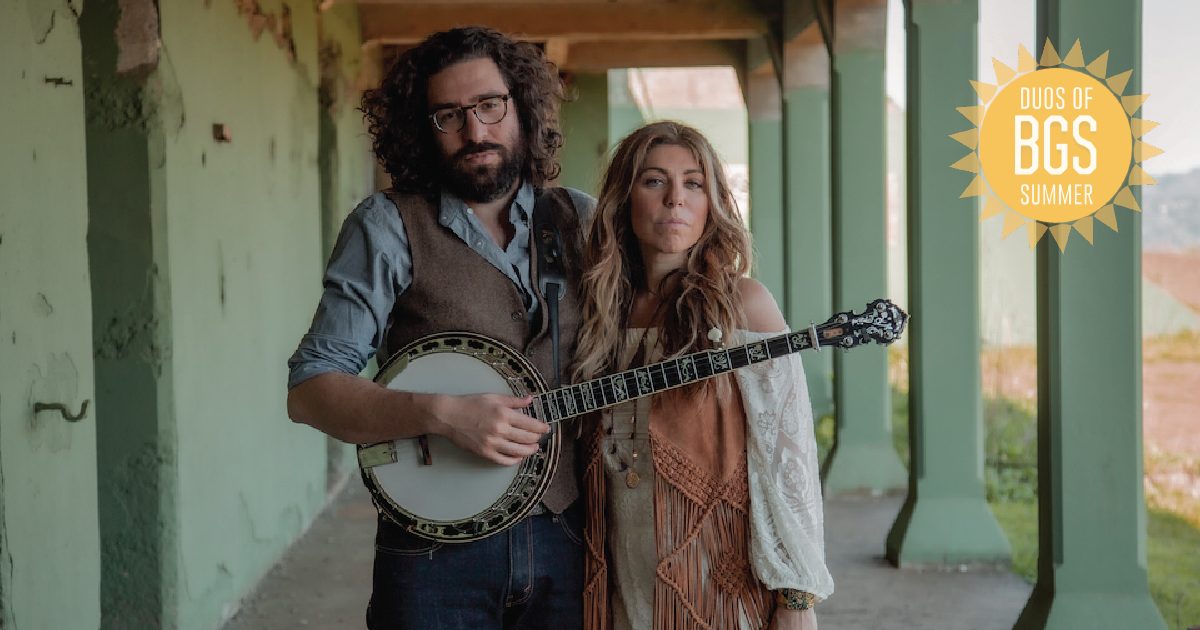
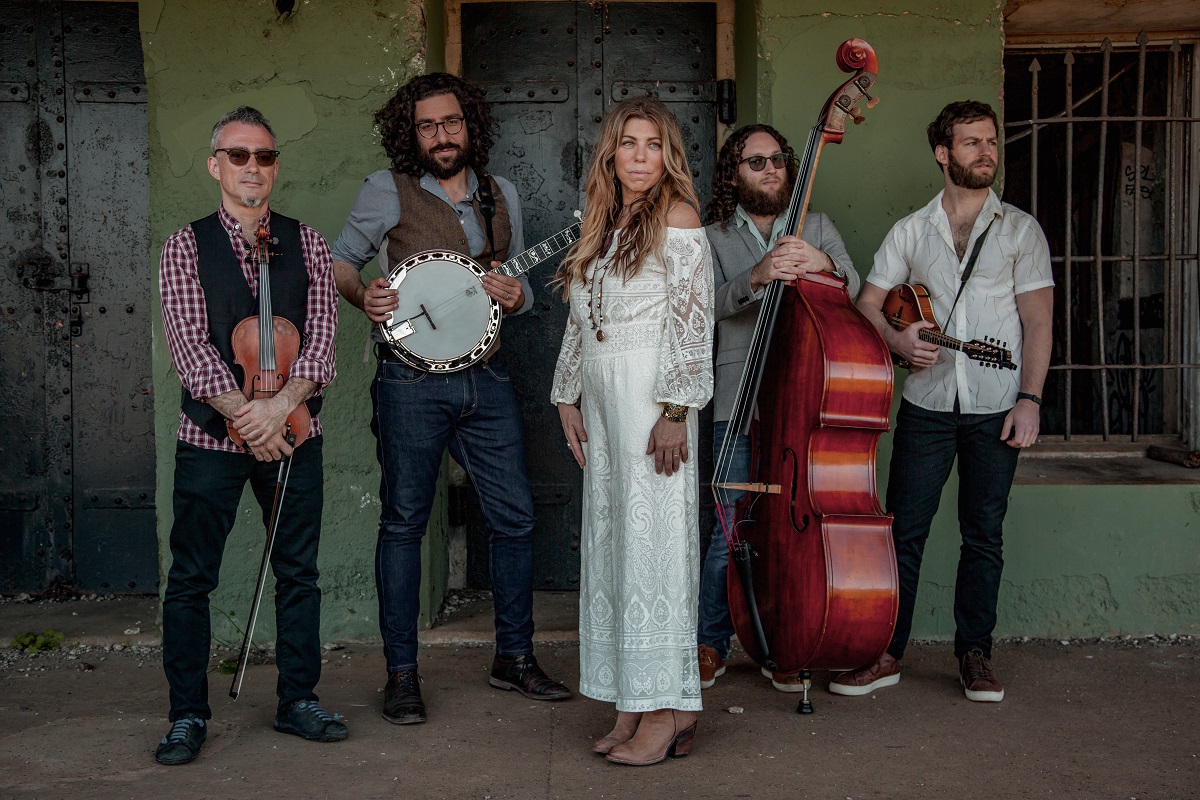
Artist: Nefesh Mountain (Eric Lindberg and Doni Zasloff)
Hometown: Brooklyn, New York City (born & raised); Montclair, New Jersey (current locale)
Latest Album: Songs for the Sparrows
If you had to write a mission statement for your career, what would it be?
