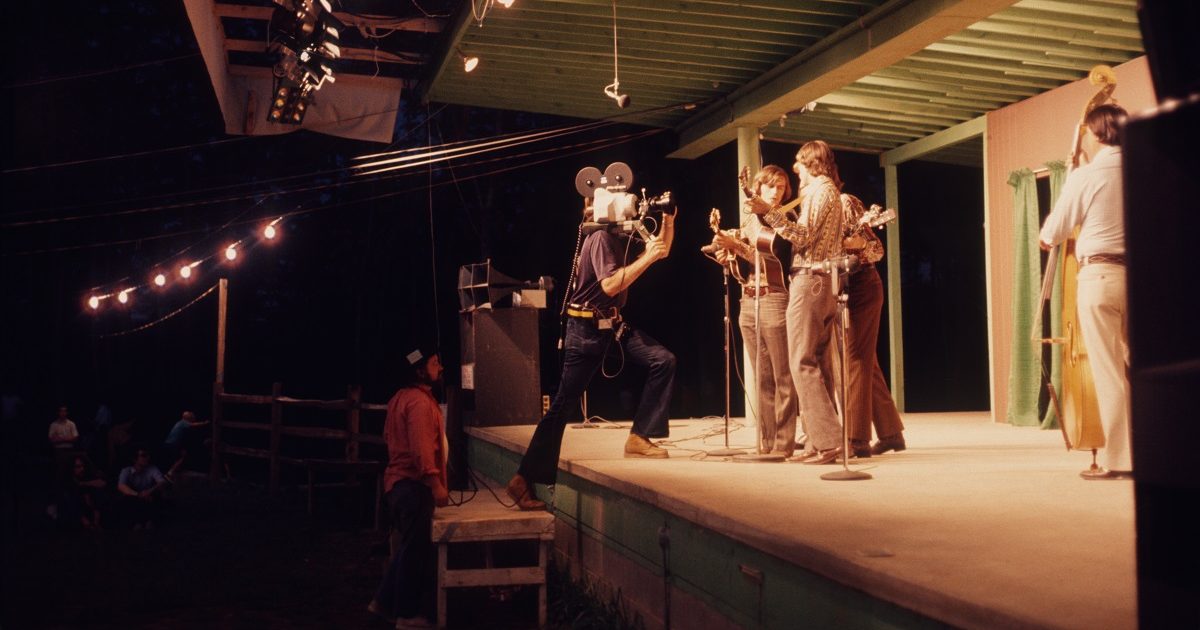
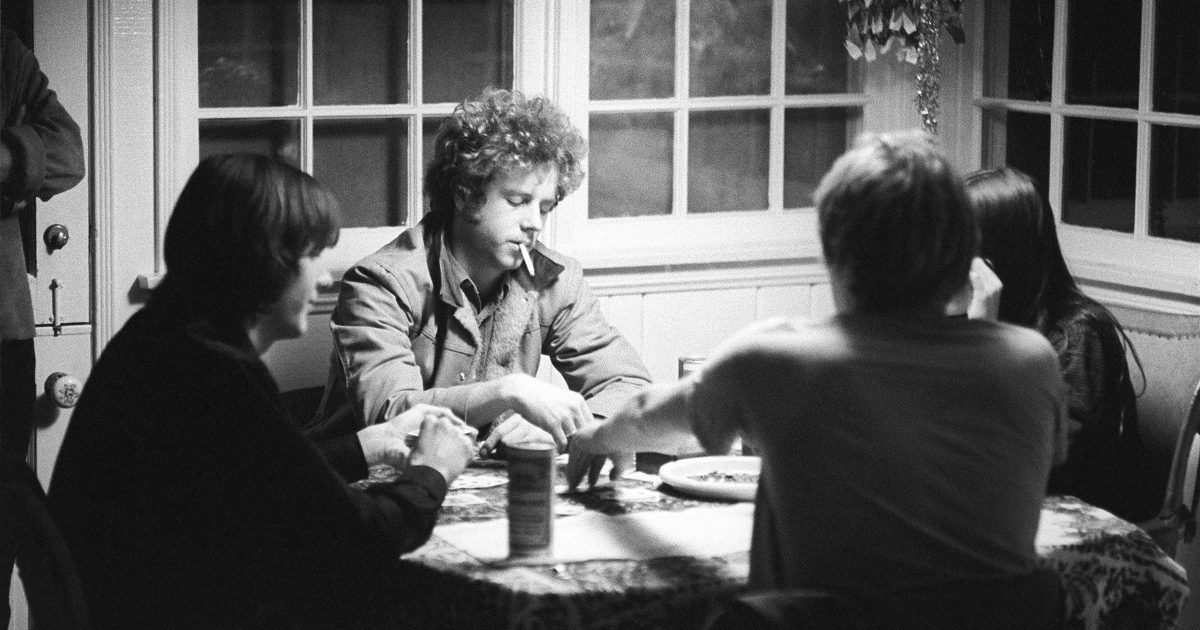
Bluegrass Country Soul captures one of Carlton Haney’s legendary festivals in Camp Springs, North Carolina, on Labor Day weekend of 1971. It is credited as the first bluegrass documentary, and is essential viewing for both lifelong bluegrass fans and those new to the genre.
