(Editor’s Note: BGS is excited to debut a brand new column and feature series, First & Latest, which examines the discographies of artists, musicians, and bands by comparing and contrasting their first album against their latest album.)
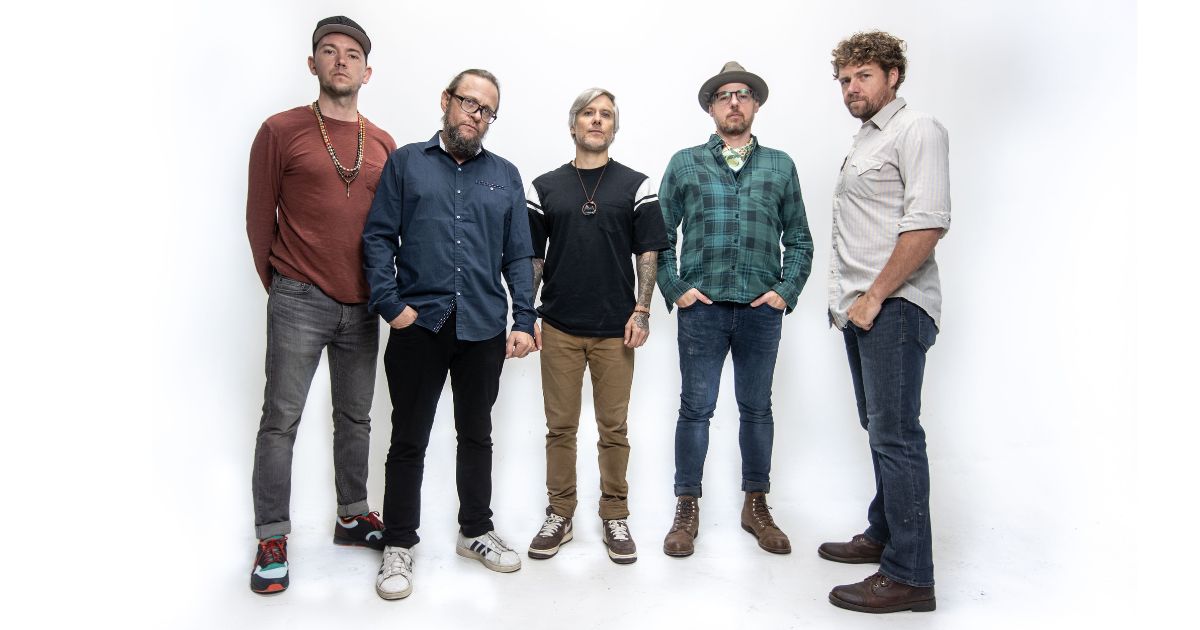
Chicago-based, long-running bluegrass outfit Special Consensus have been making records since 1979, when they released their debut, self-titled album. Since then, they’ve put out about 20 records – and they’ve criss-crossed the country and the globe spreading their modern-yet-traditional, hard-driving sound. Banjo player Greg Cahill, who is also a bluegrass industry leader and community builder, is the band’s sole remaining original member and, across those decades, has been the linchpin, the keystone of what has become a true legacy act.
To mark the occasion of their latest release, Great Blue North (released May 12 on Compass Records), we compare and contrast the band’s debut record with this new project with Cahill – it’s First & Latest, from BGS.
What goes through your mind when you hear a song from that first record, like “Like a Train?”
Greg Cahill: I cannot believe it was so long ago! This was our first time in a recording studio and we knew nothing about the process of making a record. It was truly a complete learning experience and we had a wonderful engineer who was a master at finding the exact place to punch in, and he even manually lined up and spliced the ¾” tape on one of the songs so we could use the first part of the one pass and the second part of a later pass. The album is pretty basic and far from top notch, but we did our best and actually sold a good number of that vinyl record.
At that point, did you ever think this band would have such longevity?
We had no idea about where our journey would take us. Special C actually formed sometime in 1973 – two of us were grad students and two had full time jobs. By 1975, I had finished my masters degree and was playing in local pubs and venues while working a full time job in social work, and all I wanted to do was play the banjo. It was 1975 when bass player Marc Edelstein and I decided we wanted to try playing full time – to play and tour as much as possible to get this bluegrass bug out of our system and go back to “real” jobs/life in a couple years. The other two members decided not to join us for this ride, so we found a guitar player and a mandolin player and quit our day jobs to devote full time to playing music. Marc left the band a few years later but the plan didn’t work for me – the bluegrass “addiction” only became stronger. I just “kept on keepin’ on” with no set time limit on my musical journey and now here I am today, never dreaming I would still be going strong with no set end time.