As a musician, there are times when you have to sit and write, practice and create music — this process can be so inward, so solitary and alone. But these quieter moments are also filled with their own kind of magic, the kind that personally sustains you and over time hopefully also helps define you as an artist. There are other times when you find yourself in this great shared musical community with friends, bandmates, mentors, and of course audiences and fans. In these moments, we get to experience it all together as a community. I love all of it, and this crazy cycle that we go through as artists — it’s a great question, the mission statement. And while we’ve never really thought of our career having a “mission” exactly, there is a word that comes to mind that for me applies to all aspects of our musical life, and that is inspiration. Doni and I both want to inspire new thought and ideas with our music, and hope that through song we’re able to depict a better world than the one we see sometimes these days. But inspiration also flows in all directions, and we can feel it from an audience just as easily as they can feel it from us, which is such an encouraging thought. Ultimately for me, I think it’s the drive to inspire and be inspired that fuels a song, improvisation, lyric, or melody, and I’d consider us so lucky just to continue to keep receiving, and giving inspiration back and forth throughout our career… I guess you could say invent, inspire, repeat! — Eric Lindberg
Which artist has influenced you the most … and how?
For me it’s sometimes hard to separate music from life, and vice versa — and when asked this question, I always seem to come back to the artists that’ve shaped me over the years, especially at pivotal moments in my life. As a child, I remember being obsessed with the songs on “Free To Be You And Me.” The songs, messages, and humor on this album opened up a whole new world of inspiration for me at the time. We still listen to it with our kids today! Being a strong woman in the musical world is something that is just so important to me, and in part this is thanks to my next phase of musical influences: Joni Mitchell, Carole King, Carly Simon, Dolly Parton, Emmylou Harris, and Joan Baez. For me, I came to a lot of bluegrass and old-time musical forms by way of these artists, tracing backwards from them and finding this amazing and wide world of Americana music like the Carter Family, Ola Belle Reed, Doc Watson, and so many others. Today, I’m also beyond proud that both my and Eric’s biggest bluegrass influences have become dear friends and collaborators on our albums: Jerry Douglas, Sam Bush, John Doyle, Bryan Sutton, David Grier, and Mark Schatz among others, have all had such a deep influence on our music, and we’re so grateful for it. — Doni Zasloff
This is such a hard one. There are so many people who have been heroes and “north stars” in my musical life over the years, yet there are two names that always seem to jump to mind when I get asked this question: Pat Metheny and Béla Fleck. I think that I’ve always been drawn to artists who are able to portray their own world on their own terms, and Pat and Béla have done this time and time again, not only defining their sound as composers and improvisers, but all while truly pushing the boundaries of their instruments as well — guitar and banjo, respectively. I also learned early on through them, as well as others like Miles Davis, Bill Monroe, Bill Frisell and more, the importance of composing your own music, and that has been a huge influence on me as it relates to Nefesh Mountain. When I think of Pat and Béla’s music, I actually think of their compositions first. Pat’s “Question and Answer,” “Bright Size Life,” “Farmer’s Trust,” “Letter From Home,” “Last Train Home” and Béla’s “Spanish Point,” “Whitewater,” “Big Country,” “See Rock City,” “Up and Running” to name a few, have all been huge inspirations for me. I’ve learned so much from listening to these two over the years, and not all of it has been exactly music-related. They both always seem to take risks, break rules, and push forward with an inner drive that is just so inspiring to me, and they’ve help pave this musical road out there for other folks, like us perhaps, who also want to build their own world and story on their own terms. — EL

What’s your favorite memory from being on stage?