This classic film features bluegrass music’s pioneers, as well as those who would take the music into the future. Earl Scruggs, The Osborne Brothers, Ralph Stanley, Chubby Wise, Mac Wiseman, J.D. Crowe, and Jimmy Martin were featured alongside The Country Gentlemen, Del McCoury, Sam Bush, Tony Rice, Ricky Skaggs, Keith Whitley, Alan Munde, and more. The film documents Rice’s last show with The Bluegrass Alliance and his first show with J.D. Crowe & the Kentucky Mountain Boys. Many of the festival’s legendary moments are preserved in color for posterity.
A larger than life figure who is credited as starting the first multi-day bluegrass festival, Carlton Haney organized the weekend’s festival, and serves as the de facto host of the film, sharing thoughts about bluegrass music, bluegrass festivals, bluegrass fans, and the bluegrass “stow-ry.” His passion for the music is evident, and makes for a great depiction of one of bluegrass’s most significant and one-of-a-kind personalities.
BGS: How did the opportunity to film Bluegrass Country Soul present itself 50 years ago?
Albert Ihde: It was almost by accident, in a sense. A couple of buddies of mine and I were preparing a screenplay for a company in Washington, D.C. that had hired me to write a film, and then I would direct. The only thing that they insisted on was that it had to be about a Country & Western singer. Now this is 1971, and back then they called it Country & Western. I said, “Okay. Fine. Let me do some research on that.
A buddy of mine, Bob Leonard, and I were out scouting locations in Berryville, Virginia when we saw posters for Carlton Haney’s 4th of July Festival, and Earl Scruggs was going to be playing. We thought, “Well, that looks interesting.” To make a long story short, I got in touch with John Miller, who was the partner of Carlton’s there at Berryville, and John took us on a tour of the sites because I wanted to see what it looked like. It was right on the Shenandoah. Gorgeous location. He gave us passes to the Fourth of July Festival. We had no idea what bluegrass was, compared to country music, and we thought, “This looks like it’ll be fun. We’ll go to see this.”
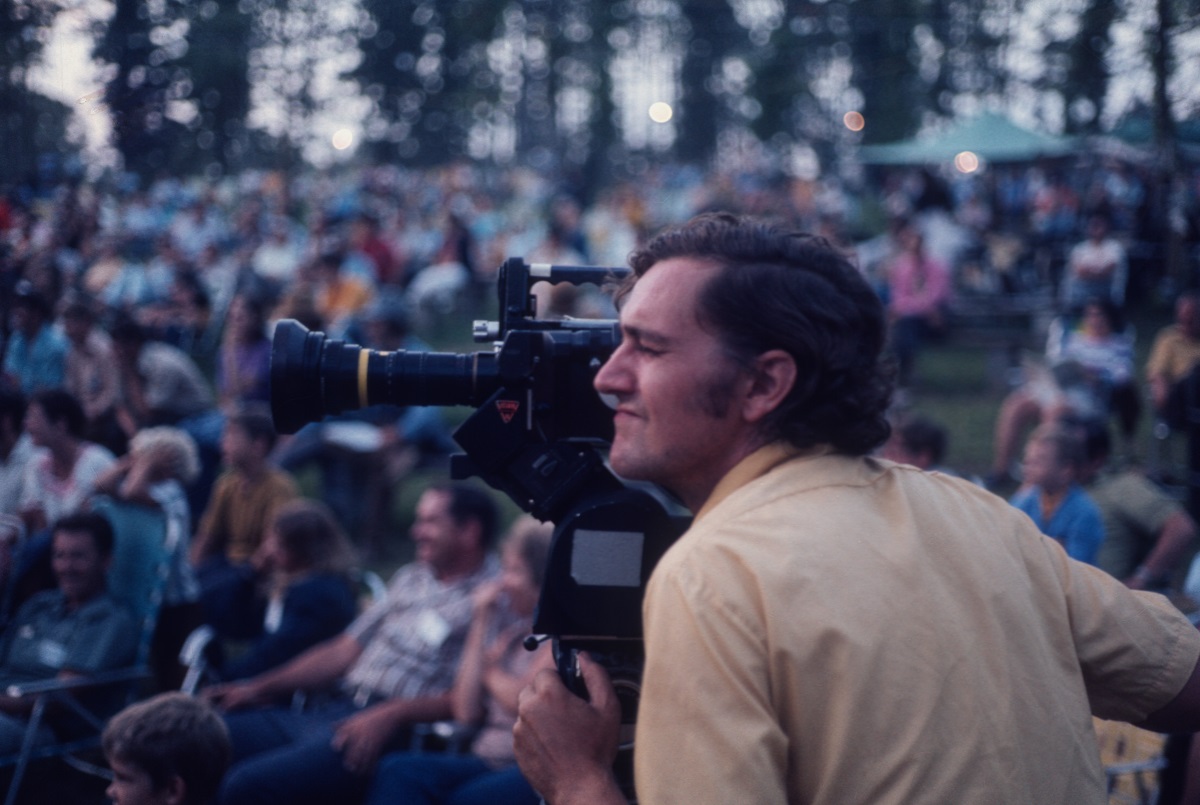

A bunch of us got a VW wagon, and my wife hooked up a camper on the back of our car. We went out, and we parked and saw it, and I have to tell you, as soon as I heard that music coming from the stage, we were all hooked. We talked to Carlton. Quite a deal! Talked to Fred Bartenstein (a local disc jockey who helped with the annual festival) and they told us more about what they were doing. I wanted to put Carlton in a film right then and there as soon as I met him.