What do you think has been the key to your spanning the decades in bluegrass – besides yourself, that is!
I have been most fortunate to have had some great musicians/people in the band over the years – and still do have wonderful bandmates. Of course I have experienced the ups and downs of playing full time – it was always worrisome when a band member left or when there were slow times but we always found side jobs and teaching opportunities to keep us moving forward. I guess I am just too stubborn to even think about not playing because I love making music so much.
There’s an energy, a drive, even in this earliest recording that you’ve continued to carry with you. Where do you think that comes from? It reminds me of classic Seldom Scene and Johnson Mountain Boys, like you’re always leaning a bit forward into the groove.
I found bluegrass music through folk music (Kingston Trio; Peter, Paul and Mary; Limelighters, etc.) and eventually Pete Seeger – whose music prompted me to buy a long-neck 5-string banjo and then a 6-string guitar and then a 12-string guitar. I played in a folk trio with friends in college, and one day I heard “The Ballad of Jed Clampett” and immediately knew I had to learn how to play the bluegrass banjo. I found the Earl Scruggs book and was obsessed with playing the banjo every free moment of my life and it was his drive and perfect tone and timing that overwhelmed me. Then I heard J.D. Crowe and he became my model and eventually my mentor of sorts, even before I ever met him. This was in the early 1970s. New Grass Revival also grabbed my ear, and I spent hours trying to learn J.D. solos but also Courtney Johnson licks, determined to not lose the drive when playing non-Scruggs/Crowe licks because at that time many folks felt that Scruggs style playing was the only “right” way to play the 5-string. It has always been about the drive for me – and I learned that from J.D. as well – he always had drive, even on slow songs that he played with superb finesse.
“The Singer” feels like that classic move of a bluegrass band playing a country song, can you talk a bit about what you remember about choosing that track and recording it?
We were city boys playing in big city pubs and venues where the general public had no idea what bluegrass music was. Although we always loved the traditional bluegrass songs and tunes, we felt we had to play some material that the general public might recognize and eventually really like our brand of bluegrass music. So we included old rock songs, country songs, and jazzy swing songs in the repertoire along with the traditional songs. I would say we actually became more traditional over the years, because we were building a local and then national and then international audience while maintaining a varied repertoire.
When I heard “The Singer” I immediately wanted to include that song in our repertoire – the song is so well written, the words are so poignant, especially knowing that Neal Allen wrote the song about his father Red Allen and also that Neal died of pneumonia while on the road. As Bill Monroe would say, “It’s a powerful number.”
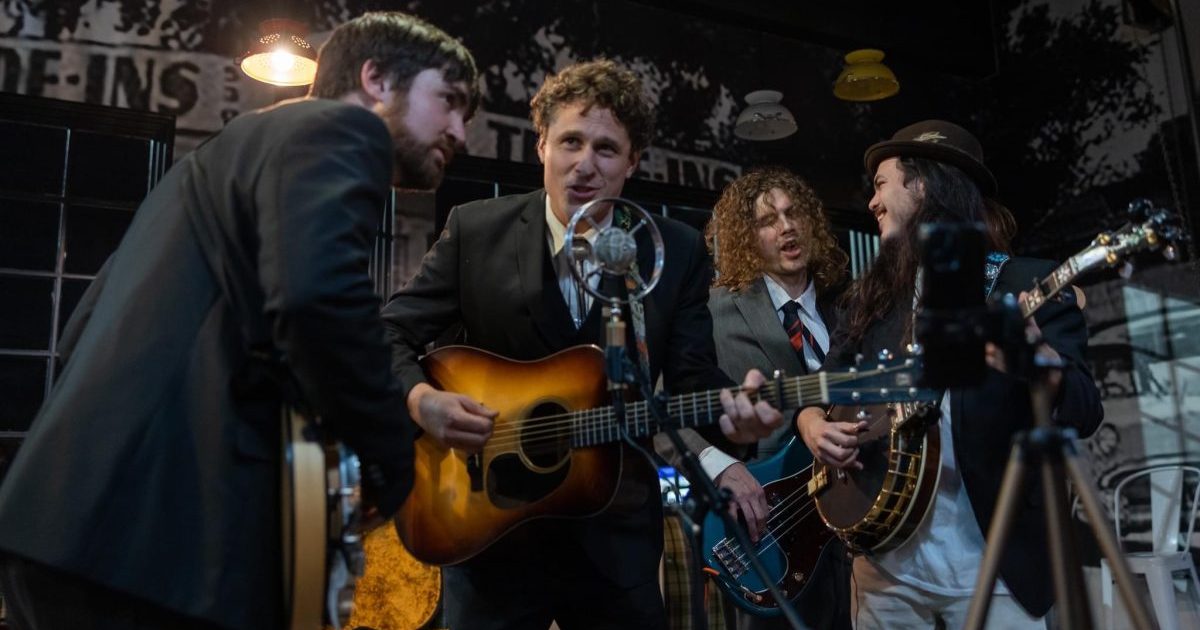
Now, about the latest album, Great Blue North, what inspired you to cross the Great Lakes for this album and do Canadian bluegrass?
