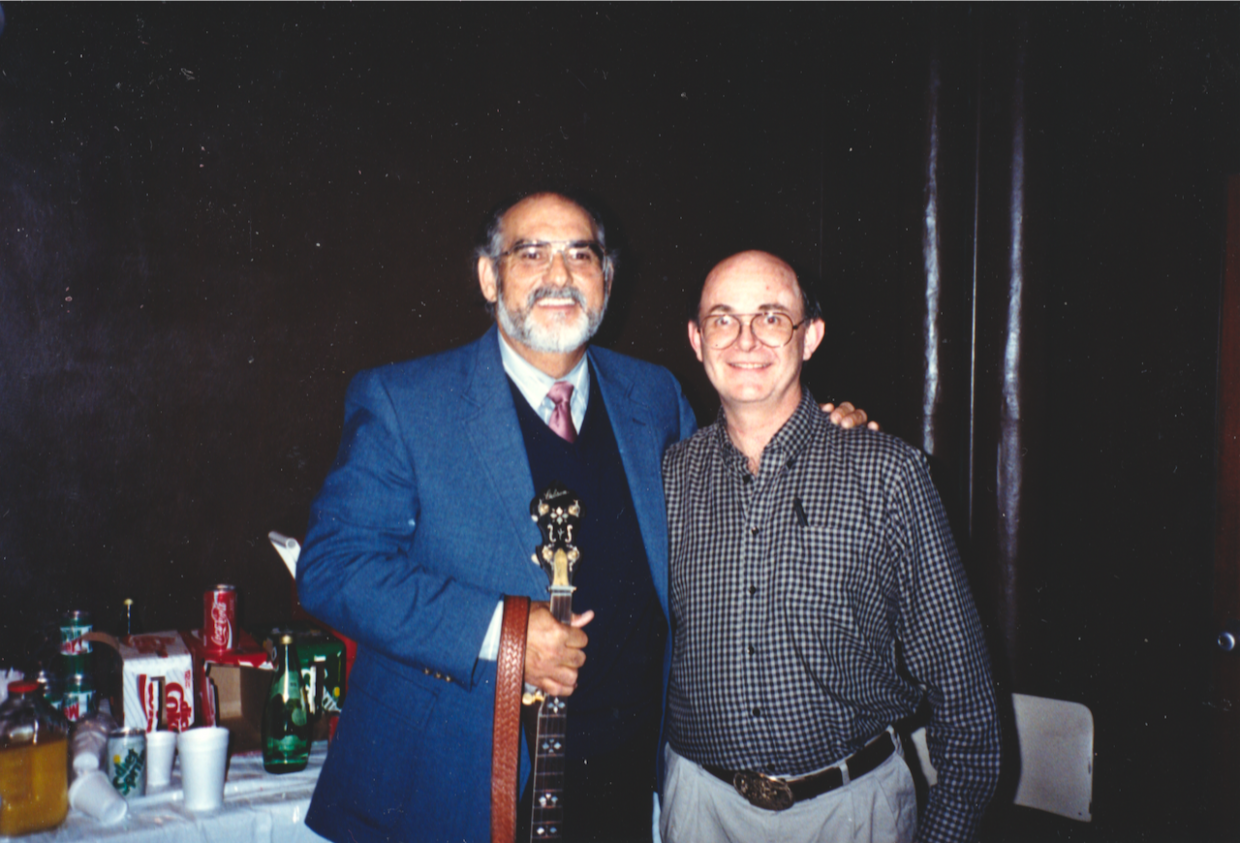
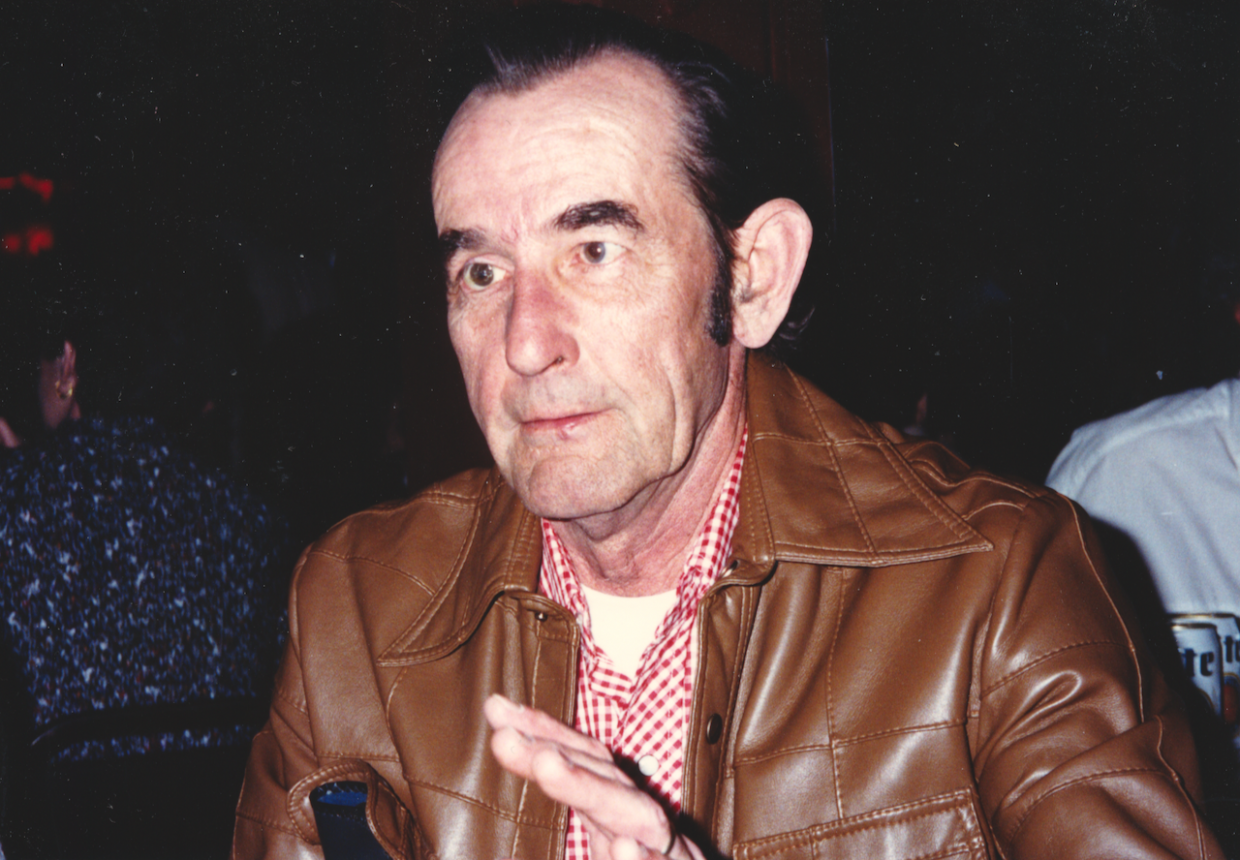
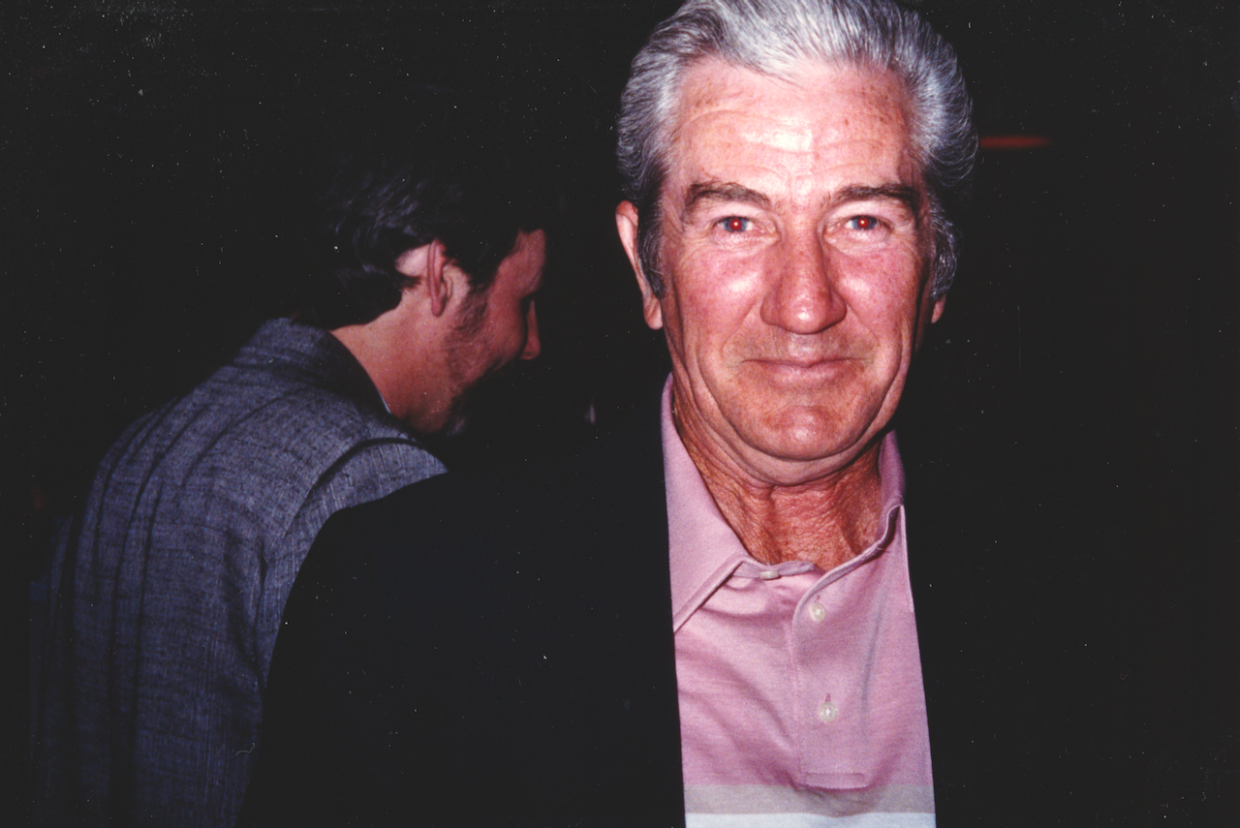
Oh yeah! I think the Blue Sky Boys and a lot of the Louvin Brothers and a lot of the earlier stuff. You