We’ve had so many incredible moments over the years, and one that always comes to mind for me was a number of years back at one of our first IBMA Wide Open Bluegrass festivals in Raleigh, NC. Our music, especially in a more traditionally bluegrass environment like IBMA, can be a bit different, to say the least. We were playing the 5:00 pm spot at the Capitol Stage, right in the center of the city, about to play a set that we knew had a few songs with Hebrew in them. I remember standing backstage looking out at a few thousand people at least, and just being terrified, scared that we would not be accepted for who we are. If you’ve never been, Wide Open Bluegrass is kind of a festival meets street fair. There are no tickets, and for these few days, about a million or so people in Raleigh come out to see some of the best bluegrass music around. So I’m looking out at this crowd that is growing by the second — and in my mind just assumed that they would all leave once they heard a lyric in Hebrew. But in the blink of an eye, I feel Eric come up next to me, grab my hand, and whisk me onto the stage — and less than 60 seconds later we were into our first song. I can barely remember any of the music from that particular performance, but what I do remember are the faces in the crowd… the smiles, the applause, the tears, the joy, the hope, and the rapidly growing numbers of people! When we got to our last song the crowd had more than tripled in size and we received our first standing ovation from the city of Raleigh, NC. It was a show and feeling I’d never forget. Of course, we’d played countless shows before and after that one, but there was a different sense of unknowing that day, of a deeper unknown, and felt like a trust fall between us and all the folks in that crowd who overwhelmingly all reached and caught us! – DZ
What other art forms — literature, film, dance, painting, etc — inform your music?
I think about this a lot, actually. I’m always curious about this connection between music, film, dance, literature and sometimes art as well — that all of it takes place, unfolds, and exists over time. A song, album, TV show, movie or book all have a specific and unique length, and I love that it’s our job as creators to ultimately tell a story within the parameters of our own medium. Our newest album, Songs for the Sparrows, is for me our most “cinematic” yet, in that we really wanted the album as a whole to take on the dramatic flow and characteristics of a film. We took a lot of time to write themes and motifs for this album, both melodically and lyrically, that would weave in and out of the songs. For us, these are our “characters” — the different voices and melodies that make appearances throughout. We also wanted a clear and definite beginning, middle, and end to the album, but overall really wanted it to feel like one story and one experience. I think the most exciting part of attempting to make music in this “cinematic” way is that it forces me to think more visually about the songs… to really focus on the images that we’re striving to create with all these beautiful acoustic instruments. There is a piece on the record called “Suite for a Golden Butterfly,” and for this one, Doni and I actually sat down and wrote out a detailed narrative before even a note of music was written. The music to all five movements came from this story that we wrote together about a Jewish family from Eastern Europe who flees to America to escape the Nazis, and for us it was such an exciting way to collaborate — each putting our own visuals, thoughts, and ideas into the music. — EL
Which elements of nature do you spend the most time with and how do those impact your work?
The natural world has had a profound influence on our music and lyrics over the years, and as songwriters and composers, we are always looking for ways to convey feelings, stories, and emotions that will resonate, both with ourselves and the listener. We all in one way or another have such a strong relationship with the world around us, and we often lean on this shared “common ground” in our songs, and really love telling our story through the lens of these universal images of rivers, canyons, forests, fields, and of course mountains! One of the great gifts of being a touring musician is having the chance to see the world. When I sit at home at my desk to write or compose a new piece, my mind will often wander on its own, referencing images of the mountains of Colorado, the coasts of Maine, the California sun, the peaks in Switzerland, the hills and valleys in Ireland. It’s a bit abstract and hard to measure, but for me, these elements of nature and personal memories come out in our work all the time — sometimes in an intended lyric or melody, and sometimes in just a few notes of an improvised solo. — EL
We’re always looking for connections in our music… ways of telling our story and how we see the world while bridging bluegrass music with our heritage as Jewish Americans. One common thread that beautifully runs through Americana music and Jewish tradition is the undeniable reverence shown for our natural world, and that connection is so encouraging for me! We so often only look at our differences these days — our backgrounds, skin color, religion, gender, or even musical genre — but over the years of traveling and making music, I’ve found that we can just as easily look at all the things that connect us, that we have in common. Strangely enough, it’s a choice that we can make every day, and it gives me comfort to know that despite our differences we’re all “Somewhere on This Mountain” all at once, all looking up at the same trees, clouds, and sky every day. — DZ
Photo credit: Lawrence Rickford