We are so fortunate to be on the Compass Records label and especially to have Alison Brown as our producer. When we begin preparations to record, the four of us and Alison begin our search for new material. We are basically on a bi-annual release schedule with the label and one of the songs Alison thought would be a good song for us to include on our 2020 release was “Blackbird,” written by the great Canadian songwriter/singer/guitar player J.P. Cormier. We loved the song but as we gathered material for that release the theme shifted to featuring a nod to Chicago, where the band has been based since beginning in 1975, because 2020 was the 45th band anniversary. Hence the 2020 “Chicago Barn Dance” release. We knew we would record “Blackbird” at some point, and after the pandemic shut-down we wanted to let folks know we were still alive and well and anxious to get back on the road, so we recorded “Blackbird” and Compass released it as a single. As we began the search for material for a new recording, Alison mentioned that it might be a good time to give a nod to our Canadian friends — since we have played there so much over the past three decades — and we all agreed. We then decided to include only songs written by Canadian writers and also to ask many of our Canadian musician friends to perform with us on some of the tracks.
Do you think being such a long-running Midwestern-based group informed the new album for you? And your connections to this material?
I think we may have had more opportunities to tour in Canada because of our Midwestern base. We did not play the big festivals when we first began touring there – we played shows for bluegrass associations and community centers in Toronto, Ontario (only an 8+ hour drive from Chicago), Winnipeg, Manitoba (13+ hour drive) and Calgary, Alberta (25-hour drive). We would head directly to Toronto or work our way through Minnesota to the Canadian gigs, which helped us get invited to the festivals. We also learned about the Canadian songwriters through so many of the great Canadian musicians whom we met and became friends with through this networking.
To me, a throughline between your first and latest albums is the arrangements, the way your band is always playing as a tight-knit ensemble, not just a handful of instruments sounding simultaneously. Where do you get the inspiration for the way your individual parts play off of and dialogue with each other?
I think we have always been focused on the power of tight and interesting arrangements. This again goes back to the fact that because we are from Chicago – not a bluegrass hub in the eyes of the general public – we had to make sure to keep the attention of the audience and not have songs begin to all sound alike. The arrangements give the band the opportunity to be more creative and to showcase the tight vocal and instrumental harmonies. I have always wanted an outside/non-band member producer to give us an objective opinion about the sound, the material and the performance. We have always had very good producers and I must say that Alison Brown is a phenomenal producer who has brought the band to another level. From our perspective, she basically considers each song on our recording to be unique and “special” – there are no “filler” tracks, and we spend however much time necessary to make each track stand out.
“Snowbird” will go down as one of Special C’s tastiest cover songs, do you have favorite covers from across the years? It’s kind of a hallmark of your band!
Although we try not to be seen as a cover band, we have chosen to cover some songs from artists that we feel we can make sound like a bluegrass song, and especially sound like a Special C song. We have been most fortunate to have been given some great songs by many great songwriters over the years and we have also chosen some songs from other genres that we thought we could have fun recording and that our fans would enjoy hearing. “Snowbird” was one of the first songs on our list once we decided on the Canadian theme after recording “Blackbird” – my wife had suggested that song many times and now it seemed like the perfect song to feature Greg Blake’s fabulous voice. Some of the covers we have done on past recordings include “Viva Las Vegas,” “Ramblin’ Fever,” “Dream of Me,” “I Cried Myself Awake,” “Big River,” “Sea of Heartbreak,” “Looking Out My Back Door,” “Sweet Home Chicago,” “City of New Orleans,” our entire Country Boy: A Tribute to John Denver recording, “Alberta Bound” and several other songs on the Great Blue North release.
I must say, that as the years pass so quickly and the time between the first record and the current recording becomes so long I realize how fortunate and blessed I have been to be able to keep making music with so many wonderful musicians/people/friends. At times I have felt that the first recording was below the professional level but because of this interview and going back to listen to it, I now truly understand that we can only do our best throughout this journey, be thankful that we are able to keep growing and learning and appreciate our accomplishments no matter how insignificant they may seem at any given time.
Photo Credit: Jamey Guy