know, I actually got to meet Charlie Louvin and photograph him. That was pretty rad. I got to meet Bill Monroe and work with him. You can’t deny the foundation of how bluegrass has influenced everything.
How did you encounter Bill Monroe? What was your assignment?
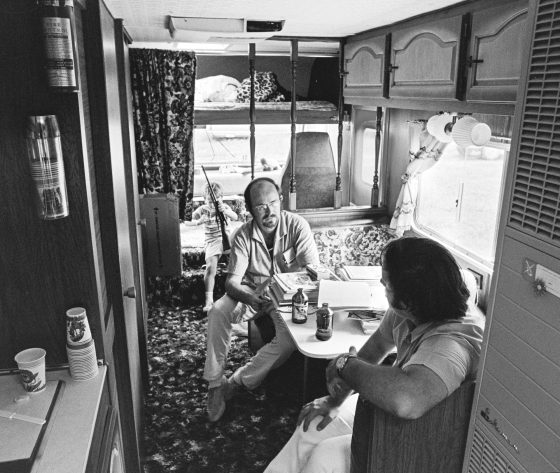
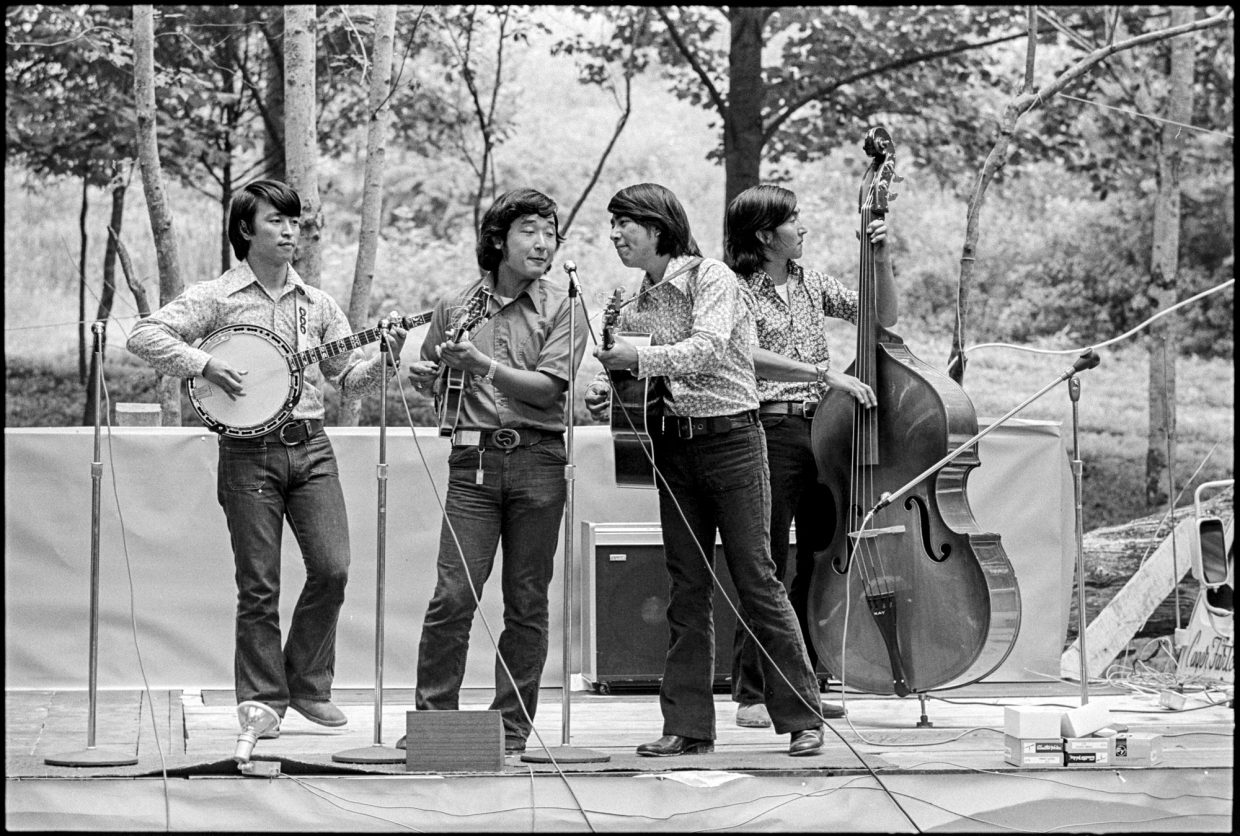
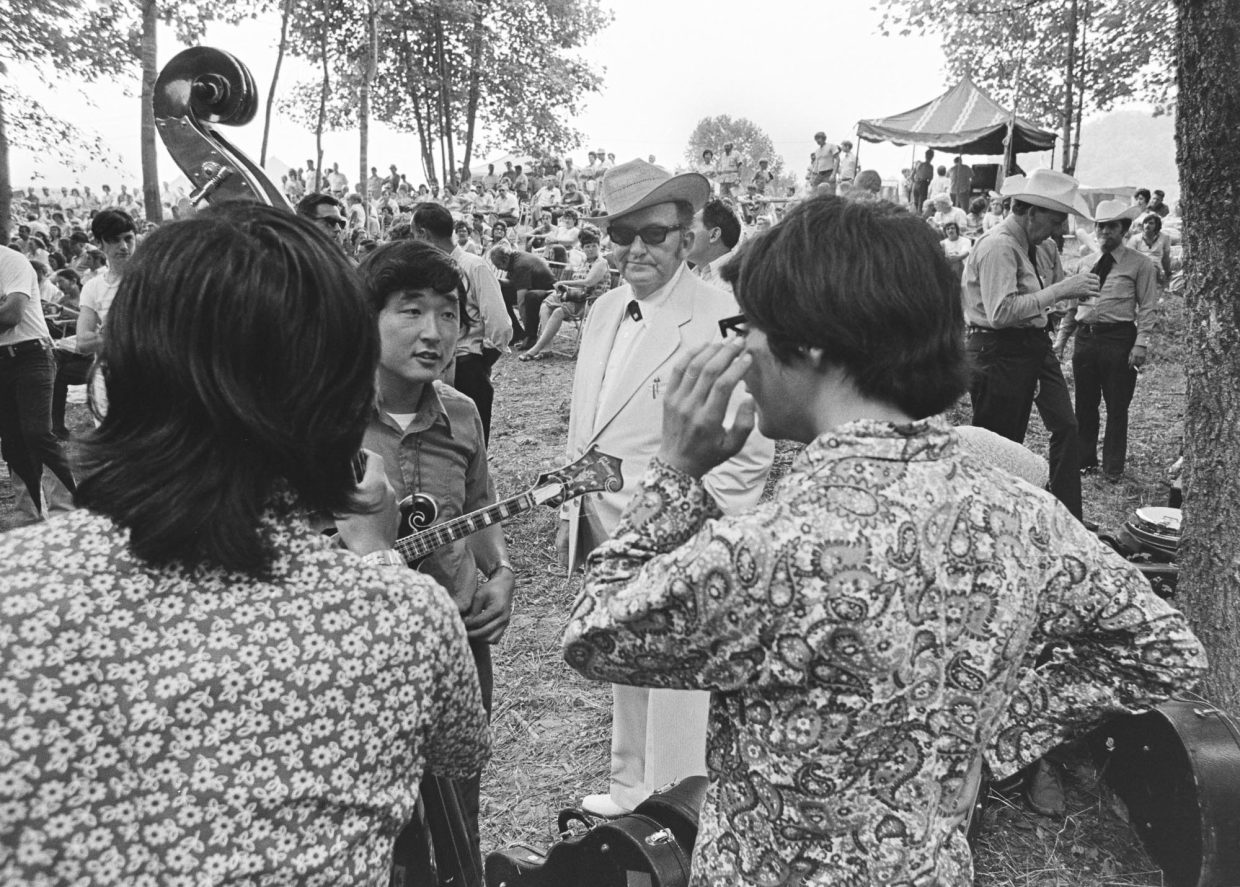
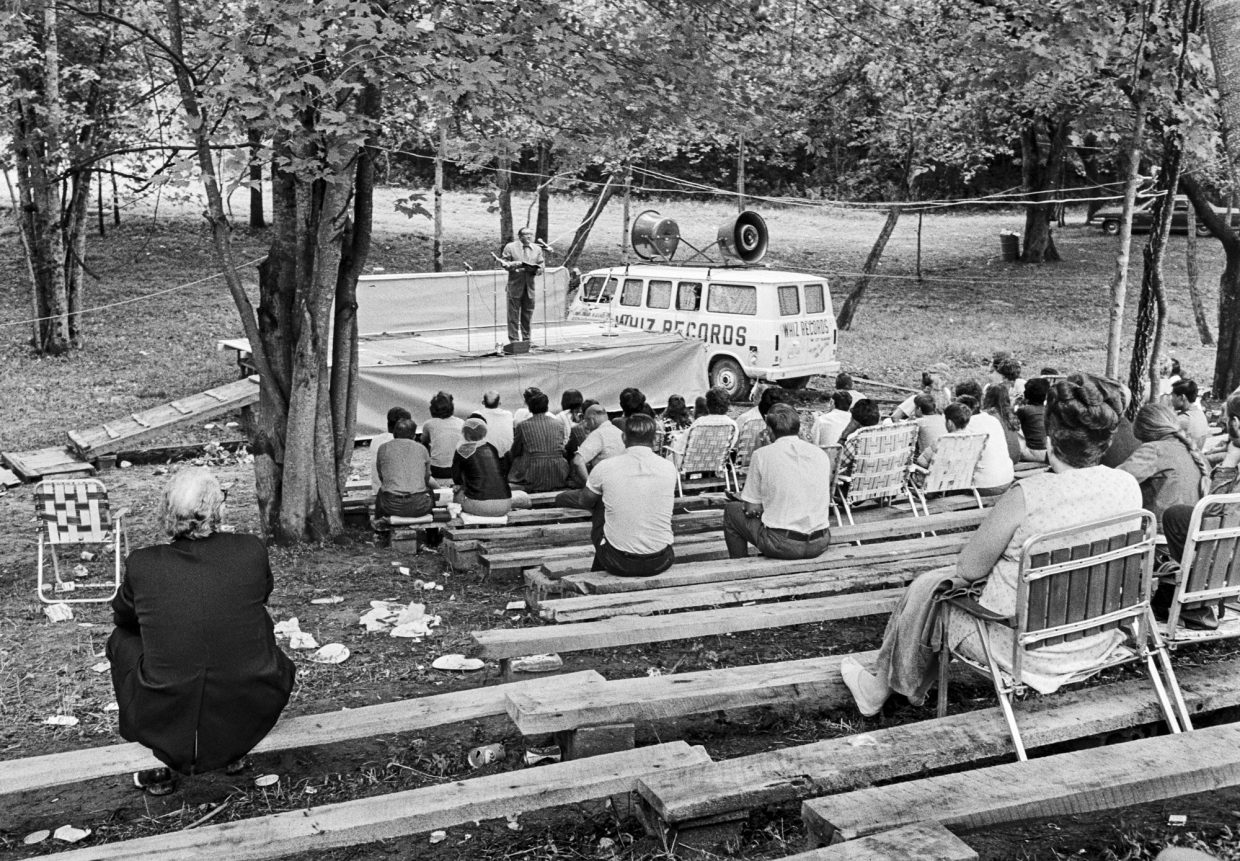
My assignment in the early to mid ‘90s was to do a country portfolio for Rolling Stone. My buddy who was the creative director, Fred Woodward, pushed Jann Wenner to doing a country portfolio. We pulled together some pretty fantastic people. It was Kitty Wells and Johnny Wright. It was Bill Monroe. Earl Scruggs. Waylon. Willie. George. Tammy. Johnny. Merle. Buck Owens. I almost got to photograph Hank Snow, but he was reluctant. When I tried to kind of push my way into that, he refused us.