We got back to D.C. and the company that hired me to write this screenplay, it turned out that they couldn’t raise the money to make the movie. So we took the film and decided we would try and find the money ourselves. Fortunately the first guy that I sent it to called us into his office. He was a major D.C. investor, philanthropist, and owned lots of real estate in D.C. He said that the thing that interested him most about the screenplay was this bluegrass festival out in Berryville. He said, “Why don’t you do a film about that?”
My partner and I looked at him and said it’s gonna be hard to raise money for a documentary, and he said, “How much do you need?” We get our calculator out, we start going through it, and we throw a figure out to him. It’s not gonna be as expensive as the film that’s going to have all the actors that would be taking us six to eight weeks to shoot. This, we could shoot in one weekend. He said, “Listen if you get Carlton Haney to agree to allow you to come and shoot the film at his festival, I’ll go out and find the money.” And we said, “Okay.”
The next day, Bob Leonard and I were on a plane to North Carolina and met with Carlton and Fred, pitched the whole idea to him, and Carlton was on board right at the beginning. He said, “Absolutely. No problem.” I said, “Well, are you gonna get all of these musicians to agree to this?” And he said, “Yes, I can do that.”
That was it! You’ve got the hippies sitting right next to the guys right off the farm in coveralls. A guy in a Confederate hat sitting right next to hippie girls. It was a great mix. And everybody got along. And it was at a time in America when the country split. Nixon and the protests trying to bring our troops home from Vietnam. It was a strange time. But the thing that happened at the festival… everybody was getting along all right! Also of course, most of the audience were bluegrass musicians of their own or were learning or wanting to be. So that’s how we got into it.
What were some things about Carlton’s personality that made him such a compelling figure to follow for a film?
A number of people have said he was like the “P.T. Barnum of Bluegrass.” So it was kinda like, just put a camera on him and let him go, because you never know what he’s gonna say! Of course, the great thing about filming is, you can always edit it, and we edited out a lot of Carlton.
At one point, it was towards the end of the weekend, we were filming Carlton out on the lot, and I say “Carlton, we need something to kind of summarize the whole thing, and put a tag on the end of the film.” He said, “Oh, that’s okay. I know exactly what to say. Do you want me to make you laugh or do you want me to make you cry?” And I looked at my cameraman, and Bob was ten years older than me, and he had a lot of experience doing this, and I looked at Bob and I said, “What do you think? Make us cry?” And Bob nodded his head “Yeah, make us cry, Carlton.” And Carlton said, “Okay, start the camera rolling.”
