Each year, March is Women’s History Month, and BGS, Good Country, and Real Roots Radio partnered all last month to highlight a variety of our favorite women in country, bluegrass, and roots music with our Women’s History Spotlight.
Each weekday in March at 11AM Eastern (8AM Pacific) on Real Roots Radio, host Daniel Mullins has been celebrating a powerful woman in roots music during the Women’s History Spotlight segment of The Daniel Mullins Midday Music Spectacular. You can listen to Real Roots Radio online 24/7 or via their FREE app for smartphones or tablets.
Then, each Friday we’ve hosted a recap here on BGS featuring the artists highlighted throughout the previous week. No list is comprehensive, but we hope to feature some familiar favorites as well as some trailblazers whose music and impact might not be as familiar to you.
Let’s look back at March and the vibrant history of women in roots music with our final edition of our Women’s History Spotlight, featuring Elizabeth Cotten, Patty Loveless, Ola Belle Reed, Alison Krauss, and Loretta Lynn.
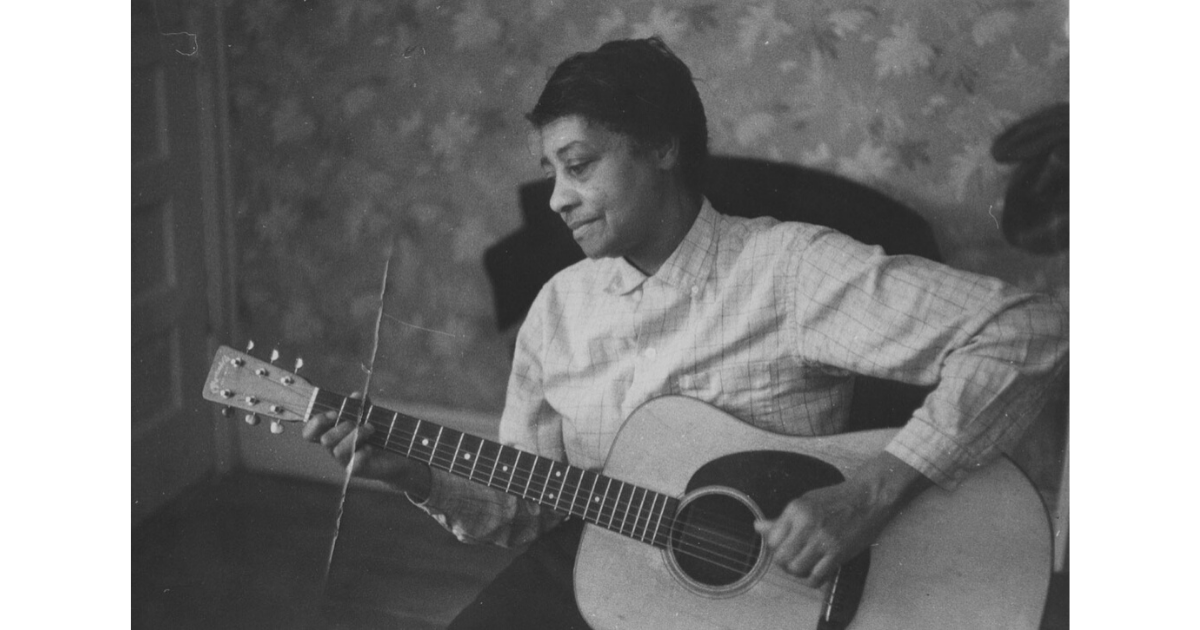
Elizabeth Cotten

Born in 1893, this North Carolina native had a profound impact on American roots music. While she learned how to play the guitar as a child, and even then began writing songs, she shelved her musical dreams and became a domestic worker, but fate had other plans for Elizabeth Cotten. Decades later (in her sixties), she became a housekeeper for the Seeger family following a chance encounter at a department store. The Seegers, of course, are known through roots music circles for the family’s reputation as talented musicians and respected musicologists, featuring Mike Seeger of the Bluegrass Music Hall of Fame, Peggy Seeger, their half-brother Pete Seeger, and more. With the family’s love for music, Elizabeth dusted off her guitar, which she hadn’t touched in decades.
The Seeger family was blown away by Elizabeth’s talent. She had a unique approach to the instrument, due to her being left-handed she would play the instrument upside-down, resulting in the strings being inverted, and allowing her to play the melody with her thumb and the bass lines with her fingers. Additionally, her signature style including some unique alternating bass lines, a technique which is now referred to as “Cotten-style.” Mike Seeger would record Elizabeth for Smithsonian Folkways, introducing her music to the world, including her original composition, “Freight Train,” which has been covered countless times, including by Bob Dylan, Joan Baez, Mac Wiseman, Jim & Jesse, Doc Watson, and more! Other hits of Elizabeth’s include “Shake Suagree” and “Oh Babe It Ain’t No Lie,” which have been recorded numerous times throughout roots music. With the popularity of the Folk Revival, Elizabeth would perform with acts such as Muddy Waters and Mississippi John Hurt, and would eventually win a Grammy in 1984, before passing away at the age of 94 in 1987.
Patty Loveless