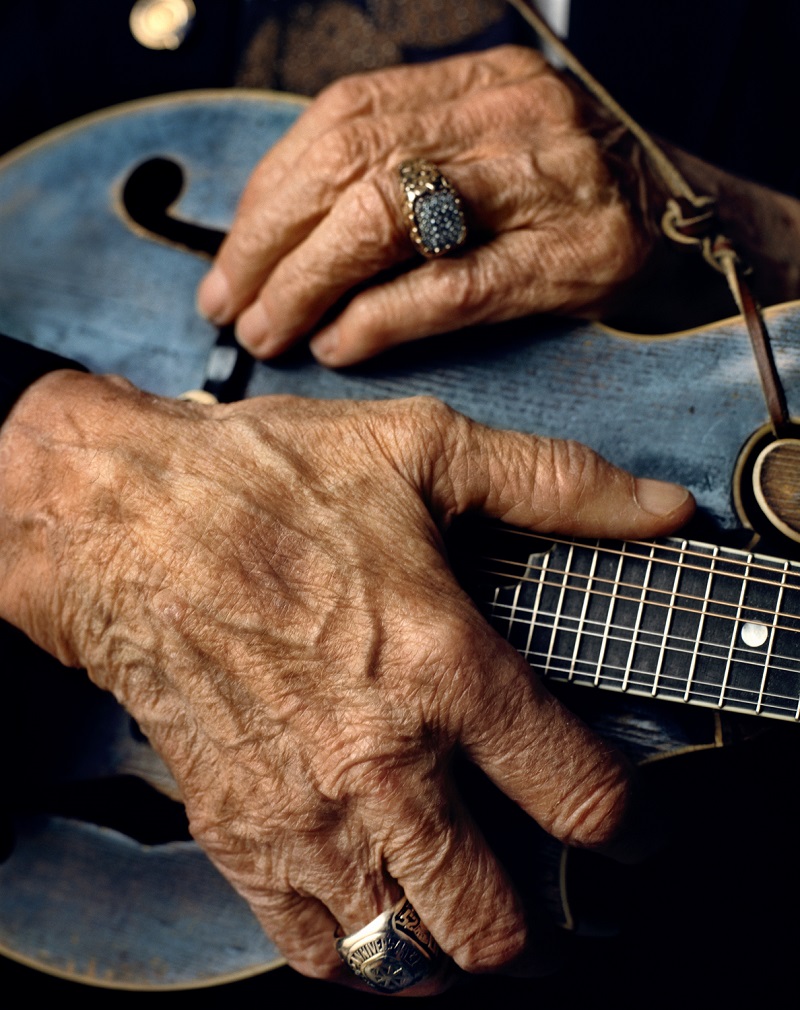
But we did come to the Opry. That was my first entrée into the Opry. We went backstage and we set up a little background. Mr. Monroe came out and he had a traditional, kind of tilted hat, a short Stetson, and he was wearing a big Jesus button on his suit. And then he said, “How’re you doing? I’m Bill Monroe.” I shook his hand and he CRUSHED my hand. I literally saw bruises for days.
That was actually a good indicator because then I saw him with his mandolin with a little cord wrapped around his neck. That was his strap, like a piece of rope, which was pretty awesome. And I sat here and I listened to him play and that was the picture where his hands were on his mandolin.

As in journalism, I would imagine you’d spend a lot of time on researching your subject. Tell me a little bit about what your preparation is for a photo shoot.
You want to fall in love with them, right? Regardless of whether you really love whatever they do, you have to take in everything you can to understand why they do what they do. A lot of it is research on the front end where we write down everything about them. I start to plan ideas. It could be something very reductive. It could be something very conceptual. But it is a process of collecting as much information as possible.
And trying to make them comfortable?
Oh, yeah. You have to invite them into an environment where they’re comfortable and then you have to observe them. And the observation is really from more of a conversation like we’re doing, right? I’m sure you can probably write 10 things about me that I just did that you thought were quirky and weird. I think when you’re working with people, just through conversation, you start to understand a lot about who they are. And the more you’re familiar with them, the better conversation you can have. We’re all journalists in that sense. It’s just a visual journal rather than a written word. We’re telling their story through our idea.
Photo Credit (Top of Story): Robby Klein. Photo of Bill Monroe’s hands courtesy of Mark Seliger.