To this day, Fred tells me, he runs into people and he says they will quote to him the lines that Carlton had in the film. “The shorthairs and the longhairs,” [and,] “You look down upon the stage and you can hear the soul of man — Ralph Stanley.” They just came out of his mouth!
The other thing was, he could not look at the lens, no matter how hard I tried. [Carlton] had this real shyness problem, and yet you put him on the stage and hand him a mic in front of ten thousand people, he was fine. But put a camera in front of him, he was looking away. Kind of shy and withdrawn. I think he was very concerned about his looks. He had terrible teeth. As somebody once said, that’s part of the times back then when nobody had health insurance or dental insurance… that was the last thing that people spent money on. So I think Carlton was a little shy about the way he looked. But he was an interesting guy.
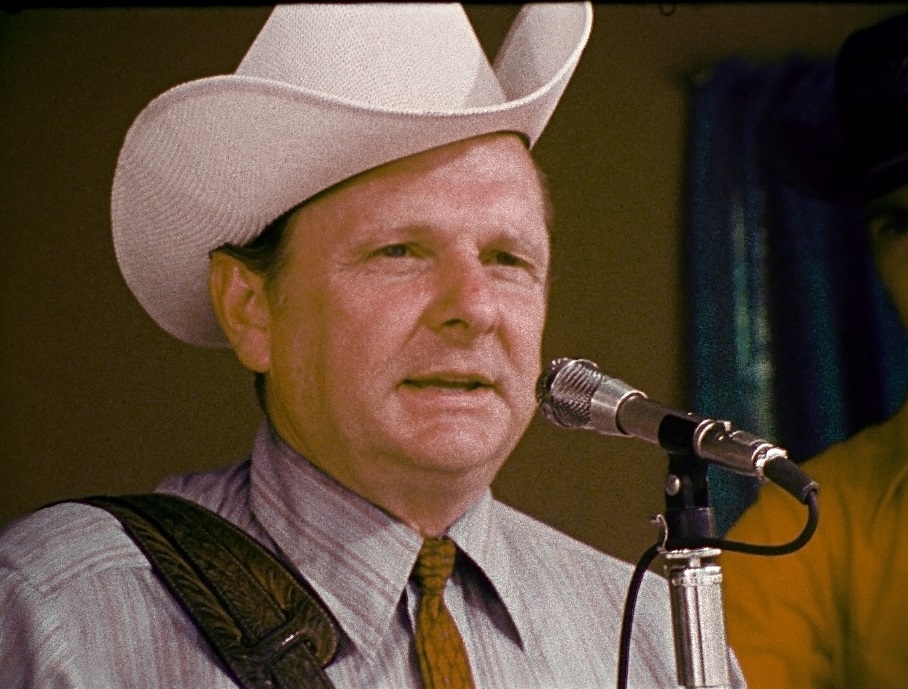

You mentioned that one thing that was so compelling about the film, and at bluegrass festivals in general, was seeing people from different walks of life united by this music and finding common ground, even if it was for a weekend. What do you think that message has for us today where we are as divided now as we were fifty years ago?
I hope it has the same result. Every time I have shown the film — and I have shown it to heads of studios in Hollywood, I showed it to corporations up in New York City — no matter where I’ve shown it, people leave the theatre with big smiles on their faces. It’s not necessarily because they’re bluegrass fans, but because they enjoy it. They had fun. They were delighted. Something about that music, about the people playing it, about the commitment that these people have to it. There’s more to it than just country music. I think that’s what Carlton was trying to say about the soul. It’s a commitment to the music that is thorough.
I don’t know whether Carlton told me this or not, but at some point I learned early on: bluegrass music is not commercial country. Meaning, you’re gonna lose your shirts on it, but you’re doing it because you love it. That really says it all, and I think that comes through with music and with Carlton and with all of the people that are on stage in the film and all the people playing out in the field… You see the commitment to the music.
Ellen [Pasternack, the project’s Executive Director and Ihde’s wife] and I have a background in professional theatre, regional theatre around the country, and what you’re always looking for working in theatre are actors who can really commit to doing a performance. It’s that commitment to the art — whether that’s music, theatre, dance, or painting — that’s where you find the joy in the art. And I think that comes through in the film, even if you don’t know anything about bluegrass. I hope that comes through still to this day, and maybe gets people thinking “past the politics” for a moment or two just to look at the music and listen to the music. And to see, “If this was going on back then, why can’t it happen again?”
Photos and trailer courtesy of Bluegrass Country Soul.