The pride of Elkhorn City, Kentucky and a 2023 inductee into the Country Music Hall of Fame, Patty Loveless was a leader of country music’s new traditionalist movement of the ’80s and ’90s, which also saw many successes for fellow Kentuckians Ricky Skaggs, Dwight Yoakam, The Judds, and Keith Whitley. The daughter of a coal miner, Patty’s neo-traditional sound was mixed with rock and roll attitude and plenty of mountain soul. Over 40 of her singles reached the Billboard Country Singles charts, including “On Down The Line,” “Timber, I’m Falling In Love,” “I’m That Kind of Girl,” “Blame It On Your Heart,” “Here I Am,” and dozens of others.
Like many country artists (especially women), Patty’s commercial success declined at a time when the artistic quality of her music did not. Her stunning rendition of Shawn Camp’s “The Grandpa That I Know” from On Your Way Home moved my father to tears for years, and I know that he was not alone in that. For many, her pair of Mountain Soul albums are still essential listening. On these projects, she celebrates her Kentucky roots with bluegrass-flavored albums littered with special guests including Earl Scruggs, Del McCoury, Travis Tritt, Ricky Skaggs, and more. Patty’s six minute-plus interpretation of the Darrell Scott-penned hit, “You’ll Never Leave Harlan Alive,” has haunted listeners for over 20 years. Even if it never tickled the Billboard Country Singles chart, there’s a reason Chris Stapleton recruited Loveless to perform the anthem with him during the 2022 CMA Awards — because it still showcases her mountain soul at its finest.
Ola Belle Reed

Picking up the clawhammer banjo as a youngster, Ola Belle Reed brought the music she heard growing up in Grassy Creek, North Carolina with her when her family migrated to the Maryland-Delaware-Pennsylvania area. Ola Belle Reed would entertain Appalachian migrants in the region with various bands, winning them over with her powerful mountain music. (She even turned down an offer to join Roy Acuff’s Smoky Mountain Boys!) The region’s Appalachian population supported Ola Belle, founding a few of the region’s more popular music parks over the ensuing decades, including New River Ranch in Rising Sun, Maryland and Sunset Park in West Grove, Pennsylvania.
Ola Belle Reed would find a new audience on Wheeling, West Virginia’s WWVA in the 1960s. In addition to presenting Appalachian music to new audiences, her legacy includes many original songs that sound as old as the hills. Songs like “High On A Mountain,” “I’ve Endured,” and “You Led Me To The Wrong” have been recorded by Del McCoury, Marty Stuart, Tim O’Brien, Robert Plant & Alison Krauss, Jason Carter, and more! Ola Belle Reed suffered a stroke in 1987. The following year, she became the first woman to be recognized with a Distinguished Achievement Award by the International Bluegrass Music Association. She passed away in 2002.
Alison Krauss

One of the most Grammy-awarded artists of all time (27 trophies and counting), Alison Krauss’s angelic voice has taken bluegrass to new heights, while she has become one of the most transcendent vocalists of her generation, branching into country, Americana, adult contemporary, rock, and more. A member of the Grand Ole Opry (the historic radio program’s youngest cast member at the time of her membership) and the Bluegrass Music Hall of Fame (currently the youngest Hall of Famer), Alison was a bit of a violin prodigy as a youngster, becoming enamored with bluegrass when she was exposed to bands like J.D. Crowe & The New South and The Bluegrass Album Band under the tutelage of John Pennell.
She recorded her debut album for Rounder Records when she was just a teenager and by the time she reached adulthood, she blossomed into a full-blown roots music star. The success of her solo albums and records with Union Station returned bluegrass to mainstream country circles at a time when it was desperately needed, providing a shot in the arm for the genre and introducing legions of new fans to the music. Krauss joins names like Flatt & Scruggs and The Osborne Brothers as some of the handful of artists to take bluegrass into the mainstream consciousness. Her ethereal voice has also resulted in highly touted collaborations with Robert Plant, James Taylor, Kenny Rogers, Brad Paisley, Shenandoah, Don Williams, and more.
Loretta Lynn

Country music’s most awarded woman artist, Loretta Lynn completely broke the mold. Nashville had had “girl singers” before, and there had even been female artists singing songs about women’s issues, but often they had been written by men (a la “It Wasn’t God Who Made Honky Tonk Angels.”) To have a woman artist singing songs about women’s issues written by a woman was absolutely groundbreaking, and frankly, it intimidated many men in the industry. While now beloved country standards, Loretta sang controversial songs about a wife’s right to say “no” (“Don’t Come Home A Drinkin’ (With Lovin’ On Your Mind)”), birth control (“The Pill”), the stigma attached to divorced women (“Rated X”), beating the tar out of women chasing after her husband (“Fist City”), and more. Coincidentally, all of the songs I just mentioned hit number one even though they were banned by some country radios stations – except “The Pill” which peaked at number five.
In addition to songs that connected to women, her heartfelt numbers about growing up in poverty in Butcher Hollow, Kentucky endeared her to fans as well and instilled a sense of pride in folks with similar backgrounds — “They Don’t Make ‘Em Like My Daddy Anymore,” “You’re Looking At Country,” and the autobiographical “Coal Miner’s Daughter.” Her vulnerability in not only openly dealing with issues in her own marriage, but unpacking her own mental health on the big screen with the Coal Miner’s Daughter biopic opened the country music industry’s eyes to so many issues that women were wrestling with behind closed doors until Loretta Lynn. Loretta continued making fabulous music late in life (check out “Miss Being Mrs,” where she sings about being a widow), until her passing at the age of 90 in 2022. For these reasons and more – and with all due respect to Kitty Wells – there’s a reason that many country music enthusiasts view the late Loretta Lynn as the Queen of Country Music (myself included).
For our final bonus video as we conclude this fun series, here is the story behind Loretta writing “You Ain’t Woman Enough.” Loretta was as real as it gets!